Unit 3 Review
advertisement

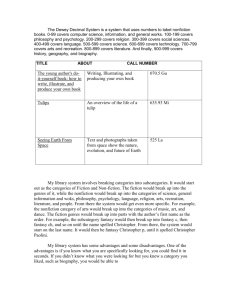
Reading - Unit 3 Skills Review Compiled by Terry Sams and Ann Lindsay, Piedmont Elementary Genre: Autobiography An autobiography tells about a real person’s life and is written by the person who lived it. It is written in the first person. “I lived with my family. . .” It can tell about a person’s whole life or only part of it. Genre: Tall Tales A tall tale is a story that has these features: A larger-than-life, or superhuman, main character with a specific job. A problem that is solved in a funny way. Exaggerated details that describe things as greater than they really are. Characters who use everyday language. Realistic Fiction and Expository Nonfiction The Storm fiction tells about imaginary people, places and events that are like those in real life main purpose is usually to entertain “Tornado Tales” nonfiction tells about something in the real world main purpose is to explain Genre: Expository Nonfiction Nonfiction is writing that is based on fact instead of imaginary events. It is a type of literature that deals with real people, events, and experiences. It explains the nature of something, or tells what something is like. It uses definitions, examples, classifications, and comparisons. Genre: Expository Nonfiction Expository Nonfiction is nonfiction that gives factual information about the real world. It explains the nature of something, or tells what something is like. It uses methods of expository nonfiction such as definition, comparison and contrast, example, and classification. Genre: Biography A biography is a story of a real person’s life, written by another person. It is written in the third-person. The author writes, “He was free! He found a job with a printer.” A biography can cover a person’s whole life or part of it. Make a Biography Genre: Realistic Fiction Realistic Fiction seems like real life with characters dealing with real life problems. The action can happen no matter how improbable, and often takes place in the present time. The situations are true or could be, but the characters are made up. Realistic Fiction may include "real people" characters who have actually lived. \ Bibliography of Realistic Fiction Realistic Fiction Activities Classic Fiction Classical literature is a term used to describe fiction and other works before the 20th century (?-1800s). This literature has been passed down through the ages because of its consistency and because it reflects the life and times of society when it was written. Examples: Oliver Twist, Robinson Crusoe, Dickens Christmas Carol, and Rikki-tikkitavi Comprehension Skill: Generalizing Sometimes as you read, you are given ideas about several things or people. When you make a statement about all of them together, you are making a generalization. A valid generalization is accurate. A faulty generalization is not accurate. Comprehension Skill: Generalization Generalization Susanita and I did everything together that summer Susanita was always ready for an adventure. Supporting Fact She was the one who showed me how to take care of horses. She used to swim in the creek holding on to La Baya’s mane. Comprehension Skill: Making Judgments Making judgments means thinking about and deciding how to react toward people, situations, and ideas in stories you read. Use what you have read and your own experiences as you make judgments. Ask yourself if the author is trying to influence you and whether he succeeds. Vocabulary Skill: Homophones Words that are pronounced the same but spelled differently are called homophones. reins and rains dear and deer Homophones also have different meanings. The understand the difference, look for clues in the surrounding words and sentences. Click on the title to practice this skill. Figurative Language – Simile and Metaphor Figurative language is a language that goes beyond the ordinary meanings of words. Similes and metaphors help make the images in the story richer and clearer. A simile uses words like or as to compare two things that are not alike. “. . . one eye. . . glittered like a blue star. . .” A metaphor also compares two things that are not alike but it does not use any words of comparison. “The shadows were the lumberjacks.” Research Skills – Locate/Collect Information When you need to locate information on a topic, where can you look? To find information about a subject, you can use resources such as books, magazines, newspapers, dictionaries, encyclopedias, videotapes, audiotapes, CD-ROMs, Internet websites, photographs, drawings, and diagrams. Research Skills: Card Catalog/Library Database The card catalogue is a set of drawers containing card filed in alphabetical order with an author card, a title card, and a subject card for each book in the library. In many libraries, the same information is located on the computer and it is possible to search the library database by author, title, or subject. Research Skills: Card Catalog/Library Database Books in a library are classified by the Dewey decimal system. Each book is assigned a call number, which is found on the spine of the book and also on the card in the card catalog or in the computer database. Research Skills: Schedules Schedules are specialized charts that list events and tell when those events take place. Things to look for in a schedule are: What information is shown? What system of time does the schedule use? When does event occur? What happens at certain time in schedule? Research Skill – Schedules TE 337j The Birth of a Baby Bird Time Day 3 before hatching Day 2 before hatching Day 1 before hatching Day of hatching Event Beak pierces inner sac Egg tooth chips away first hole. Bird rests. Baby bird pushes off cap of shell and pulls away from cracked shell. Plural Nouns Adding s Adding es Adding ies This skill shows up in Spelling Unit 3-2 and is on the Reading Unit Test. Verbs Adding –s and -es monkeys holidays delays flowers friends tigers supplies enemies hobbies memories Adding –s and -es mysteries eyelashes ashes beaches bunches circuses glasses classes taxes suffixes