Supply and Demand
advertisement

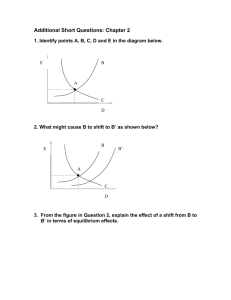
Supply and Demand Overheads Equilibrium Equilibrium is defined a state of rest; a situation that, one achieved, will not change, unless some external factor, previously held constant, changes. Market Equilibrium A market is said to be in equilibrium if the price in the market is such that the quantity supplied (QS) in the market and the quantity demanded (QD) in the market are equal. Price Demand and Supply of Hamburger Patties Supply = Demand 3.5 3 2.5 2 1.5 1 D0 S0 0.5 0 0 2000 4000 3333.33 6000 8000 6666.66 10000 12000 Quantity Quantity Price (per lb) supplied 0.3 0.60 0.90 1.20 1.50 1.80 2.10 2.40 2.50 1000 2000 3000 4000 5000 6000 7000 8000 9000 Quantity demanded 9800 8600 7400 6200 5000 3800 2600 1400 200 Excess supply and excess demand Excess supply At a given price, the excess of the quantity supplied over the quantity demand is called the excess supply. Excess supply = QS (P) - QD (P) Quantity Price (per lb) supplied 0.3 0.60 0.90 1.20 1.50 1.80 2.10 2.40 2.50 1000 2000 3000 4000 5000 6000 7000 8000 9000 Quantity demanded 9800 8600 7400 6200 5000 3800 2600 1400 200 At a price of $2.10, excess supply (QS (P) - QD (P) ) is given by 7,000 - 2,600 = 4,400 Quantity Price (per lb) supplied 0.3 0.60 0.90 1.20 1.50 1.80 2.10 2.40 2.50 1000 2000 3000 4000 5000 6000 7000 8000 9000 Quantity demanded 9800 8600 7400 6200 5000 3800 2600 1400 200 At a price of $1.20, excess supply (QS (P) - QD (P) ) is given by 4,000 - 6,200 = -2,200 Excess demand At a given price, the excess of the quantity demanded over the quantity supplied is called the excess demand. Excess Demand = QD (P) - QS (P) Quantity Price (per lb) supplied 0.3 0.60 0.90 1.20 1.50 1.80 2.10 2.40 2.50 1000 2000 3000 4000 5000 6000 7000 8000 9000 Quantity demanded 9800 8600 7400 6200 5000 3800 2600 1400 200 At a price of $0.90, excess demand (QD (P) - QS (P) ) is given by 7,400 - 3,000 = 4,400 Quantity Price (per lb) supplied 0.3 0.60 0.90 1.20 1.50 1.80 2.10 2.40 2.50 1000 2000 3000 4000 5000 6000 7000 8000 9000 Quantity demanded 9800 8600 7400 6200 5000 3800 2600 1400 200 At a price of $2.10, excess demand (QD (P) - QS (P) ) is given by 2,600 - 7,000 = -4,400 Market Equilibrium A market is in equilibrium when the price is such that the quantity supplied is equal to quantity demanded. A market is in equilibrium when the price is such that excess supply equals excess demand equals zero. Excess supply and excess demand and price pressure When the quantity demanded in the market exceeds the quantity supplied at a given price, QD (P) > QS (P) there is excess demand, and the price will tend to rise. Excess demand and excess supply and price pressure When the price in the market rises, quantity demanded falls & quantity supplied rises until an equilibrium is reached at which quantity demanded equals quantity supplied. The process of price rising so that excess demand falls to zero is called price rationing Price Graphical analysis of excess supply QS (P) > QD (P) 3.5 3 Supply = Demand Price Falls 2.5 2 1.5 1 D0 S0 0.5 0 0 2000 4000 6000 8000 10000 12000 Quantity Price Graphical analysis of excess demand Supply = Demand 3.5 3 Price Rises 2.5 2 1.5 1 D0 S0 0.5 0 0 2000 4000 6000 QD (P) > QS (P) 8000 10000 12000 Quantity Algebraic analysis of supply and demand Equilibrium Supply = Demand To find an equilibrium in a market: 1. Set supply equal to demand and solve for P. 2. Substitute P in the supply and demand equations to get the quantities. Example Demand Equation QD = 20 - 2P Demand Price QD = 20 - 2P 14 12 10 8 6 4 2 0 D0 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24 Quantity Example Supply Equation QS -4 + 2P Supply Price QS -4 + 2P 14 12 10 8 6 4 2 0 S0 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24 Quantity Price Demand and Supply QD = 20 - 2P QS -4 + 2P 14 12 10 8 6 4 2 0 D0 S0 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24 Quantity Example Calculation Set supply equal to demand and solve the equation for P. QD = 20 - 2P = -4 + 2P = QS 20 - 2P = -4 + 2P +4 +4 24 - 2P = 2P +2P +2P 24 = 4P 24 = 4P 4 4 6 = P QD = 20 - 2P = 20 – 2(6) =8 Some notes on solving equations We get equivalent equations if on both sides of the equality sign we do the following: a. add the same number b. subtract the same number c. multiply by the same number 0 d. divide by the same number 0. Comparative Statics or What happens when things change Demand Shifts Increases in demand (shifts to the right) will increase the equilibrium price and quantity. Decreases in demand (shifts to the left) will decrease the equilibrium price and quantity. Price Changes in Demand 16 S0 D0 D1 D2 14 12 10 8 6 4 2 0 0 5 10 15 20 Quantity 25 Supply Shifts Increases in supply (shifts to the right) will decrease the equilibrium price and increase the equilibrium quantity. Decreases in supply (shifts to the left) will increase the equilibrium price and decrease the equilibrium quantity. Price Changes in Supply D0 S0 S2 S1 14 12 10 8 6 4 2 0 0 5 10 15 20 Quantity Price Ceilings A price ceiling occurs when some outside force sets a price for the market that is below the equilibrium price. When quantity supplied & quantity demanded differ, the short side of the market — whichever of the two quantities is less — will prevail. Price Price Ceiling Supply Demand 3.5 3 Queuing 2.5 2 1.5 1 D0 S0 0.5 0 0 2000 4000 6000 QD (P) > QS (P) 8000 10000 12000 Quantity The results: Queuing Shortages A black market Price Floors A price floor occurs when some outside force sets a price for the market that is above the equilibrium price. When quantity supplied & quantity demanded differ, the short side of the market — whichever of the two quantities is less — will prevail. Price Price Floor Supply Demand QS (P) > QD (P) 3.5 3 Excess Supply 2.5 2 1.5 1 D0 S0 0.5 0 0 2000 4000 6000 8000 10000 12000 Quantity The results: Excess supply Unemployment