Slide 1
3
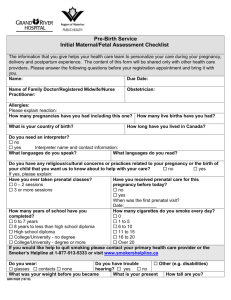
Prenatal
Development
John W. Santrock
© 2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Slide 2
Prenatal Development
• What Is the Course of Prenatal Development?
• What Are Expectant Parents’ Experiences Like
During Prenatal Development?
• What Are Some Potential Hazards to Prenatal
Development?
© 2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
What Is the Course of Prenatal Development?
Slide 3
The Germinal Period
• First two weeks after conception
– Creation of zygote
– Continued cell division
– Attachment of zygote to uterine wall
– Differentiation of cells has begun
© 2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
What Is the Course of Prenatal Development?
Slide 4
Parts of the Zygote
• Blastocyst: inner layer of cells that
develops during the germinal period
– Later develops into embryo
• Trophoblast: outer layer of cells that
develops during germinal period
– Provides embryo nutrition and support
© 2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
What Is the Course of Prenatal Development?
Slide 5
The Embryonic Period
• Two to eight weeks after conception
– Rate of cell differentiation intensifies
– Support systems for cells form
– Organogenesis: organ formation
– Embryo has three layers of cells
© 2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
What Is the Course of Prenatal Development?
Slide 6
Parts of the Embryo
• Endoderm: inner layer of cells form digestive
and respiratory systems
• Ectoderm: outermost layer of cells form skin
parts, nervous system, and sensory receptors
• Mesoderm: middle layer of cells form bones,
circulatory system, muscles, excretory and
reproductive systems
© 2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
What Is the Course of Prenatal Development?
Slide 7
Embryo’s
Life-Support System
• Placenta: intertwines but does
not join mother and baby
• Umbilical cord: connects baby
to placenta
• Amnion and amniotic fluid:
provides baby’s environment
© 2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
What Is the Course of Prenatal Development?
Slide 8
The Placenta and the Umbilical
Cord
Uterus
Umbilical
cord
Placenta
Fig. 3.2
Umbilical
vein
Umbilical
arteries
Fetal portion
of placenta
Maternal portion
of placenta
© 2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
What Is the Course of Prenatal Development?
Slide 9
The Fetal Period
• Begins two months after conception;
lasts about seven months, until birth
• Largest prenatal size and weight gains
• Fingers, toes, skin, features, lungs,
other structures, and reflexes all
develop to prepare for birth
© 2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
What Is the Course of Prenatal Development?
Slide 10
The Fetal Period
• The three trimesters are not same
as the three prenatal periods
• At birth, average baby weighs 7.5
pounds and is about 20 inches
long
© 2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Third
trimester
begins
About 16.518 inches
long, weighs
4 to 5 pounds
32 weeks
About 14-17
inches long,
weighs 2.5
to 3 pounds
19 inches
long, weighs
6 pounds
Less than
1/10th of an
inch long
About 11-14
inches long,
weighs 1 to
1.5 pounds
About 10-12
inches long,
weighs 1/2
to 1 pound
Fig. 3.3
First
trimester
begins
Slide 11
The three
trimesters
of prenatal
development
Less than
1 inch long
About 5.5
inches long,
weighs about
4 ounces
About 3
inches long,
weighs about
1 ounce
Second trimester
begins
© 2009 The McGraw-Hill
Companies, Inc.
All rights reserved.
What Is the Course of Prenatal Development?
Slide 12
The Brain
• At birth – 100 billion neurons
• Basic architecture assembled during
first two trimesters
– Neural tube: first 18–24 days
– Neurogenesis
– Neuronal migration: 4–6 weeks after
conception
© 2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
What Are Expectant Parents’ Experiences Like During Prenatal Development?
Slide 13
Confirming the Pregnancy and
Calculating the Due Date
• Pregnancy test checks for human
chorionic gonadotropin (HCG)
• Pregnancy calculated from first day
of the woman’s last menstrual period
– Lasts about 280 days or 40 weeks
• Fetal life begins at ovum fertilization
© 2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
What Are Expectant Parents’ Experiences Like During Prenatal Development?
Slide 14
Early Signs and Symptoms
of Pregnancy
© 2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
What Are Expectant Parents’ Experiences Like During Prenatal Development?
Slide 15
Three Trimesters and
Preparation for Birth
First trimester
Very tired; nausea and
pregnancy sickness; breasts
change; emotional changes
Second trimester
Less fatigue and nausea; uterus
expands into abdominal cavity
Third trimester
Anticipates end; uterus expands
to point below breastbone
© 2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
What Are Expectant Parents’ Experiences Like During Prenatal Development?
Slide 16
Preparation for the
Baby’s Birth
• Braxton Hicks contractions increase
• Cervix becomes softer and thinner
• Awkwardness
• Fatigue and desire for pregnancy to end
• Nesting urge and spurts of energy
© 2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
What Are Expectant Parents’ Experiences Like During Prenatal Development?
Slide 17
Nutrition and Weight Gain
• Nutrition
– Need for protein, iron, vitamin D,
calcium, phosphorus, magnesium
increases 50 percent, water is
essential
• Weight Gain
– 25 to 35 pounds associated with
best reproductive outcomes
© 2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
What Are Expectant Parents’ Experiences Like During Prenatal Development?
