The Digestive System
advertisement

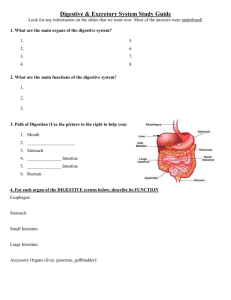
Amanda Dermer Keane Archibald Dayana Jimenez Courtney Blazer Chapter 18: Lesson 1 Eighth Graders Age: 13-14 Digestion Absorption Elimination Digestive System The purpose define the function of each organ the pathway food takes through the digestive tract Work Sheet Fill in the Blank Digestive System The organs and parts of the digestive pathway: Oral cavity Pharynx Esophagus Stomach Small Intestine Large Intestine Digestive System Teeth Tongue Liver Pancreas The process that breaks down food into substances that can be absorbed by the body for energy, growth, and repair. Ingestion: Mouth, Teeth & Tongue The function of the mouth is to ingest food sources The teeth are used for mastication breaking food down into smaller pieces The tongue forms food into a ball to prepare for swallowing Ingestion: Mouth, Teeth & Tongue The mouth, teeth, and tongue play a role in mechanical digestion. Mechanical digestion physically prepares food for chemical digestion by enzymes. Salivary Glands Secretes saliva a watery solution containing an enzyme that starts the digestion Cleanses the mouth Dissolves food chemicals Moisten food Salivary Glands The salivary glands begin the process of chemical digestion. Pharynx After leaving the mouth, food is passed on to the pharynx. As you swallow: Uvula: prevents food from passing into the nasal cavity. Epiglottis: prevent food from entering the respiratory tract. Esophagus Food passes through the pharynx into the esophagus Extends from the pharynx to the stomach Primary Function; Carry foods and liquids to stomach Peristalsis moves food though the digestive tract Stomach Located below the esophagus A hollow, saclike organ Consists of three layers of muscles Flexible, allowing it to expand when you eat. Stomach A temporary “storage tank” where the chemical breakdown of proteins begin. The food is mixed together with gastric juices, secretions from the stomach’s lining containing pepsin and hydrochloric acid. Stomach As the stomach fills: stomach contract churn the food and gastric juices together This produces chyme a creamy, fluid mixture of food and gastric juices . The passage of digested food from the digestive tract into the circulatory system. The small intestine is the major absorption site. Small Intestine The major part of digestion and absorption 20 to 23 feet in length Secretions from the pancreas, liver, and intestinal juices complete the chemical breakdown of all food. Small Intestine Millions of fingerlike projections called villi Each villus contains a network of capillaries which absorb digested food particles from the small intestine. Once food particles enter the capillaries in the villi, they are carried throughout the body by the blood. Small Intestine Three parts to the small intestine Duodenum Food enters here from the stomach Jejunum The middle section of the SI Ileum Allow one way flow into the large intestine. The Liver & Pancreas Liver: 2nd largest organ in the body. Acts to clear the blood of toxins then excreting them in the bile. Bile is a yellowish-green, bitter fluid important in the breakdown of fats. Liver & Pancreas The pancreas produces 3 enzymes: Trypsin, which digests proteins Amylase, which digests carbohydrates Lipase, which digests fats Located in the C of the SI’s duodenum. Gallbladder Storage organ for bile produced from liver Located below the liver The small intestine stimulates the release of bile into the duodenum. Not required for digestion Large Intestine Starts Ascending colon Ends at the anus. A.K.A. the colon 5 to 6 feet long Large Intestine Unabsorbed materials: leave the small intestine in the form of liquid and fiber enter the large intestine Absorbs most remaining Water Vitamins The expulsion of undigested food or body wastes. Elimination Harmless bacteria in the large intestine change the consistency of the undigested food into a semisolid waste, called feces Feces passes from the body through the anus Termed “bowel movement” Activity: Place that Organ Lifestyle & Dietary Factors Eat at least 3 servings from a variety of fruits and vegetables to avoid constipation Practice good hand washing hygiene Throw food away after it falls on the floor Wash all foods before eating Decrease caffeine consumption See Fact Sheet for More Dietary Info Dietary Activity Unhealthy Diet Scenario Medications Some over the counter drugs that will help aid in the relief of constipation and diarrhea. Diarrhea a. Imodium AD b. Pepto-Bismol Constipation a. Citrucel b. Ex-Lax Stats of Constipation & Diarrhea Deaths due to Constipation & Diarrhea Constipation 17% Infectious Diarrhea Constipation Infectious Diarrhea 83% Create your own digestive tract Each group will be representing a different part the digestive tract A member from each group will stand in front of the class and explain their organs function during the process of digestion Be creative and have fun with the activity