Photosynthesis: Chemical Reaction & Process Explained
Photosynthesis chemical reaction
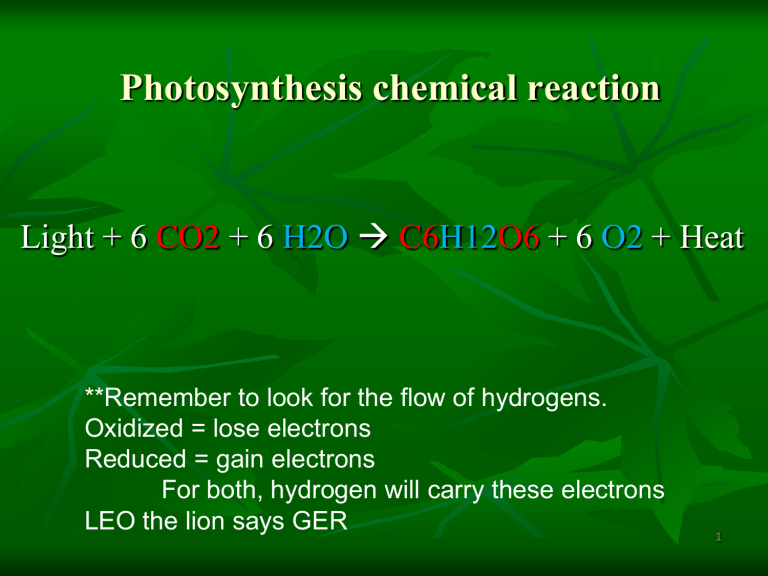
Light + 6 CO2 + 6 H2O
C6 H12 O6 + 6 O2 + Heat
**Remember to look for the flow of hydrogens.
Oxidized = lose electrons
Reduced = gain electrons
For both, hydrogen will carry these electrons
LEO the lion says GER
1
Purpose of each portion for photosynthesis
Reactants
Light = Original source of energy
CO2 = gains hydrogens to become glucose (sugar)
H20 = break water to release hydrogens to provide electrons, release oxygen as byproduct
Products
C6H12O6 (glucose) = sugar (food).
O2 = byproduct (not used)
Heat = imperfect energy conversion (2 nd law of thermodynamics)
2
Photosynthesis -
Method of converting sun’s energy into chemical energy usable by cells
Autotrophs : self feeders, organisms capable of making their own food
Photoautotrophs
: use sun’s energy e.g. plants photosynthesis-makes organic compounds
(glucose) from light
Chemoautotrophs : use chemical energy e.g. bacteria that use sulfide or methane chemosynthesis-makes organic compounds from chemical energy contained in sulfide or methane
**** Photosynthesis does not give plants energy. It provides them with the food (glucose) that mitochondria can then use to create energy (ATP).
3
Autotroph - Plants
4
Autotroph - Algae
5
Autotroph - Phytoplankton
6
Autotroph - Bacteria
7
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis takes place in specialized structures inside plant cells called chloroplasts . Chloroplasts are located in the leaves of plants (so that’s where photosynthesis occurs).
8
Leaf and Chloroplast structure
9
Light absorbing pigments in chloroplast
Chlorophyll IS NOT the only light absorbing pigment in plants. It is just the most abundant
(which is why chloroplasts (and thus plants) are green).
Different pigments are responsible for absorbing different wavelengths of light. Remember
ROYGBIV.
Pigments include chlorophyll a, chlorophyll b, carotenoid, among others.
If chlorophyll are green, what colors of light do they absorb?
10
Chloroplast structure
11
Overall Reaction
**** Cellular Respiration Equation is exact opposite of photosynthesis equation (minus the sunlight)
6CO
2
+ 6 H
2
O + light energy → C
6
H
12
O
6
+ 6O
2
Carbohydrate made is glucose
Water is split as a source of electrons from hydrogen atoms releasing O
2 byproduct as a
Electrons increase potential energy when moved from water to sugar therefore energy is required
Why does it take 6 carbon dioxide and 6 waters to make 1 glucose (and release 6 oxygen)??
****To remember this equation, think “what does a plant need and what does it make”
**** It “needs” CO
2 to turn into glucose, water for electrons, and sunlight.
Energy from sunlight breaks water. H + are taken from water and given to
CO
2
.
**** It makes glucose for food and oxygen as a byproduct (waste). Adding
H + to CO
2
12 generates glucose and taking H+ from water generates oxygen.
Chloroplast
See the green light being reflected
13
Chlorophyll absorbs the blue but reflects the green.
14
Light Reactions Overview:
***H
2
0 + Light energy O
2
+ ATP + NADPH
**This part makes the “batteries” (ATP and NADPH) for making sugar in the next step
**** Note that this is where we use water and light as well as make oxygen. What other parts of the photosynthesis equation are not used / made here (so they have to be in next step)?
15
****
ELECTRON TRANSPORT CHAIN pumps H+ ions into the thylakoid space and CHEMIOSMOSIS uses this to make ATP using ATP Synthetase
16
Pumping the H+ (protons) into a confined space to build up potential energy.
See the similarity in structure and function?
17
Calvin Cycle (light independent or “dark” reactions) – occurs in stroma
ATP and NADPH generated in light reactions used to fuel the reactions which take CO
2 the carbons into glucose.
and break it apart, then reassemble
Called carbon fixation : taking carbon from an inorganic molecule (atmospheric CO
2
) and making an organic molecule out of it (glucose)
**** Basically, Calvin Cycle uses products from light reactions to make glucose.
**** Even though this is called the “dark reactions” they still occur mostly during the day. Why?
18
Calvin Cycle Overview:
**** 6 CO
2
+ ATP + NADPH C
6
H
12
O
6
(glucose) + ADP (P)
+ NADP +
**** Note that ATP and NADPH are not in overall equation because they are constantly recycled (ATP ADP + P and NADPH NADP+)
19









