THE CNS and Nerves
advertisement

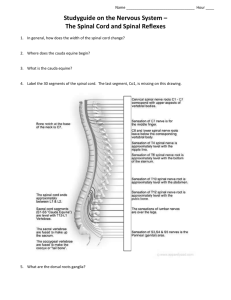
Central Nervous System Brain Made up of: • Brain • Spinal Cord Spinal Cord Meninges http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=uOL_o6NBqBo 0 Protect and cover the spinal cord and brain 3 Layers 0 Duramater 0 Arachnoid mater 0 Pia mater Gross Anatomy of the Spinal Cord 0 Anterior median fissure and posterior median sulcus 0 Divide spinal cord in to right and left halves 0 Central canal 0 Contains spinal fluid 0 Gangalion 0 Swelling which contains cell bodies of neurons Gray Matter 0 Divided into horns 0 Anterior 0 Posterior 0 Lateral 0 Only in thoracic and upper lumbar White Matter 0 Organized into tracts 0 axons with common origin or destination 0 Similar message Plexuses 0 Where bunches of nerves meet 0 Names describe regions the nerves supply or course they take Major Plexuses 0 Cervical 0 Brachial 0 Lumbar 0 Sacral Review Questions ****Add this question to your worksheet 10. Describe each major plexuses 0 HW: Read section 10.3 (Spinal Cord Functions) and answer the following questions 0 How are somatic and autonomic reflexes similar and different? 0 Self Quiz question #1 Image for Analysis Question Components of a Reflex Arc http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wLrhYzdbbpE A pathway that produces a reflex 1. Sensory receptor 0 Responds by sending nerve impulse 2. Sensory neuron 0 Sends msg to . . . 3. Integrating center 0 Processes info 4. Motor neuron 0 Pass msg to effector 5. Effector 0 Responds to stimulus Analysis Question 6. You go to the doctor, the doctor hits you under the patella with a rubber hammer. Your knee involuntarily jerks. Explain what happened. 7. Is the patellar reflex an example of a positive or negative feedback loop? Explain your answer. The Patellar Reflex What’s going on in the body? 1. Sensory neuron sends info through the dorsal root ganglion into the spinal cord 2. Signal splits in two 0 motor neuron to the quadriceps 0 What does this cause? 0 Interneuron sends message to motor neuron in the hamstring 0 What does this cause? ***The signals work together Summary Questions 1. What is the difference between spinal reflexes and cranial reflexes? 0 Integration in spinal cord = spinal reflex 0 Integration in brain = cranial reflex 2. What is the difference between autonomic and somatic reflexes? 0 Effector is skeletal muscle = somatic 0 Effector is smooth muscle, cardiac muscle or glands = autonomic BrainPop 1. The largest region of the brain is the __________________. 2. What does the cerebellum control? 3. Is there a correlation between brain size and intelligence? Tour De Brain 0 What are the found major parts of the brain? 0 Brain stem, diencephalon, cerebrum, and cerebellum 0 What does the brain stem consist of? 0 Midbrain, pons, and medulla oblongata 0 What does the diencephalon consist of? 0 Thalamus, hypothalamus, and pineal gland What Protects the Brain? 1. Cranium 2. Cranial meninges The Medulla Oblongata 0 https://www.youtube.co m/watch?v=cu7A8LIzL1 o 0 Based on what you learned yesterday, is the clip accurate? Why or why not? Did you Know?? 0 The brain uses 20% of the body’s oxygen 0 Brain damage may occur if brain neurons are deprived of O2 for more than 4 minutes 0 If blood entering the brain has low glucose levels mental confusion, dizziness convulsions and loss of consciousness may occur Blood Brain Barrier 0 Capillaries that protect harmful substances from getting into the brain 0 What is able to cross? 0 Lipid-soluble substances 0 Anesthetics Cerebrospinal Fluid 0 Protects brain and spinal cord 0 Carries 0 O2 0 Glucose 0 Removes 0 Wastes 0 Toxins The Brain Stem 0 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=snO68aJTOpM Lobes of the Brain How to Remember the Parts of the Brain 0 http://www.thepsychfiles.com/20 08/09/episode-72-videomemorize-the-parts-of-the-brain/ The Lobes of the Brain Lobe Frontal Temporal Parietal Occipital Function The Lobes of the Brain Lobe Function Frontal • • • • Motor function (movement voluntary) Decision making, behavioral control, decision making Reasoning, thinking, planning Personality and impulse control Temporal • • • • Memory (visual and verbal), facial recognition Hearing (auditory) Understand language Hearing, speech Parietal • Sense of touch, taste • Spatial awareness/relationships • Perception (uses the senses) Occipital • Vision • Visual perception • color and object identification The Limbic System 0 Regulates emotion, behavior and long-term memory Consists of the: 1. Hippocampus 2. Hypothalamus 