3-1 PowerPoint
advertisement

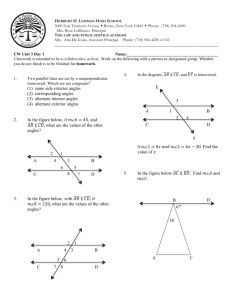
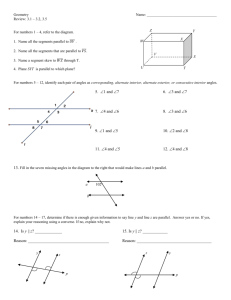
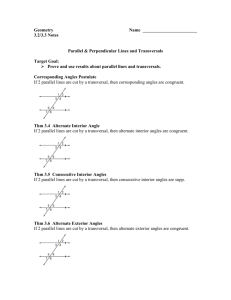
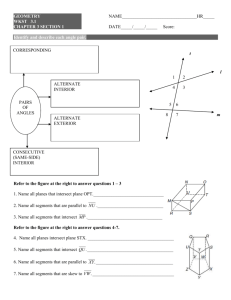
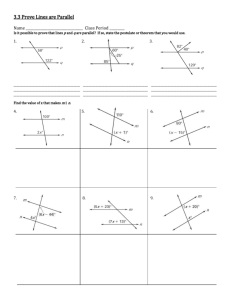
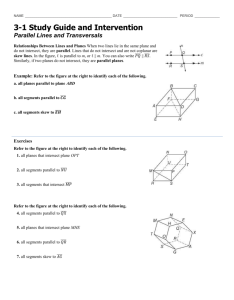
3.1: Lines and Angles 1 Today’s Objectives To identify relationships between figures in space To identify angles formed by two lines and a transversal Parallel Lines Parallel lines are coplanar lines that do not intersect. Arrows are used to indicate lines are parallel. The symbol used for parallel lines is ||. In the above figure, the arrows show that line AB is parallel to line CD. With symbols we denote, 𝐴𝐵 𝐶𝐷 . 3 Skew Lines and Parallel Planes Two lines are skew if they do not intersect and are not in the same plane (not coplanar). Ex: CG and EF are skew. All planes are either parallel or intersecting. A B Parallel planes are two planes that do not intersect. Ex: Plane ABC and Plane EFG D C are parallel planes E H F G 4 Examples: 1. 2. 3. 4. Name all segments that are parallel to Name all segments that intersect Name all segments that are skew to Name all planes that are parallel to plane BCG. A Answers: D 1. Segments BC, FG, & EH. 2. Segments DH, DC, AE & AB. 3. Segments CG, BF, FE, & GH. 4. Plane ADH. H B C E F 5 G Example: 1) What are the lines parallel to CD? 𝐴𝐵 𝐸𝐹 2) What lines are skew to CD? 𝐻𝐴 𝐺𝐵 𝐸𝐻 𝐹𝐺 3) Name the parallel plane to CDA. 𝐸𝐹𝐺 6 Transversal Definition: A line that intersects two or more lines in a plane at different points is called a transversal. When a transversal t intersects line n and m, EIGHT angles are formed t m Exterior angles: Outside the lines Interior angles : Between the lines n 7 Corresponding Angles Corresponding Angles: Two angles, on the same side of the transversal, that occupy corresponding positions, one interior and one exterior. 2 and 6, 1 and 5, 3 and 7, 4 and 8 1 3 5 7 2 4 6 8 8 Alternate Angles Alternate Interior Angles: Two angles that lie between the lines on opposite sides of the transversal (but not a linear pair). 3 and 6, 5 4 and Alternate Exterior Angles: Two angles that lie outside the lines on opposite sides of the transversal. 1 3 5 7 2 2 and 7, 8 4 6 8 9 1 and Consecutive Angles (aka Same-Side) Consecutive Interior Angles: Two angles that lie between the lines, both on the same side of the transversal. 3 and 5 , 4 and 6 Consecutive Exterior Angles: Two angles that lie outside the lines, both on the same side of the transversal. 1 and 7 , 8 2 and 1 3 5 7 2 4 6 8 10 Vertical Angles & Linear Pair Vertical Angles: Two angles that are opposite angles. Vertical angles are congruent. 1 4, 2 3, 5 8, 6 7 Linear Pair: Supplementary angles that form a straight line (sum = 180) 1 & 2 , 2 & 4 , 4 &3, 3 & 1, 5 & 6, 6 & 8, 8 & 7, 7 & 5 1 3 5 7 2 4 6 8 11 Example List all pairs that fit the description a. Corresponding < 4 and < 2 < 3 and < 1 < 5 and < 7 b. Alternate Exterior < 4 and < 8 < 1 and < 5 c. Alternate Interior < 2 and < 6 < 3 and < 7 d. Consecutive Interior < 3 and < 2 < 6 and < 7 < 6 and < 8 Example Complete the statement with corresponding, alternate exterior, alternate interior, or consecutive interior. 1. < 4 and < 8 are Alternate interior 2. < 2 and < 6 are Alternate exterior 3. < 1 and < 8 are Consecutive interior 4. < 7 and < 2 are Consecutive exterior 5. < 4 and < 6 are Corresponding 6. < 5 and < 7 are Vertical Take Home Message Parallel and skew lines When a transversal intersects two other lines, 8 different angles are formed Alternate vs Consecutive (same-side) Interior vs. Exterior