Forces and Motion Lab Worksheet - PhET Simulation
advertisement

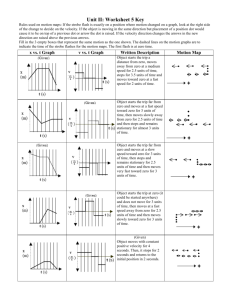
Forces and Motion Lab Name________________________ Hr. _____ Background information: The force vector describes a specific amount of force and its direction. You need both value and direction to have a vector. Scientists refer to the two values as direction and This is a magnitude (size). vector: This is a vector showing Newton’s second law of motion- You can add two vectors by simply joining them head-totail: Vectors can also be added or subtracted to show motions. Forces and Motion Basics Forces and Motion phET GETTING STARTED: 1) Google PHET Forces and Motion Basics 2) Click on the 1st hit. 3) Click Run Now! 4) WARM UP: (TUG OF WAR) Make sure all of the boxes in the upper right hand corner are checked. Create a scenario on the rope pull which in which the forces are BALANCED. Draw a picture of the VECTOR ARROWS and the NET FORCE (SUM OF FORCES) ARROW in the space below. 1. What is the NET FORCE on the cart? a. Balanced b. unbalanced c. net force d. none of these Create a scenario on the rope pull in which the forces are UNBALANCED. Draw a picture of the VECTOR ARROWS and the NET FORCE (SUM OF FORCES) ARROW in the space below. 2. What is the NET FORCE on the cart? a. Balanced b. unbalanced c. net force d. none of these 1 PART 1: (MOTION) Click on the Motion Tab. Play around with the simulation so that you know how to use it. Make sure that all of the boxes in the upper right hand corner are checked (Force, Value, Masses, and Speed) *There is no FRICTION in this scenario. Place the refrigerator on the skateboard. APPLY a force of approximately 100 N. Once the skateboard is moving let go. Answer the following questions. 3. What happens to the SPEED of the Skateboard/Refrigerator when there is no longer a force being applied? a. balanced b. unbalanced c. net force d. remains constant 4. Are the forces acting on the Skateboard/Refrigerator BALANCED or UNBALANCED? a. balanced b. unbalanced c. net force d. none of these 5. What are the FORCES acting on the Skateboard/Refrigerator? a. FnFg Fa F1 b. F3Fg Fa Fs c. FuFg Fa Fp d. none of these Will the Skateboard/Refrigerator ever stop moving? Why or why not? EXPLAIN! Reset the simulation and click all of the boxes again. Place the refrigerator on the skateboard and APPLY a force of approximately 100 N. This time, DO NOT stop applying the FORCE to the refrigerator/skateboard. Answer the following questions. What happens to the SPEED of the Skateboard/Refrigerator when the FORCE is continuously applied? Are the forces acting on the Skateboard/Refrigerator BALANCED or UNBALANCED? Will the Skateboard/Refrigerator ever stop changing? Why or why not? EXPLAIN! PART 2: (FRICTION) Click on the Motion Tab. Play around with the simulation so that you know how to use it. Make sure that all of the boxes in the upper right hand corner are checked (Forces, Sum of Forces, Values, Masses, Speed) Play around with the simulation so you know how it works. How does the presence of FRICTION affect the movement of the objects in the simulation? BEFORE the object starts moving, what do you notice about the FRICTION FORCE and the APPLIED FORCE? (Are the FORCES BALANCED or UNBALANCED?) AFTER the object starts moving, what do you notice about the FRICTION FORCE and the APPLIED FORCE? (Are the FORCES BALANCED or UNBALANCED? Place 1 50 kg box on the ground. How much FORCE is required to put the box in MOTION?__________ Place the 2nd 50 kg box on top of the 1st. PREDICT how much FORCE will be required to put the box in MOTION._____________________________________________ Try it. 2 What was the ACTUAL FORCE REQUIRED? _____________________________________ How are these 2 FORCES related? ________________________________________________ Can you use this to PREDICT how much force is required to move the REFRIGERATOR? PREDICTION_____________________ACTUAL____________________ The Moving Man In this activity you will investigate velocity using charts. Velocity is the rate of speed in which something happens. will use charts to describe the velocity, direction, and time a man’s movement. Click on the following link: http://phet.colorado.edu/en/simulation/movingThis is a screen shot of the website. You man Click: Run Now! It should take time to load. When it loads this screen should appear: Use this Sim to complete today’s activities. On the introduction tab, check the velocity vector box. Explore the introduction page by either moving the man (by clicking and dragging him) or by moving the blue, red, and green tabs. You can also type in a position, velocity, or acceleration amount in the box (between -10 to 10) and press return. Be sure to view the playback. Before you press play chose how fast or slow you want to view the playback. Directions: Reset all. Slowly move the man to the tree, stop, and press pause. Press Playback. Slide the tab so that the playback will play at a slow speed. Press play. ● What do you notice about the position, velocity, and acceleration bars? Reset all. Quickly move the man to the house, stop, and press pause. Press Playback. Slide the tab so that the playback will play at a slow speed. Press play. ● What do you notice about the position, velocity, and acceleration bars? 3 How can charts help us track movement? Click on the Charts tab on the left top corner of the page. A screen that looks like this should appear: Familiarize yourself with the charts page by moving the man in different directions and velocities. Make sure to playback, slow down, watch the movement on the charts and pay attention to the velocity rate. To set the man at a specific position: First move him to the position you want him to start. Then press pause. Last press clear. At this point the time should return to 0 and the charts will be clean. When you are ready to begin, move the man. Look at the charts to the below. Complete the fill-in which describes the moving man’s velocity, the direction he takes, and the time it takes for him to move about. Word Bank (words may be used more than once) house quickly tree stops slowly 6. The moving man starts at the _______________. a. tree b. house c. slowly d. stops 7. He begins walking __________ towards the house. a. quickly b. stops c. slowly d. tree 8. He soon _______ for seconds to say hello to a neighbor. a. stops b. quickly c. slowly d. house 9. He then begins walking _______________ and immediately stops. a. stops b. quickly c. slowly d. house 10. He realizes his shoe is untied. It takes him __________ seconds to tie his shoe. a. 1 b. 3 c. 6 d. 9 11. He quickly begins walking towards the _______________. a. house b. tree c. slowly d. stops 12. He _______________ when he realized he dropped his wallet. a. slowly b. stops c. quickly d. house 13. a. 1 He picks up his wallet and the change that fell out. It takes __________ seconds to pick everything up. b. 2 c. 5 d. 20 4 Briefly explain your description. (For example, What on the charts tell you that the moving man was moving quickly, slowly, has stop, or what direction he is moving?) Application Phase Activity 2: a. Play with the moving man for 2 minutes on the Charts page. Move the man around using various velocities, directions, and make him stop once or twice. b. Draw a picture of the moving man’s movement below and describe his movements. 14. What do you notice about the time it takes to travel when the velocity is low? a. less time b. more time c. same time. 15. What do you notice about the time it takes to travel when the velocity is high? a. less time b. more time c. same time. 16. It takes a _______________ (shorter, longer) time to reach a destination if your velocity is _______________ (low, high). a. shorter, low b. shorter, high c. longer, low d. longer, high If there is extra time try making the letters M, N, or W on the charts by moving the man and describe it. If you really have time,.... check out this link and use vectors to solve the problems http://pbskids.org/zoom/games/3puckchuck/ 5 http://www.physics4 kids.com/extras/quiz _motion_laws/index. html 6