File - The Components of a computer
advertisement

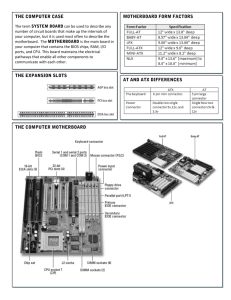
Computer system components By Corey Burton GPU • GPU stands for ‘graphics processing unit’. The GPU can help the computer run smoothly. GPU is used for computing 3D functions generally. The GPU does things like lighting effects, object transformations and 3D motion. NIC • NIC stands for ‘network interface card’. This card enables the computer to be connected to the network cable. These cards generally use a Ethernet cable. CPU • CPU stands for ‘central processing unit’. This is the main thing that runs your computer. It can process more complicated functions or basic instructions. Every time something is needed to be done it gets sent to the CPU to be completed. The CPU never stops running when the computer is on, it constantly keeps on processing. Case • The case of the computer protects everything from getting damaged the things inside the case are very valuable and fragile, so by having the case it will prevent you from breaking the components inside. Fan • The fans main job in the computer is to keep everything cool, it either works by spinning and bringing cold air in or taking hot air out. PSU • PSU stands for ‘power supply unit’. The power supply unit's job is to change the power supplied from the outlet into available power for the many parts inside the computer case. RAM • RAM stands for ‘random access memory’, it is made up of small memory chips, the memory modules formed by these small memory chips are installed in the RAM slots in a motherboard. Every time something gets loaded on your computer it gets loaded from the hard drive in to the RAM, its is transferred to the RAM because RAM is much faster at reading data than the hard drive. This also prevents any lag. The bigger RAM your computer has the more data can be added to the hard drive. BIOS • BIOS stands for ‘basic input/output system’. BIOS is pre- installed on windows based computers, the computer uses the BIOS to start up. The CPU accesses the BIOS prior to the operating system being loaded. The BIOS makes sure all hardware connections are running smoothly and locates all the devices. If everything is ok then the BIOS will load up the operating system into the computers memory, this finishes the boot-up process. Expansion Slots • The expansion slots are located in the computers motherboard, the expansion slots allows extra devices to be added to the computer. There are three types of expansion slots PCI-E, AGP and PCI. Motherboard • The mother board is the main circuit board of your computer. There are many things attached to the motherboard such as: CPU, ROM, RAM, Expansion Slots, PCI Slots and USB ports. The motherboard also controls your hard drive so effectively, the motherboard is what makes everything work in your computer. Optical Drive • The word optical refers to the lasers which can read the data on discs. CD’s and DVD’s are put in to the optical drive and it job is to read the discs so the computer can understand. The most common optical drives are: CD-ROM, CD-RW, DVDROM, DVD-RW, and Blu-ray drives. The laser does two types of things it reads data and writes data the laser used to write data is a lot more powerful. HDD • HDD stands for ‘Hard DISK DRIVE’ and stores all your computer data, all your folders and files are located here. The data is stored on stack mounted disk that spin fast to enable data to be accessed immediately the computers drive, the data from this is stored in the hard drive so when the computer is turned off the data is saved. Northbridge • The Northbridge is the main processor and manages data in the CPU. It connects the CPU to other primary computer components.(RAM , FSB, PCI Express cards, and the AGP card). The Northbridge is also connected to the Southbridge which controls all other components. Southbridge • The Southbridge is the lesser of the two Bridges. Its designed to connect the Northbridge to other components (hard drives, network connections, USB and Firewire devices, the system clock, and standard PCI cards). Its job is to send and receive data to the CPU which is connected to Northbridge and also connected to the computers processor. IDE • IDE stands for ‘Integrated Device Electronics’. IDE is a standard electronic interface, integrated device electronics basically means how the technology integrates the electronics controller into the drive itself, it is used between a computer motherboard’s data paths or bus. Most computers now used a more advanced IDE called enhanced integrated device electronics. And because of this in todays computers, the IDE controller is often built in to the motherborad. SATA • SATA stands for ‘Serial advanced technology attachment’ it is an interface that connects ATA’s to the motherboard. SATA transfer rates start at 150MBps, which is faster than even the fastest 100MBps ATA/100 drives. PCI • PCI stands for ‘peripheral component interconnect’. PCI is designed by Intel and can be used in both a mac and pc. PCI is sometimes used by graphics card. PCI-E • The PCI express is controlled by the computers motherboard. The PCI-E is used more often than the normal PCI. As it is more advanced to keep up with technology. AGP • AGP stands for ‘Accelerated Graphics Port’. This is an expansion slot that was created just for graphics cards. AGP can render graphics faster than the PCI making it more reliable. The AGP is built in to the motherboard of the computer, but because AGP need an expansion slot, they can only be used in desktop computers. With the arrival of the PCI express in 2004 the AGP slots were removed from computers completely in 2006.