PPT: Allies Strike Back
advertisement

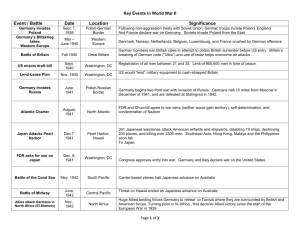
“Allies Strike Back” 1941-1945 European Theatre Operation Barbarossa • June 22, 1941: Hitler launches Operation Barbarossa: Invasion of Soviet Union • The Russians practiced a Scorched Earth Policy: Destroy everything the German’s would pass through • Hitler’s largest Mistake of the War. 1942 • January: 26 nations sign the United Nations agreement • Beginning of the Battle of Stalingrad. • November: Operation Torch: Allied forces (110.000 men) under Dwight D. Eisenhower land in North Africa. Battle of Stalingrad • On April 5, 1942, Hitler ordered his Armies to Stalingrad, Soviet forces would be completely cut off from their own oil supply. • Operation Uranus: The Red Army secretly began to mobilize one million troops, 14,000 heavy guns, 979 tanks, and 1,350 aircraft to attack the Germans Stalingrad • The German Blitzkrieg stalled in Stalingrad • German troops were prepared for Summer fighting, not the harsh Russian winters • The Germans lost 147,000 men and 91,000 were taken prisoner. • The Red Army lost 500,000 men in the battle. • Stalingrad was the first battle where the German Army surrendered. 1942- Northern Africa • Famous North African Tank Battles • Axis Powers led by Erwin Rommel (Desert Fox) • Allies led by Dwight Eisenhower and Bernard Montgomery • Battle of El Alamein first victory for Allies in Northern Africa General Erwin Rommel 1943 • January 14: Casablanca Conference: FDR and Churchill announce they will accept nothing less than an unconditional surrender from the Axis powers • May: German forces in Africa defeated, Rommel moved to European front. 1943 • July-August Operation "Husky": Allied forces invade Sicily, Italy. The greatest Airborne-Amphibious Operation of WWII; 3.000 ships and landing-craft with 8 Divisions. • November: Teheran Conference: First "Big Three" conference to discuss the upcoming Allied invasion of western Europe The Big Three December 24: General Eisenhower chosen Commander in Chief of Allied Forces in Europe. 1944 • January: Leningrad freed from Germans • June 4: Allied Forces capture Rome • June 6: D-day D-day: Normandy Invasion • D-Day does not stand for Doomsday, it was a code word for the specific operation • June 6: 5,000 ships and landing-crafts carried 5 Allied divisions to the French coast. • At the first 48 hours, 107,000 men landed. D-day 1944 • June 12: In total 326.000 men, 104.000 ton material and 54.000 vehicles were carried to the French coast • June 17: 587.000 landed • July 2: In total 929.000 men, 586.000 ton material and 177.000 vehicles landed • August 15: About 2.000.000 men landed Battle of the Bulge • December, 1944: Was the last major offensive by the German Army. • Battle was primarily Ground infantry, Armored vehicles and planes. Bulge Facts • Over a million men: 500,000 Germans, 600,000 Americans and 55,000 British. • 100,000 German casualties, killed, wounded or captured. 81,000 American casualties, including 23,554 captured and 19,000 killed. • 1,400 British casualties 200 killed. 800 tanks lost on each side, 1,000 German aircraft. 1945 • Through the late winter/spring Allied Forces pushed Axis forces back into Germany. • The Big Three meet at Yalta to discuss Post-War Europe, beginning of disagreements between USSR and Allies: Possible start of Cold War 1945 • April 16: FDR dies, Vice-President Truman becomes President • April 30, 1945 Hitler, trapped in his Berlin Bunker, shoots himself • May 8 1945: Germany formally surrenders July 1945: Potsdam Conference: Splitting of Germany into Four Allied Zones, Discussion of Japanese surrender. “Allies Strike Back” 1941-1945 Pacific Theatre December th 7 1941 • Japanese Air Force attack US Naval Base at Pearl Harbor Hawaii, and attack the Philippines the same day. December th 8 1941 • United States officially declares war on both Japan and Germany. • “A Day which will live in Infamy” The U.S. would use the Pearl Harbor Bombing as a Propaganda Source throughout the war. • For the next several months the Japanese military cannot be stopped. . . . • Under the command of General Tojo, the Japanese attacked many targets General Tojo Battle of Coral Sea: May 1942 • Largest all air battle of the war, huge losses for American airmen. • First battle to stop Japanese Aggression June 1942: The Battle of Midway • Turning Point in the War: Major Victory for US American Intelligence broke Japanese military codes, • planned sneak attack against Japanese battle plan of Midway island. • First Allied Victory Island Hopping • Allied strategy to avoid Japanese stronghold, hopping to Japan • Led by Douglas MacArthur and Chester Nimitz July-November 1942: Battle of Guadalcanal • 1st Offensive Victory of the Allies • 1st territory taken from the Japanese 1944- Battle of Leyte-Gulf • First use of Japanese Suicide Pilots • Kamikazes “Divine Wind” 1945 Iwo Jima / Okinawa • Fiercest battles of the war • Despite little chance of victory, Japanese would not surrender 1945 • March -- Tokyo Air Raid : Bombing runs over Tokyo: These attacks on the mainland were part of the American effort to force Japan toward a surrender agreement. • July: At the Potsdam Conference, Stalin agrees to enter the war against Japan in August. • President Truman learns about the A- bomb at the potsdam conference • To save American lives, President Truman orders the use of the A-bomb on Japan. • August 6 1945: The bombing of Hiroshima (Little Boy) • August 9 1945: The bombing of Nagasaki (Fat Man) • Hiroshima- August 6th – 140,000 people killed • Nagasaki- August 9th – 80,000 people killed • September 2: Japan officially surrenders • Two important points of Japan’s surrender 1. The Emperor openly announces he was not a living god, shocking loyal followers 2. Japan was not, and still is not allowed to have any military forces.