3. Amygdala Hypothalamus 0 All about homeostasis 1. Regulates hormones 0 Which gland releases hormones? Pituitary gland 2. Regulation of emotional and behavioral patterns 0 E.x. 3. Regulation of eating and drinking Continued 4. Control of body temp 0 Based on blood temp 5. Circadian rhythm and consciousness 0 Sleeping and wakefulness 0 Stress response = Cortisol release 0 Regulates breathing, pulse, blood pressure and arousal Why do you think the rat acted this way? 0 When the rat turns a wheel, it receives an electrical stimulus to the medial forebrain bundle, which is rewarding. The rat will continue to do this indefinitely and pass up food, sex, and other “natural” rewards for the artificial stimulus. Hippocampus 0 Encodes “short-term” memories into longterm memories 0 What happens if it is damaged? 0 Can not form new long- term memories Amygdala 0 Linked to fear, aggression and pleasure 0 Positive correlation between size and aggression 0 Shrinks upon castration 0 What happens when it is removed? 0 Person becomes tame and indifferent Fear Conditioning 0 A little boy named Albert was fond of white animals, including rats. One day, a scientist by the name of James Watson made a loud, unpleasant noise with a hammer while Albert was looking at a white rat. He cried and seemed very frightened. Now every time Albert sees a rat, even when there is no noise, he starts to cry. What happened? 0 Albert’s amygdala has learned to associate white rats with loud noises. Since he is afraid of loud noises, he is now afraid of rats by association. This is called “fear conditioning” Cingulate Cortex 0 Allows the thalamus to “talk to” the hippocampus 0 Emotional events 0 Memories linked to 0 Smells 0 Pain Phineas Gage 0 http://www.youtube.co m/watch?v=c6kRP41ygr I 0 http://www.youtube.co m/watch?v=kR7_oMSUB FE Phineas Gage 1. Which areas of his brain were damaged during the 2. 3. 4. 5. accident? Based on the clip you saw create a definition of localization. Why do you think Phineas’ behavior changed after the accident? Based on what you have learned about the limbic system, why do you think that it is called the emotional brain? Have there been any other accidents similar to Phineas’s accident? If so, what happened to the individual? Left Brain vs Right Brain 0 Do you consider yourself a right brained person or a left brained person? Why? 0 Go the website listed to the right and take the quiz print out your results and paste them in your NB 0 When you get to the page with the drop down menu answer I don’t want to answer to all questions. 0 http://www.wherecreati vitygoestoschool.com/v ancouver/left_right/rb_t est.htm 0 http://testyourself.psyc htests.com/testid/3178 Mr. Split Brainy Analysis 1. How would you describe the abilities of the left hemisphere? What leads you to think this? Use data from the experiment to support your answer. 2. How would you describe the abilities of the right hemisphere? What leads you to think this? Use data from the experiment to support your answer. 3. Based on the data you collected during the experiments, which abstract should you send to be published? What leads you to think this? Split Brain Experiments 0 Performed by Dr. Sperry on people with Epilepsy 0 Excessive nerve signaling 0 Corpus Callosum was severed 0 Hemispheres were still able to learn but had no idea what the other hemisphere learned. What came out of the Spilt Brain Experiments? 0 Hemispheres have specialized tasks 0 Left: Analytical, verbal processing and speaking 0 Right: Space perception, music, art, rudimentary words and phrases, emotional context to language. 0 Provides a good example: http://physics.weber.edu/carroll/honorstime/split_brain.htm Corpus Collasum 0 Connect comparable structures on both sides 0 Allows data to be processed on both sides Medial surface of right hemisphere 0 What happens if it gets cut? Corpus Callosum The Two Hemispheres 0 Which structure separates the structures? 0 Corpus callosum 0 Some functions lateralized 0 Certain functions controlled by a specific hemisphere 0 Never 100%, meaning? 0 Right 0 Music, creativity, images, color, ect. 0 Left 0 Logic, language, reasoning, #’s, critical thinking Contralateral Organization 0 Sensory info sent to opposite hemisphere Left visual Right visual field field 0 Meaning? 0 How is this achieved? 0 Data crosses over in pathways 0 Motor nerves cross Optic nerves 0 E.x. 0 This this restricted to vision? Left Visual Cortex Corpus Callosum Right Visual Cortex Lateralization of the Brain Verbal left hemisphere Nonverbal right hemisphere