5 Themes of Geography
advertisement

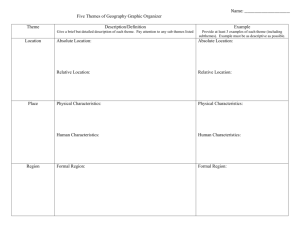
5 THEMES OF GEOGRAPHY 5 THEMES OF GEOGRAPHY Geographers study the world by looking at Location Place Region Movement Human-Environment Interaction #1 LOCATION: WHERE IS IT? Absolute Location The exact place on the earth where a geographic feature is found 3322 RR 620 South Austin, TX LTHS Room J206 Latitude = 30 degrees, 19.7 minutes North Longitude = 97 degrees, 58.2 minutes West Relative Location Describes a place in comparison to other places or landmarks around it Across the street from LTHS 170 miles northwest of Houston #2 PLACE: WHAT IS Describes the physical IT LIKE? features and cultural characteristics of a location. #3 REGION: HOW ARE PLACES SIMILAR OR DIFFERENT? Describes an area of the earth’s surface with similar characteristics, usually more than one Criteria for defining region depends on geographer’s purpose Similar Characteristics • Physical • Political • Economic • Cultural Three Categories of a Region • Formal • Functional • Perceptual GEOGRAPHIC REGIONS: WHAT DEFINES A REGION? Physical landforms, climate, vegetation Human (natural) characteristics (cultural) characteristics language, religion, ethnicity, population FORMAL REGION Defined by a limited number of related characteristics. Continents Climate Culture Examples? United States and Canada Latin America Europe Russia and the Republics Africa Southwest Asia South Asia East Asia Southeast Asia, Oceania, and Antarctica FUNCTIONAL REGION Organized around interactions and connections between places, especially around some central point. Example: City and suburbs Highways Subways Bus lines PERCEPTUAL REGIONS A region in which people perceive, or see, the characteristics of the region in the same way How we stereotype them Is it always the same for everyone? What are the perceptions of the following regions: Texas New York Hollywood Africa Middle East SUB-REGIONS Further classification of Regions based upon physical features and human characteristics. Examples: The United States is in the North American Region. However, the U.S. has several sub-regions: Northeast, Midwest, South, etc. #4 MOVEMENT How and why people, plants, animals, and ideas move through time and place How do geographers analyze movement? By looking at three types of distances: linear, time, and psychological #5 HUMAN: ENVIRONMENT INTERACTION People learn to use what the environment offers them and to change that environment to meet their needs. WHAT IS HUMAN ENVIRONMENT INTERACTION? There are two key human/environment interaction: Humans adapt to the environment. They alter what they do and how they do it. Humans modify the environment. They change the landscape to suit their needs. Changes can be positive or negative Positive: Makes places safer or more livable Negative: Pollutes or destroys beauty IMPORTANCE OF 5 THEMES??? They give us a “geographic lens” through which to view the world. Every unit of study this year will focus in some way on these themes.