Presentation - Bodleian Libraries
advertisement

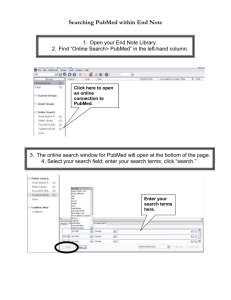
MEDLINE : PubMed & Ovid compared Juliet Ralph Radcliffe Science Library www.ouls.ox.ac.uk/rsl What is MEDLINE? MEDLINE is the bibliographic database produced by the National Library of Medicine (USA) covering: Medicine Nursing Dentistry Veterinary medicine Allied health Pre-clinical sciences. What is MEDLINE? It contains over 17 million references to journal articles, including reviews and clinical trials Gathered from 4,600 biomedical journals published in the United States and in 70 other countries Dating back to 1950, with daily updates Electronic version of Index Medicus, Index to Dental Literature, and the International Nursing Index. Index Medicus Started in 1879 by Dr John Shaw Billings, Librarian at the Office of the Surgeon General, United States Army A monthly classified index of the current medical literature of the world The first of its kind Printed volumes 1879-1950 are at the Radcliffe Science Library Subject Headings Records are indexed with Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) : a huge list of standard terms (over 22,000) for indexing journal articles and books in the life sciences. Each article is tagged with 10-15 headings or subheadings. “Major” headings are marked with an asterisk. This allows you to retrieve articles on a subject even if they don’t have your keyword in the title. Different routes to Medline The free one PubMed: www.pubmed.gov And those we subscribe to 1. Ovid new OvidSP interface from 1st Feb. 2008 2. SCOPUS includes Medline & Embase 3. CSA illumina: 1997 onwards can be searched simultaneously with TOXLINE (toxicology). All on Oxlip www.bodley.ox.ac.uk/oxlip/ A note about coverage PubMed provides access to Medline - PLUS very recent articles not yet indexed: On arrival they are initially tagged [PubMed - as supplied by publisher]. Most progress to "in-process" status and later to "indexed for MEDLINE". Publishers also send details for articles that appear on the Web before the journal issue's release. They are tagged [Epub ahead of print]. The Ovid platform Access to Medline – PLUS these other biomedical databases: AMED – complementary medicine British Nursing Index Cinahl – nursing Embase – medicine & pharmacology Global Health – public health & tropical medicine HMIC – Health Management Information Consortium PsycInfo – psychology ALL MOVING TO OvidSP ON 1ST FEBRUARY 2008. Isn’t Medline all I need? Although it’s pretty comprehensive for clinical enquiries it has a strong US bias. EMBASE (electronic version of Excerpta Medica) has better coverage of European journals and also includes more references to drugs and therapeutics. In Ovid & PubMed you can Search using free text keywords or MeSH headings View your search history Combine searches Limit results by language, date, age groups, etc. Can also limit to Clinical Queries. Search for a specific reference or check a faulty/incomplete reference “View similar” articles Save searches Set up email alerts for new articles Different buttons, similar function In PubMed: MeSH Database History Limits Single Citation Matcher MyNCBI to save searches & set up e-mail alerts OvidSP equivalent: Search tools>Map term Search history Limits Find citation Personal Account for saved searches & alerts Links to full text : OvidSP •In our subscription databases you’ll see the linking tool •This gives access to all the e-journals Oxford is entitled to •…Even when you’re “off campus” •Remote access is possible with an Athens account •Self-register at www.oucs.ox.ac.uk/athens/ Links to free full text: PubMed •Many articles are freely available and indicated in the results list by icons such as •Free full text •Free in PubMed Central Links to Oxford full text: PubMed •What about “Abstract only” Abstract? or No •Full text (especially latest issues) isn’t always freely available •But if Oxford subscribes to the journal AND you are within the Oxford network you get access. •Go into the record and look for links such as What’s new on OvidSP? Basic Search mode : “Natural Language” Searching Search Aids, eg Narrow or Broaden search, add Related Terms Links to related authors or journals Results are ranked by relevance (not date) Adopts the widely used Truncation symbol * Eg disease* retrieves diseases, diseased etc Natural Language searching Ask a question or describe a topic in ordinary English What are the current criteria for use of prophylactic defibrillators in MI? Ovid produces validated terms: criteria prophylactic defibrillators heart attack Expands to include word variations, strong synonyms, acronyms, alternative spellings Do not “force phrasing” with quotation marks, brackets or hyphens Be as concise as possible Use nouns more than verbs Why use PubMed? Freely available on the web URL easy to remember Quick and easy to search For very recent articles Clinical Queries – Search by Clinical Study Category – Find Systematic Reviews – Medical Genetics Searches Why use OvidSP? For a new topic or a more “guided” search Use the MeSH headings from one relevant article to go to others (hyperlinks included in “Complete Reference”) “Find citing articles” (in other Ovid journals) Direct export to RefWorks and other reference management packages Links to e-journals plus library catalogues (for print holdings, if not available electronically). And search multiple databases on OvidSP Simultaneously – You can Deduplicate results (using Search History) OR Do a search in one database then rerun it in another – Click on Change database – Select new database – Open and re-execute Here to help Contact your Subject Librarian Listed at www.ouls.ox.ac.uk/libraries/librarians Online enquiry service “Ask an Oxford Librarian” www.ouls.ox.ac.uk/bodley/ask Health Care Libraries enquiries@hcl.ox.ac.uk Radcliffe Science Library enquiries.rsl@ouls.ox.ac.uk juliet.ralph@ouls.ox.ac.uk Over to you Getting started with OvidSP Try the tutorial at www.informs.intute.a c.uk/informs_perl/ju mp.pl?270-4011