File - Queen's University Belfast
advertisement

Achieving a Healthy Work/life
balance & the impact of
Gender on Mental Health
Queen’s University Belfast
John Foster
2014
Carecall
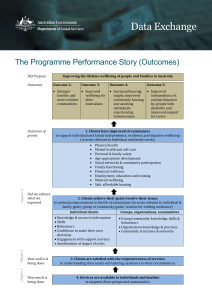
Course Objectives:
Learning Outcomes
• Develop strategies to manage work/life balance
• Balance in personal lifestyles
• Planning for success in work and life
• Develop self-confidence in a pressurised world
• Identify sources of support
The Power of Emotions
1. Fear of the Unknown
2. ‘People don’t know me’
3. Challenging NEGATIVE self-talk
4. ‘Men are from Mars and Women are from
Venus’
TRUST vs. MISTRUST
Bombarded by Life Choices
•
•
•
•
Work relationships
Family relationships
Friendships
Managing pressure to be “all
things to all people”
• Alcohol, drugs, technology,
gambling, sex
• Self-doubt, self-criticism
• Emotional Intelligence
Introduction to mental health
Emotional Health and Mental Wellbeing
Key elements as identified by World Health Organisation (WHO)
Subjective wellbeing - feeling good about yourself
Self-efficacy - self-belief, able to tackle difficult tasks
Autonomy - freedom and choice
Resilience - the ability to cope with the stresses of life
Emotional potential - recognition of the ability to realise one’s emotional
potential
Intellectual potential - recognition of the ability to realise one’s
intellectual potential
Work productively and fruitfully - making a worthwhile contribution
Social wellbeing - Making a worthwhile contribution to the community
Intergenerational dependence - connectedness and support
World Health Organisation (2003) {adapted}
The element of mental wellbeing
Flourishing Mental Health
Emotional wellbeing
•Happiness
•Confidence and,
•The opposite of depression (diagnosis of a complete state of mental health)
Social wellbeing
•Good relationships with others
•When neglected, is shown to manifest conversely in conduct disordered
behaviour, delinquency, interpersonal violence and bullying
Psychological wellbeing
•Autonomy and control
•Problem solving
•Attentiveness or involvement
•A sense of coherent identity
Aim for flourishing Mental Health
Mental health is more than the absence of illness
What are you going to do to protect and promoting your
emotional health and mental wellbeing in the workplace?
Are you working to live or living to work?
Common Thinking Errors
Challenging Questions
• How do you do your reality testing?
• What are alternative explanations?
• How do you achieve perspective?
• How does goal-directed thinking help?
•To address gender inequalities requires commitment and action from everyone, at all
levels of the organisation
•To tackle the unequal representation of women in science requires changing cultures and
attitudes across the organisation
•The absence of diversity at management and policy-making levels has broad implications
which the organisation will examine
•The high loss rate of women in science is an urgent concern which the organisation will
address
•The system of short-term contracts has particularly negative consequences for the
retention and progression of women in science, which the organisation recognises
•There are both personal and structural obstacles to women making the transition from
PhD into a sustainable academic career in science, which require the active consideration
of the organisation
The Vitruvian Man
This image provides the
perfect example of
Leonardo da Vinci’s keen
interest in proportion.
Virginia Satir, founding member of Mental Research Institute (MRI)
Carol Gilligan
• Gender Differences
• Images of Self
• The Masculine Ascent Up the Steps of Justice
• Not All People Are Men
• For Whom Do You Care?
In a Different Voice, 1982. Harvard University Press
Carol Gilligan, Professor of Psychology, New York University.
Steve Biddulph
The five truths of manhood
1. You are going to die.
2. Life is hard.
3. You are not that important.
4. Your life is not about you.
5. You are not in control of the outcome.
Steve Biddulph, Professor of Psychology, Melbourne and Author