File
advertisement

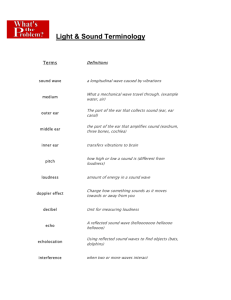
VOCAB PREVIEW—DO YOU KNOW ANY OF THESE WORDS? Sound wave Pitch Loudness Pupil Nerves illumination opaque Optical illusions outer ear frequency Decibel Iris Nearsightedness transparent reflection inner ear middle ear doppler effect tinnitus cornea lens retina farsightedness Translucent diffraction SOUND WAVES • A sound wave is a longitudinal wave generated by a vibrating material. • It is then carried through a medium and transfers energy. • Sound waves travel in all directions away from their source • Sound has to have a medium • Sound can not travel in a vacuum Middle Ear Three bones (hammer, anvil, stirrup)- act as levers to increase the size of the vibration Inner Ear Outer Ear collects sounds Turns vibrations into signals for the brain Sound is: 1. Collected (by outer ear) 2. Amplified (by middle ear: hammer, anvil, stirrup) 3. Converted to Electrical signals for the brain (by inner ear) 1. Sound waves vibrate the ear drum (lightly stretched membrane in middle ear) 2. Vibration of ear drum vibrates hammer-anvil-stirrup 3. Oval window vibrations create waves in liquid in cochlea 4. Movement of liquid causes tiny hair cells to bend 5. Bending of hair cells stimulates nerves, sends electrical signals to brain Do Not Copy HSW Sound/How we hear VIDEO (not saved) HSW New Hearing Implant VIDEO The speed of sound depends on the 1. Medium 2. Temperature Cool AIR Warm LIQUID Slower SOLID Faster Fastest in solids Slowest in gases Pitch- how high or low a sound seems Frequency- (number of waves in a given amount of time) Frequencies Heard by Different Animals bat 2,000- 110,000 hz porpoise 75- 150,000 hz Cat 45- Beluga 64,000 hz 1,000- 123,000 hz Elephant 16- 12,000 hz Human 20- 20,000 hz dog 67- 45,000 hz Doppler effect: apparent change in frequency of sound caused by motion of observer or source. Sound waves are moving forward/same direction of the train: Constructive interference makes it sound louder. http://www.windows2universe.org/earth/images/doppler_e ffect_jpg_image.html&edu=high Loudness- how well a sound can be heard Decibel-measures loudness 0 dB: softest humans can hear 120 dB: hurts Which one is loud? Which one is soft? How do you know? HEARING PROBLEMS Damage to the cochlea or any part of the inner ear usually results in permanent hearing loss. Tinnitus- caused by long term exposure to loud sound PROTECT YOUR HEARING HOW CAN YOU PROTECT YOUR HEARING? Use ear plugs Use a lower volume Move away from loud sounds LIGHT WAVES • Are transverse waves • Can travel through a vacuum (empty space) • Travels faster than sound • Faster in empty space • Slowest in solids • Travels in straight lines 1. Cornea- membrane that protects the eye HUMAN EYE 2. Pupil-opening of the eye that light passes through 3. Iris-controls size of pupil (colored part) 4. Lens-refracts light to focus an image on back of eye 5. Retina- back of eye that pick up light with rods & cones 6. Nerves-attached to rods & cones send info to brain Rods: sense dim light Cones: sense bright light Light bounces off an object and enters our eyes. We see red because red light is reflected off of the red object. Near sightedness person can see something clearly if it is nearby; blurry vision of things far away; eye is too long Far sightedness person can see something clearly far away; blurry vision of things up close; eye is too short Illumination- We see objects because a light is reflecting off of it into our eyes. We see a light source even in the dark because it goes directly into your eyes. Room with a lamp on Room with a lamp off Materials can be classified in 3 ways 1. transparent clear 2. translucent cloudy slightly 3. opaque light cannot OPAQUE TRANSLUCENT TRANSPARENT Reflection: when the wave bounces back towards the source Refraction: the bending of a wave as the wave passes from one medium to another at an angle Diffraction: the bending of waves around a barrier or through an opening Diffraction What do you notice? Optical Illusions Optical Illusions Optical Illusions http://www.colorbasics.com /Optical-Illusions/ What do you see? HUMAN EAR HUMAN EYE Turn to your neighbor. Name 2 new things you learned about the ear and the eye.