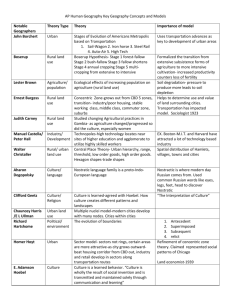
STATE ORGANIZATION AND
NATIONAL POWER
Large-area Influences
on State Power
Colonialism
Large-area Influences
on State Power
Economic dimensions of power
Economic trends
Understanding a country’s global economy
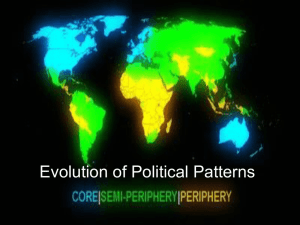
World-System Analysis
View the world as an interlocked system of states
Perspective ties political geography more closely to
economic geography
World Systems Theory:
core, semi-periphery, periphery
The world economy has a three-tier structure.
A. Core-higher levels of Ed., higher salaries,
more technology
B. Periphery: lower levels of Ed., lower salaries,
less technology
C. Semi-periphery: places where core and
periphery processes are both occurring, places
that are exploited by the core but in turn exploit
the periphery.
*core takes advantage of cheap labor, less taxes,
lax environmental standards in the periphery,
semi acts as a buffer between the two.
Freidrick Ratzel: Organic Theory
A state, which is a collection of humans,
would function and behave as an
organism.
Hitler used this theory to expand his
territory.
The Heartland Theory
-Land based power (not sea)
would rule the world.
Eurasia=Heart is resource
rich, pivotal area from
Eastern Europe to Eastern
Siberia. This area would be
the base for world conquest.
1. Who rules Eastern Europe
commands the Heartland.
2. Who rules the heartland
commands the world island.
3. Who rules the World Island
commands the world.
When this theory was proposed
Russia was in disarray. No
one foresaw would be a
super power
Rimland Theory: Nicholas
Spykman
Eurasian Rim, not its heart
held the key to global power.
1. Who controls Rimland rules
Eurasia.
2. Who rules Eurasia controls
the destinies of the world.
The rimland is a fragmented
zone, won’t be under the
power of 1 super power. A
divided rimland is key to the
balance of power of the world.
Today: Western Europe vs.
China
The Character of State Territory
Population vs. territory size
E.g., China
Acquisition of colonial empires
½ world’s states < 5 million people
Organizational capacity more important
Core areas
Usually the original nucleus of a state
Play an important role in a state's development
No core area vs. Multicore states
E.g., Nigeria's three cores mark ethnic and cultural
diverse areas of the state
The Character of State Territory
Capital cities
Political nerve center
Former colonies tried to imitate European model
Primate cities
A capital city by far the largest and most economically
influential
Common in agriculturally-dominant economies
Forward capitals
Reunification and capitals
Forward capital in Canada
Internal Political-Geographic
Structure
All states confront divisive forces
The needs of a well-functioning state
Clearly bounded territory with adequate
infrastructure
Effective administrative framework, a
productive core area, and a prominent capital
Unitary & Federal Systems
Early European nation-states were unitary states
The federal state arose in the New World
Federalism accommodated regional interest by
vesting primary power in provinces
Switzerland
Location for a capital city challenging for
federations
Britain and India
Today’s divisive forces in Europe
European reconstruction
Resources
De Blij, Harm, J. (2007). Human Geography People, Place and Culture.
Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley & Sons Inc.
Domosh, Mona, Neumann, Roderic, Price, Patricia, & Jordan-Bychkov,
2010. The Human Mosaic, A Cultural Approach to Human Geography. New
York: W.H. Freeman and Company.
Fellman, Jerome, D., Getis, Arthur, & Getis, Judith, 2008. Human
Geography, Landscapes of Human Activities. Boston, MA: McGraw-Hill
Higher Education.
Pulsipher, Lydia Mihelic and Alex M. and Pulsipher, 2008. World
Regional Geography, Global Patterns, Local Lives. W.H. Freeman and
Company New York.
Rubenstein, James M. (2008). An introduction to human geography The
cultural landscape. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson Prentice Hall.
Benewick, Robert, & Donald, Stephanie H. (2005). The State of
China Atlas. Berkeley: University of California Press.