Lewis Energy types

ENERGY:
What do we remember?
ENERGY
Where is energy found and when?
Energy is around you all the time
What is energy?
Ability to do work
When work is done, what happens to energy?
Energy is given off
What is the SI unit for energy?
Joules (J)
Energy has the same SI unit as what?
Work
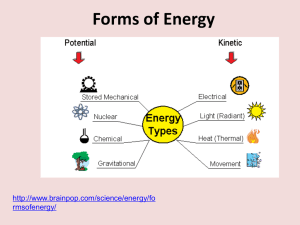
What are the two states of energy?
What can you tell me about KINETIC
ENERGY?(KE)
• Greek = kinetikos = “moving”
• Energy of motion/movement
• Depends on mass and speed
• KE = mv 2
2
• ↑ speed = ↑ KE
• ↑ mass = ↑ KE
• Speed has greater effect than mass
What can you tell me about
POTENTIAL ENERGY (PE)
• Energy of position/shape
• Stored energy
• Gravitational Potential Energy (GPE)
– (GPE) = weight x height
– N x m = J
MECHANICAL ENERGY (ME)
• Objects total energy of motion and position
• ME = PE + KE
• PE ↑ = KE ↓
• PE ↓ = KE ↑
• ME remains constant
Pendulum
8
Car on an incline
9
Energy can take different forms…
THERMAL ENERGY
• KE
• Total energy of particles (atoms and molecules) that make up object
• ↑ movement = ↑ KE = ↑ temp. = ↑ thermal energy
• Particles far apart have more energy than particles close together.
Least energy
Energy vs. Thermal energy
Particle movement
Most energy most thermal energy
Amount of particles
CHEMICAL ENERGY
• PE
• Compound energy that changes arrangement of atoms
• Stored in bonds between atoms
• Chemical rxn takes place
ELECTRICAL ENERGY
• KE
• Moving electrons back and forth through wire or current
• Produced at power plants
SOUND ENERGY
• PE and KE
• Energy of vibrations
• Transmits energy to air
• Carried through solids, liquids, and gases
• Travels in waves
LIGHT/RADIANT ENERGY
• Not all light can be seen
• Vibrations of electrically charged particles
• Travels through waves and empty space
NUCLEAR ENERGY
• Produced from change of nucleus
• Two types
– Fission: splitting nucleus (electrical energy)
– Fusion: joining nuclei (sun)
• Uranium:
– stores a lot of PE
– energy used from nuclei being split
– generated at nuclear power plants
VENN DIAGRAM OF FORMS OF
ENERGY
POTENTIAL
ENERGY
KINETIC
ENERGY
THERMAL
CHEMICAL
SOUND
LIGHT/RADIANT
ELECTRICAL
NUCLEAR
ENERGY CONVERSIONS
• Transfer/change/conver sion of energy from one form to another
• Can be transferred converted to more than one form
Energy Conversions
“Breakfast is the most important meal of the day.”
Eating
Chemical
Energy
Being active Body temperature
Kinetic
Energy
Thermal
Energy
Energy Conversions electrical light and sound electrical light and thermal chemical electrical electrical kinetic and sound electrical kinetic, thermal, and sound
Energy Conversions
Energy Conversions
Energy Conversions
Explain the energy conversions below.
ENERGY AND MACHINES
• Machines make work easier by changing
– Size
– Direction
– or both of the force required to do the work
• Machines transfer energy and convert energy
Why are energy conversions important?
• It is useful for every day life.
– Ex. Wind used to cook a meal
• Efficiency
– Ex. Energy efficient light bulbs and appliances
WHERE DOES THE ENERGY GO?
• Energy is never lost but converted to other forms of energy
• Hills and friction help to tell what happens to energy
• Energy is used to overcome friction
• Some of the energy is always converted to thermal energy
Law of Conservation of Energy
• Energy can neither be created or destroyed
• Closed system- well-defined group of objects that transfer energy between each other.
• Total amount of energy always the same
• Ex. Roller coaster, light bulb
Perpetual motion machine
• Runs forever without additional energy
• Energy in = Energy out
• Will never happen because some energy is turned into thermal energy.
REFERENCES
• http://www.glenbrook.k12.il.us/gbssci/phys/ mmedia/energy/ce.html
http://www.physicsclassroom.com/mmedia/energy/se.html