Understanding Market Structure and the Competitive Environment
advertisement

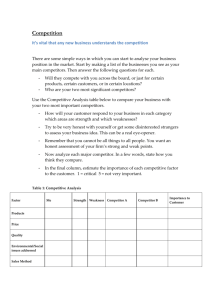
CHAPTER 11 Competitive Interaction ADDED TOOLS FOR EXTERNAL ANALYSIS • • • • • Strategic Group Map Mobility Barriers Strategy Canvas Competitive Response Profile Principles of Competitive Advantage KNOWING THE COMPETITION 1 Understand the competitive landscape 2 Evaluate the competition 3 Beat the competition 4 Understand the market structure and competitive environment UNDERSTANDING THE COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE • Identify strategic groups and mobility barriers – Understand structure of competitive environment – Direct and indirect competitive groups within an industry should not be ignored STRATEGIC GROUP ANALYSIS • Identify main differences in the ways firms in the industry compete (low-cost vs. fullfare airlines with a Strategic Group Map – Determine most relevant factors for horizontal and vertical axes – Score industry players on chosen factors and plot on chart – Clusters represent strategic groups STRATEGIC GROUP MAP—PLOT INDUSTRY PLAYERS STRATEGIC GROUP MAP—IDENTIFY INDUSTRY CLUSTERS BARRIERS TO MOBILITY • Switching strategic groups is difficult because it is hard and slow to reconfigure activities or activity systems – This inability to jump between groups is known as a barrier to mobility STRATEGIC GROUP ANALYSIS • A strategic group map can reveal important potential changes in an industry – e.g. are companies in one group beginning to appeal to the primary markets of another? • Are there empty spaces on the strategic group map that might invite successful entry? STRATEGY CANVAS • Assess relative strengths and weaknesses against specific customer purchase criteria – Uncover how companies attempt to offer unique value to customers relative to competitors • Identify new ways to compete with rivals KNOWING THE COMPETITION 1 Understand the competitive landscape 2 Evaluate the competition 3 Beat the competition 4 Understand the market structure and competitive environment EVALUATING THE COMPETITION • Examine motives and likely behavior of individual competitors – Use analysis to identify your own competitive moves which bring most advantageous effect • Evaluate competition by developing a competitor response profile which identifies characteristics of a competitor to assess likely responses to rival actions COMPETITOR RESPONSE PROFILE 1. “What drives the competitor?” – Objectives and undergirding assumptions which point to potential rival moves 2. “What is the competitor doing or capable of doing?” – Competitor’s strategy, resources, and capabilities 3. “How will the competitor respond to specific moves?” DELTA COMPETITOR RESPONSE PROFILE • To leverage the benefits of international scale for overall cost savings • To capture a greater share of market b providing home city to destination travel for international passengers • Passengers want to fly the same airline domestically and internationally • Scale savings exist by having a global footprint which permits competitive pricing on international routes Delta • Delta is likely to largely ignore entry into its international city-pair markets by Southwest as long as these entries remain few • Position as an international travel choice to as many customers as possible by building an extensive travel network • Locations in major cities • Airline partners that provide global reach • Fleet of large aircraft • Reliable and service-oriented travel KNOWING THE COMPETITION 1 Understand the competitive landscape 2 Evaluate the competition 3 Beat the competition 4 Understand the market structure and competitive environment HOW TO BEAT THE COMPETITION Four Principles for Identifying Potential Competitive Moves: 1. 2. 3. 4. Know your strengths and weaknesses Bring strength against weakness Protect and neutralize vulnerabilities Develop strategies that cannot be easily imitated or copied (go where the competitor is not) KNOW YOUR STRENGTHS AND WEAKNESSES Strengths: Resources and capabilities that deliver unique value Weaknesses: Resources and capabilities subject to rapid obsolescence, easy imitation, or high costs not recouped by value A careful assessment of strengths and weaknesses form the foundation of competitive strategy KNOW YOUR STRENGTHS AND WEAKNESSES • Target strengths against competitors' weaknesses for greatest competitive effect • Example: Google leveraging software engineering strength to develop the Android operating system, helping it grab smartphone market share from Microsoft PROTECT AND NEUTRALIZE VULNERABILITIES • Strengthen or neutralize weaknesses • Starbucks protected its atmosphere by surrounding it with a large variety of great tasting coffee blends, food items, store convenience, and brand positioning DEVELOP STRATEGIES THAT CANNOT BE EASILY COPIED “To be certain to take what you attack is to attack a place the enemy does not protect.” –Sun Tzu • Avoid missing new opportunities by only copying moves by competitors – companies often fail to see how they could do something altogether different. • Competitors may occupy distinctive positions in their market so that they can profitably coexist KNOWING THE COMPETITION 1 Understand the competitive landscape 2 Evaluate the competition 3 Beat the competition 4 Understand the market structure and competitive environment UNDERSTANDING MARKET STRUCTURE AND THE COMPETITIVE ENVIRONMENT • A firm’s circumstances define which competitive actions are available and likely to be effective • Understanding the market context creates the scope for competitive action TWO TYPES OF MARKET ENVIRONMENTS Stable Set of competitors faced by a firm, the supporting technologies, and the environmental factors are changing slowly Dynamic Rapid product releases, new entrants, or market consolidations which affect the shape of the industry STRATEGIC RESPONSES IN STABLE ENVIRONMENTS Monopoly A market of one firm or Description one highly dominant firm Important Considerations Reinforce the monopoly Raise barriers to entry Strategic Moves Limit competitive access to scarce resources Innovate and Patent Introduce new products frequently Oligopoly A market of a few firms (2-5) which monitor and react to specific rival behavior Make moves carefully because rivals will detect their moves and respond accordingly (tit-for-tat) Monitor and mimic rival behavior Employ tit-for-tat strategies (Take most beneficial action, while expecting competition to do the same. If a competitor defects, respond aggressively) Perfect Competition A market with many firms Firms are price takers rather than price setters Homogeneous goods Merge or consolidate markets (to increase bargaining power) Pursue a low cost strategy Pursue a differentiation strategy Create switching costs STRATEGIC RESPONSES IN A DYNAMIC ENVIRONMENT Reconfigure processes and capabilities to emphasize innovation and speed Seek Transient Advantage SUMMARY AND TAKEAWAYS • Understanding the competitive landscape can help a firm identify strategic groups and potential areas for opportunities • Developing a competitive response profile allows a company to examine areas for opportunities and assess possible responses to rival actions • A company can beat the competition by identifying its strengths and weaknesses, bringing strengths against competitors’ weaknesses, neutralizing its own vulnerabilities, and developing strategies that cannot be easily imitated or copied • Understanding the market structure may influence the strategies a firm might employ