read with and to your child
advertisement

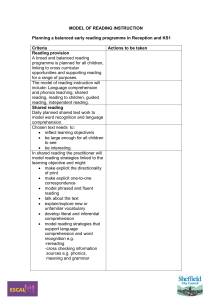
•Guided reading in school and at home •Choosing books •Every child an enthusiastic reader •Comprehension skills Reading at school •Guided reading in school and at home •Choosing books •Every child an enthusiastic reader •Comprehension skills • • • • • Shared Reading Guided Reading Individual Reading Quiet Reading Paired Reading • DM Developing Reading Skills In order to become good readers, children need to: - be read stories - share books - use illustrations to aid understanding - decipher the meaning of new words from their contexts - know the letter sounds (phonics) DM How do children learn to read? • Pupils become successful readers by learning to use a range of strategies to get at the meaning of a text • Recognising and understanding the words on the page is no guarantee that the text will be understood. • DM Letters and Sounds Some children in years 5 and 6 will still need support in: • • • • • Recognising sounds Reading tricky words on sight Blending for reading Segmenting for spelling Applying skills – reading or writing a sentence DM Principles of Guided Reading • Children are grouped by ability • Children read guided reading book at home – at least twice • The book will be at the top of their ability – parental support • Children discuss what they have read during the week (see next page for range of questions) VH Reading assessment focus (AF) grids AF 1 • • Use a range of strategies, including accurate decoding of text, to read for meaning Skimming and scanning AF 2 • • • Understand, describe, select or retrieve information, events or ideas from texts and use quotation and reference to text How did Christopher Robin get the tail back on Eeyore? Tell me something about the family this book is about – names, occupations, nationality, ages AF 3 • • • Deduce, infer or interpret information, events or ideas from texts Why did Pooh come over all funny when he saw Eeyore jumping around with his tail back? Why were the old couple suspicious when he broke up and divided the chocolate? AF 4 • Identify and comment on the structure and organisation of texts, including grammatical and presentational features at text level Why has the author not spelled the word ‘tremendous’ correctly when Avery uses it? Explain the significance of the title of this chapter. • • AF 5 • • • AF 6 AF 7 • • Explain and comment on writers’ uses of language, including grammatical and literary features at word and sentence level What is the play of words that Pooh uses when he says Eeyore was ‘attached’ to his tail? P5. ‘Joseph must act quickly…He must get hold of them…He must lift the guard…Why has the author used ‘must’ so often in this paragraph. What effect does it have? • Identify and comment on writers’ purposes and viewpoints and the overall effect of the text on the reader Why does the author call the sentry ‘burly’ when Ruth first meets him? He has chosen this word deliberately? What does it mean, first? Why does the author have the cook as a merry, cheerful person? What is he trying to emphasise? • • • Relate texts to their social, cultural and historical contexts and literary traditions Compare Ruth’s school to your own experience in this school. Can it be done? Why were some Poles willing to attack the well-equipped Nazis with only their own bare hands? Helping your child with comprehension VH Perfect answers • Why was the place bleak and silent? • Why was Mrs Krause so reticent about the fate of the children? Why did she keep quiet? • David put the bottle of whisky inthe pillowcase. True or False • ‘The place was bleak and silent. So many people were dead, or had fled or were hiding.’ • ‘Mrs Krause was reticent because she didn’t want to have to tell him that his children were dead; it was a horrible way to die. She didn’t want him to lose all hope.’ • ‘It is false as David did not put the bottle of whisky in thepillowcase. He carried it himself.’ Children can improve their reading by: • Correcting mistakes faster • Using expression • Noticing and using punctuation marks • Reading at a faster pace with greater fluency • Identifying interesting words • Showing an interest in longer texts VH • Skimming and scanning Assessing reading • Teachers assess children's reading regularly using teacher assessments, past tests and Benchmarking • Children need to be able to understand what they have read and be able to answer questions about the text • Children must demonstrate a good level of comprehension DM Helping your child to read (KS2) • Make reading fun! Share books and other forms of print – read with and to your child • Encourage your child to discuss the books that they bring home • Praise your child for reading longer books but let them read easier books occasionally • Ask your child for his/her opinion of the book • Play “Boggle” or other word games VH Libraries • Are free! • Can try out loads of books and find out what you really like • Stock a range of new titles monthly • Expose you to books you didn’t even know existed • If you don’t like the book, it doesn’t matter, no money has been wasted! VH Making your child an enthusiastic reader • Read to them…excitedly (model) • Let your child see that you enjoy reading • Value your child's choice of book • Encourage them to read anything and everything! • Be positive when you hear your child read VH