Slide 18
Exercise During Pregnancy
• Exercise for shorter
time intervals
• Decrease intensity as
pregnancy progresses
• Avoid prolonged
overheating
• Avoid high-risk
activities
• Warm up, stretch, cool
down
• After exercise, lie on
left side 10 minutes
• Wear supportive shoes
and bra
• Reduce exercise
significantly in the last
four weeks
© 2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
What Are Expectant Parents’ Experiences Like During Prenatal Development?
Slide 19
Prenatal Care
• Prenatal care varies enormously in
– Education
– Screening for manageable conditions and
treatable diseases
– Information on risks and choices before,
during, and after pregnancy
• Good prenatal care makes a difference
© 2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
What Are Expectant Parents’ Experiences Like During Prenatal Development?
Slide 20
Prenatal Care
• Other countries outside the U.S.:
– Have lower rate of low-birth-weight infants
– Receive free or low-cost prenatal and
postnatal care
– Enjoy liberal paid maternity leave
© 2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
What Are Expectant Parents’ Experiences Like During Prenatal Development?
Slide 21
Prenatal Care
• Factors affecting prenatal care in U.S.
– Individual and social characteristics
• Undesired pregnancy
– Inadequacy of health care system
– Ethnic group differences
– Age group differences (adolescents, adults)
© 2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
What Are Expectant Parents’ Experiences Like During Prenatal Development?
Slide 22
Cultural Beliefs About Pregnancy
•
•
•
•
•
Satisfying ‘questionable’ food cravings
‘Hot-cold’ theory of illness
Role of extended family
Stoicism in Asian cultures
Pregnancy as a natural occurrence or a
medical condition
© 2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
What Are Expectant Parents’ Experiences Like During Prenatal Development?
Slide 23
Cultural Beliefs About Pregnancy
• Latino cultures in U.S.
– Less use of family planning services than
other Americans
– Beliefs about contraceptives
– Seek advice of older women and mothers
– Use of curanderos
– Undocumented illegals wait much longer
© 2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
What Are Expectant Parents’ Experiences Like During Prenatal Development?
Slide 24
Cultural Beliefs About Pregnancy
• Asian cultures in U.S.
– Chinese expectant mothers’ behaviors
linked to character formed in the womb
•
•
•
•
Listening to classical music linked to patience
Charitable behavior linked to morality
Avoid dishonest people
Dispel negative thoughts and feelings
© 2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Slide 25
© 2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
What Are Some Potential Hazards to Prenatal Development?
Slide 26
Some General Principles
• Teratogen
– Any agent that causes a birth defect
– About half of potential effects appear at birth
• Severity and type of defect affected by
– Dose
– Genetic susceptibility
– Time of exposure
© 2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
What Are Some Potential Hazards to Prenatal Development?
Slide 27
Prescription and
Nonprescription Drugs
• Prescriptions given during pregnancy
– Antibiotics, analgesics, asthma medications
– 1961: thalidomide tragedy
• All drugs (prescribed, illegal) can have
effects on unborn fetus
© 2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Teratogens and Timing of Their Effects
on Prenatal Development
Slide 28
Zygote
1 2
Embryonic period (wks)
Fetal Period (wks)
3
4
5
6 7 8 9 16 32 38
Central nervous system
Most
Heart
serious
Arms
damage
Eyes
from
teratogens
Legs
in first 2–8
Ears
weeks
Teeth
Period of susceptibility
Palate
to structural defects
External genitalia
Period of susceptibility
to functional defects
Fig. 3.8 (modified)
© 2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
What Are Some Potential Hazards to Prenatal Development?
Slide 29
Psychoactive Drugs
• Psychoactive drugs
– Act on nervous system and change moods
– Alter states of conscious and modify
perceptions
– Extent of risk and harm varies
© 2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
What Are Some Potential Hazards to Prenatal Development?
Slide 30
Psychoactive Drugs
•
•
•
•
Caffeine and nicotine
Alcohol – Fetal Alcohol Syndrome (FAS)
Cocaine and heroin
Methamphetamine and marijuana
© 2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
What Are Some Potential Hazards to Prenatal Development?
Slide 31
Incompatible Blood Types
• Between mother and father
• Between mother and baby
– Blood group (A, B, O, AB)
– Rh factor (positive, negative)
– Vaccine within 3 days of birth
© 2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
What Are Some Potential Hazards to Prenatal Development?
Slide 32
Environmental Hazards
•
•
•
•
•
•
Father’s exposure to lead, radiation
X-ray radiation
Pollutants and toxin wastes
Fertilizers and pesticides
Lead-based paints
Petrochemicals
© 2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
What Are Some Potential Hazards to Prenatal Development?
Slide 33
Maternal Diseases
• Diseases and infections cross the
placenta barrier
– Rubella
– Diabetes
• Sexually transmitted infections
– Syphilis
– Genital herpes
– AIDS, HIV infection
© 2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
What Are Some Potential Hazards to Prenatal Development?
Slide 34
Other Maternal Factors
• Maternal diet and nutrition
– Folic acid and iron
– Fish: PCBs and mercury levels
• Maternal age
– Highest risks: adolescents, over 35 years
• Maternal emotional states
© 2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
What Are Some Potential Hazards to Prenatal Development?
Slide 35
Other Paternal Factors
• Father’s diet and low vitamin C
• Drug use effects on sperm
• Smoking during pregnancy – effects of
second-hand smoke
• Father’s age at conception
© 2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Slide 36
3
The End
© 2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.