I. Theories of Development

Theories of
Development
Jean Piaget; one of the century’s 20 most influential scientists (as named by
Time Magazine in 1999)
What is Cognitive
Development?
• Def: The progressive changes in our ability to solve mental challenges
• Before 1952 – children simply knew less, not differently , than adults
• Jean Piaget (1952) –
– Children are not miniature adults
– They aren’t “dumber” than adults either
– They just think differently A simple task now, sorting by color wasn’t always so easy
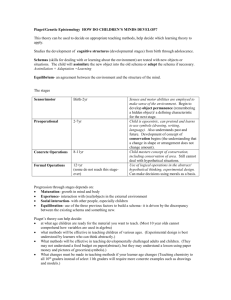
What are
Schemas?
• Def: A framework that helps us add new experiences to our world
– Basic building block of intellectual development
– Schema of a dog
• Fur, 4 legs, cuddly, etc
– Two ways to adapt schemas: Assimilation and Accommodation
Initially, a baby may think of all fourlegged animals as dogs, but later that changes based on the baby’s experience with other four-legged animals
How are Schemas
Adapted?
Assimilation
• Takes new information and applies it to an OLD schema
• Ex. Stuffed Animal
Schema
– Cuddle-able? Yes
– Suckable? Yes
– Throwable? Yes
– Conclusion: Stuffed
Animal!
Accommodation
• Takes new information and creates a NEW schema (usually by changing an old one)
• Ex. Stuffed Animal
Schema
– Cuddle-able? Yes
– Suckable? No!
– Throwable? No!
– Conclusion:
– New Schema: Doggie
What is Piaget’s Theory of Cognitive
Development?
• 4 Stage Approach
• Sensorimotor Stage
– Birth to 2 years
– Experience world through senses
• Practicing Reflexes
• What are babies born with?
– Object permanence
• Objects exist even when not perceived
• By 6-8 months babies figure it out
– Stranger Anxiety
– Piaget underestimated babies abilities
Young children glance at this one but seem to realize there's nothing unusual about it.
However, they spend significantly longer looking at this one, suggesting that they realize it’s impossible. That is they realize that the carrot should still be visible in the space.
What is Piaget’s Theory of Cognitive
Development?
• Preoperational Stage
– 2 to 6 or 7 years
– Representing things with words and images
– Use intuitive rather than logical thinking
– Pretend play
– Language Development
– Egocentrism (other slide)
– Theory of Mind (other slide)
What is Piaget’s Theory of Cognitive
Development?
• Egocentrism
– Seeing things from only one point of view
• “Do you have a brother?”
Yes, Jim
• “Does Jim have a brother?
No
– Often referred to as selfish
– For many, egocentrism remains throughout life
What is Piaget’s Theory of Cognitive
Development?
• Theory of Mind
– The ability to infer others’ mental states
• In other words, the ability to put yourself in someone else’s shoes
• An extension of egocentrism
Children who have mastered this task will correctly answer that Sally will look in the basket; children with autism will continue to say the box.
What is Piaget’s Theory of Cognitive
Development?
• Concrete Operational Stage
– 7 to 11 years
– Thinking logically about concrete events
• Thinking forward and backward
(4+8 = 12; 12-4 = 8)
– Grasping concrete analogies and doing math
– Can solve the conservation problem correctly
• Change in shape does NOT mean change in quantity
What is Piaget’s Theory of Cognitive
Development?
• Formal Operational Stage
– About 12 through adulthood
– Abstract Reasoning
• Problem solving using hypothetical propositions
• Ex. Freshman at Johnson often ask, “What about if XYZ happens?” Because they cannot grasp a hypothetical proposition and must concretely get an answer to
EACH proposition, they have not yet entered this stage of development!