Organic Chemistry Lab 2 – N.10 – Acetanilide
advertisement

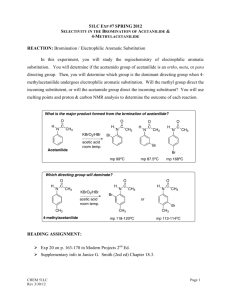
Preparation of Acetanilide O H3C N H Acetanilide N-Phenyl-acetamide 3/12/2016 1 Contents:- An introduction to Amides. - Classification of amides. - Physical properties of acetanilide. - Solubility of acetanilide. - Uses of acetanilide. - Preparation method. - Mechanism of reaction. - Procedure. 3/12/2016 2 An introduction to amides Amides are derivatives of organic acid (Carboxylic acid) with the general formula (RCO-NR2) in which a carbon atom is attached to oxygen in double bond and also attached to an amino group. R1 O R C N R2 3/12/2016 3 Classification of amides Amides are divided into three types, according to the substituents on nitrogen. 1- Primary amides:When R1 and R2 equal to hydrogen group. R1 O R C H N C H3C N H O H O C N H H R2 3/12/2016 Formamide Acetamide 4 Classification of amides 2- Secondary amides:When R1 or R2 substituted by an alkyl or phenyl group. CH3 O H C N H H N-Methyl-formamide 3/12/2016 C CH3 O O H3C N H N-Phenyl-formamide C N H N-Methyl-acetamide 5 Classification of amides 3- Tertiary amides:When both R1 and R2 substituted by an alkyl or phenyl group. CH3 O H C N H CH3 N,N-Dimethyl-formamide 3/12/2016 C CH3 O O H3C N CH3 C N CH3 N-Methyl-N-phenyl-formamide N,N-Dimethyl-acetamide 6 Amides in daily life: The simplest naturally occurring amide is urea, a water-soluble white solid produced in the human body from carbon dioxide and ammonia through a complex series of metabolic reactions Urea is a one-carbon diamide. Its molecular structure is Urea formation is the human body’s primary method for eliminating “waste” nitrogen. The kidneys remove urea from the blood and provide for its excretion in urine. With malfunctioning kidneys, urea concentrations in the body can build to toxic levels. 3/12/2016 7 The complex amide melatonin is a hormone that is synthesized by the pineal gland and that regulates the sleep–wake cycle in humans. Melatonin levels within the body increase in evening hours and then decrease as morning approaches. High melatonin levels are associated with longer and more sound sleeping Lidocaine (xylocaine), a substance commonly administered by injection as a dental anesthetic, is a synthetic molecule that contains both amide and amine functional groups 3/12/2016 8 Acetanilide O H3C N H Acetanilide N-Phenyl-acetamide 1- Acetanilide is a solid organic compound, type secondary amide with white to grey color, an odorless. 2- The molecular weight of acetanilide (135) and molecular formula is (C8H9NO), with melting point (115C0) and boiling point (304C0). 3/12/2016 9 Solubility of acetanilide Acetanilide soluble in hot water ,alcohol (small alcohol) ethanol and methanol, ether, chloroform, acetone, glycerol, and benzene. 3/12/2016 10 Preparation method 1- Reaction of aniline with acetyl chloride. NH2 O O C + Aniline 3/12/2016 H3C NH C CH3 + HCl Cl Acetyl chloride Acetanilide 11 Preparation method 2- Reaction of aniline with an ester. NH2 O O C + Aniline 3/12/2016 H3C An ester R NH C CH3 + R OH O Acetanilide Al cohol 12 Preparation method 3- Reaction of aniline with acetic acid. NH2 O O C + Aniline 3/12/2016 H3C NH C CH3 + H2O OH Acetic acid Acetanilide Water 13 Preparation method 4- Reaction of aniline with acetic anhydride. Today’s Reaction The Synthesis of Acetanilide, an Amide, through a Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution (addition / elimination) reaction between Aniline, an Amine, acting as the Nucleophile, and an Acyl group from Acetic Anhydride acting as the Electrophile. The Reaction 3/12/2016 14 3/12/2016 15 Uses of acetanilide 1- Chemically it used to prepare several substituted aromatic compounds, such as sulfanilamide O H2N S NH2 O sulfanilamide 2- Industrially it used as a dye in dying process. 3-Pharmaceutically it used as intermediate to prepare several drugs such as acetaminophen OH O N H 3/12/2016 acetaminophen 16 Procedure 1-In a conical flask containing (60ml) of distilled water add (2ml) of concentrated hydrochloric acid (HCl). 2- Add (3ml) of aniline to the solution with shaking. 3- Add (3ml) of acetic anhydride to the solution in a small portion, using a burette for such addition. then boil the solution to about (5min). 4- Add (10ml) of (10%) sodium bicarbonate to the hot solution. 5- Cool the solution at room temperature, then in an ice bath. 6- Separate the produced precipitate from the solution by filtration process. 7- Dry, weight out then calculate percentage yield of the prepared acetanilide. 8- All the addition should be stepwise inside the hood. 3/12/2016 17 Safety Acetic Anhydride causes irritation of tissue, especially the nasal passages. Aniline is toxic, can be absorbed through the skin 3/12/2016 18