The Nine Planets, Part # 2
advertisement

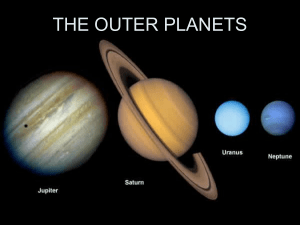
The Nine Planets—Part #2 NAME: _______________________________ http://www.nineplanets.org Jupiter 1. How does Jupiter’s mass compare to Earth’s? 2. Why is this planet named “Jupiter? 3. The three celestial objects brighter than Jupiter are: 4. Name the four (4) Galilean moons of Jupiter: 5. How does the density of Jupiter vary with depth? 6. Jupiter’s composition: 7. What planet has a similar composition? 8. Jupiter’s core is probably 10-15 Earth masses. What lies directly above the core that makes up the “main bulk” of the planet? 9. The element in #8 is a gas on earth. On Jupiter, it may be liquid because the temperature is ____________________ and the pressure closer to the core is ______________________ . 10. The bands of color that we see on Jupiter are due to atmospheric “zones” and “belts.” They are areas of different air movement (wind). How fast are some of the winds on Jupiter? 11. GRS is an abbreviation for: 12. What is the GRS? 13.How does the size of the GRS compare to that of the earth? 14.How many satellites does Jupiter have? 15. What is unique about Io? (Click on the picture right side of the erupting volcano.) Jupiter Key Questions: How do rotations and the CORIOLIS EFFECT create Jupiter’s wind belts? Why does Jupiter have more “moons” that any other planet? SATURN 16. In Roman mythology, Saturn is: 17. What is Cassini? Huygens? For more information, see: http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/cassini/main/index.html 18.Saturn’s average density: 19.Saturn’s composition: 20.How do Saturn’s atmospheric bands compare to Jupiter’s? 21.Saturn’s rings are made of: 22.They are __________ thick and _______________________________ wide. 23. Titan, a satellite of Saturn is unique because it: 24. Titan’s atmosphere: Saturn Key Questions: What ARE Saturn’s rings? How did Saturn’s rings form? URANUS 25. The name for Uranus has what origin? 26. There has been only one NASA mission to Uranus: 27. Uranus’ most unique feature is the tilt of its rotational axis. Describe (Key question): 28. Composition: 29.Why is Uranus blue (Key Question)? NEPTUNE 30. Neptune is named for the Roman god of: 31.Venus is the “twin” of Earth. What is the “twin” of Neptune? 32. Describe Neptune’s composition: 33. Triton, one of Neptune’s moons, is one of only four known sites of volcanism in the solar system. What is unique about these “volcanoes?” 34. Who was triton in mythology? 35. How many moons does Neptune have? Neptune Key Questions: What is unique about the orbit of Neptune’s moon, Triton? PLUTO key question: If Pluto is no longer a planet, what IS a planet? (Three criteria.) How is Pluto now classified?