Measuring Simple Harmonic Motion
advertisement

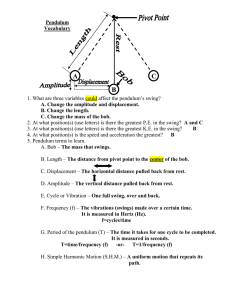
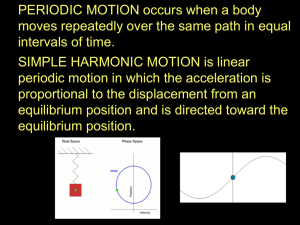
Measuring Simple Harmonic Motion Chapter 12 Section 2 Measuring The Motion There are 3 things that determine the motion of a mass in simple harmonic motion. Amplitude Period Frequency Amplitude Amplitude – The maximum displacement from the equilibrium position. Can be measured in different ways Pendulum – The angle (radians) between the equilibrium position and the maximum displacement. Spring-mass – The maximum amount (meters) stretched or compressed from the equilibrium position. Period Period – The time it takes to execute a complete cycle of motion. For example: If it takes 5 seconds for a person on a swing to swing back and forth, then the period of the motion would be 5 seconds. SI units for period – Seconds (s) Variable given for period – Capital letter (T) Displacement For Period The displacement of an object in simple harmonic motion during the time of 1T (time to compete one cycle) is “ZERO.” Frequency Frequency – The number of cycles or vibrations per unit time. For example: The person on the swing completes one cycle in 5 seconds, the frequency would be 1/5 cycles per second or 0.2 cycles per second. Units For Frequency SI units for frequency – S-1 Variable for frequency – lower case letter (f) In the case of the person swinging, the frequency would be: This is known as Hertz (Hz) 0.2 cycles per second = 0.2 Hz A typical TV set has a frequency of 60Hz, which means 60 frames per second. Differences Between Period and Frequency Period is time per cycle. Frequency is the number of cycles per unit time. They are inversely proportional. Equations For Frequency and Period 1 𝑓= 𝑇 1 𝑇= 𝑓 If the period or the frequency is known, this relationship can be used to calculate the other value. Period (s) Frequency (Hz) Determining The Period of a Pendulum The strings length and the free fall acceleration determine the period of a simple pendulum. Things that don’t determine the Period: Amplitude (for angles less then 15 degrees) Mass of the bob Simple Pendulum Equation 𝑙 𝑇 = 2𝜋 𝑔 𝑇 = 𝑃𝑒𝑟𝑖𝑜𝑑 𝑠 𝑙 = 𝐿𝑒𝑛𝑔𝑡ℎ 𝑚 𝑚 𝑔 = 𝐴𝑐𝑐𝑒𝑙𝑒𝑟𝑎𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛 𝑑𝑢𝑒 𝑡𝑜 𝐺𝑟𝑎𝑣𝑖𝑡𝑦 (9.8𝑠2) Example Problem #1 A desktop toy swings back and forth once every 1.0 seconds. How tall is this toy? Example Problem #1 Answer length = 0.25m Example Problem #2 What is the period of a 3.98m long pendulum? Example Problem #2 Answer T = 4.00 seconds Period of a Mass-Spring System The mass attached to the spring and the spring constant (k) determine the period. Things that don’t determine the period: Amplitude Period of a Mass-Spring System Equation 𝑚 𝑇 = 2𝜋 𝑘 𝑇 = 𝑃𝑒𝑟𝑖𝑜𝑑 𝑠 𝑚 = 𝑀𝑎𝑠𝑠 𝑘𝑔 𝑘 = 𝑆𝑝𝑟𝑖𝑛𝑔 𝐶𝑜𝑛𝑠𝑡𝑎𝑛𝑡 𝑁 𝑚 Example Problem #3 A 1.0 kg mass attached to one end of a spring completes one oscillation every 2.0 seconds. Find the spring constant. Example Problem #3 Answer k = 9.9N/m