File
advertisement

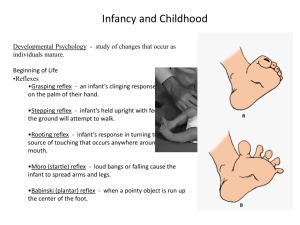
Prenatal Development and Infancy Twins • 1 egg, 1 sperm = 1 zygote. This divides into 2 and each forms a baby: identical (monozygotic) twins • 2 eggs, 2 sperm = 2 zygotes with diferent genetic material forms fraternal (dizygotic) twins Vid – prenatal dev from fertilization http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UgT5rUQ9EmQ Human Dev Quiz Name: ______________________ 1. Human sperm and eggs each carry 46 chromosomes. T or F? 2. Fraternal twins are dizygotic. T or F? 3. A virus is an example of a teratogen. T or F? 4. A hollow ball of cells is called a ___________ 5. Implantation of the embryo in the uterus lining occurs on day 12 10 30 Human Dev Quiz Name: ______________________ 1. Human sperm and egg each carry 23 chromosomes. T or F? 2. Identical twins are dizygotic. T or F? 3. A teratogen is a toxic substance that negatively affects a developing embryo. T or F? 4. A hollow ball of cells is called a ___________ 5. Implantation of the embryo in the uterus lining occurs on day 12 10 30 1. FAS stands for ______________________ 2. The structure where materials are exchanged between the mother and fetus’ blood is the _____________________ 3. A girl and boy are born at the same time. They are _______________ twins. 4. The human heart first develops around ____ after fertilization 1 week 6 weeks 20 weeks 5. Cell division of a zygote is called _________, and as cells divide they get smaller/bigger/ stay same size 1. FAS stands for ______________________ 2. The structure where materials are exchanged between the mother and fetus’ blood is the _____________________ 3. A girl and boy are born at the same time. They are _______________ twins 4. The human heart first develops around ____ after fertilization 1 week 6 weeks 20 weeks 5. Cell division of a zygote is called _________, and as cells divide they get smaller/bigger/ stay same size Prenatal Development – • Conception: a human begins as a fertilized egg (zygote). Combo of genes from mother and father. • Prenatal weeks 0 – 8: Embryo. A bunch of cells with some (but not much) definition. • Prenatal weeks 8 – 38: Fetus. Organs and cell specialization occurs. Growth. • Birth: At 9 months. Prenatal development animations – LINKS NO LONGER WORK • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=NhoU4y0Jt04 • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=JjkFL54Uado • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kHybTthWwn0 What determines your personality? • Combination of genetics (nature) • And experience/environment (nurture) • Genes from both parents give you your basic biological structures (your body) and some aspects of your personality, disposition and intelligence • Sex chromosomes determine if you are male XY or female XX Things that influence prenatal development • Teratogens are environmental agents (such as drugs or viruses or chemicals), • Diseases (such as German measles), • Physical conditions (such as malnutrition) may impair prenatal development and lead to birth defects or even death How We Develop During Infancy Motor Development SensoryPerceptual Development Motor Development – infant reflexes http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8dI1UOziOgg A reflex is an unlearned response to a specific stimulus The Babinski reflex occurs when an infant fans her toes upward when her feet are touched The grasping reflex occurs when an infant grasps any object that touches their palms The rooting reflex leads an infant to turn its mouth toward anything that touches its cheeks and search for something to suck The sucking reflex leads an infant to suck anything that touches its lips The stepping reflex occurs when an infant is held upright, used to learn to walk Infant reflex modeling • Pretend you’re a baby and perform the basic reflexes. • How do these reflexes help a baby? • Babies have basic survival needs – food, physical protection • Babies can’t talk and ask for what they need Sensory-Perceptual Development VIDEO BELOW • Preferential-looking technique is used to study vision • Two visual stimuli are displayed side by side, and the researcher records how long the infant looks at each stimulus • If the infant looks at one stimulus longer, it is inferred he can tell the difference between the two stimuli and has a preference • Video: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8J-JflThHks Sensory-Perceptual Development • Habituation: decrease in response to a stimulus once it becomes familiar. Getting used to something. • Infants look longer at novel (new) stimuli • This tells us the baby can tell the difference between new and old • Infants also intensity their sucking of a pacifier in their mouths when confronted with a novel stimulus Sensory-Perceptual Development • Vision is the least-developed sense at birth • Newborns’ visual acuity is 20/400 to 20/800 • Reaches 20/20 within the first year • Color vision develops by 2 to 3 months • Such stimulation is necessary for proper development of the visual pathways and cortex during infancy • Newborns need to practice looking to form good eyesight Sensory-Perceptual Development • Hearing in the newborn is more fully developed than vision • Can distinguish mother’s voice • This develops in the womb before birth • By 6 months, an infant’s hearing is comparable to that of an adult • Steadily declines from there. Never as good again Sensory-Perceptual Development • The senses of smell, taste, and touch are also fairly well-developed at birth • Infants can differentiate the smell of their mother • Infants have innate understanding of objects and movement – ex, solids cannot pass through each other. Sensory-Perceptual Development • The brain contains about 100 billion brain cells (neurons) at birth = stars in our galaxy! • Infant’s brain is immature, connections between neurons need to be formed • Without visual experiences, the visual pathways do not develop - vision permanently lost • During infancy, networks of neurons used become stronger. Those not used disappear. Brain cell = Neuron