Phylum Echindermata
advertisement

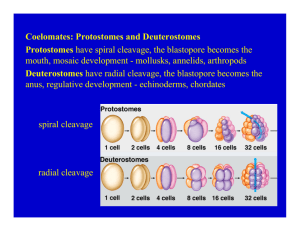
Echinoderms Phylum Echindermata •Share common features with chordates •Radial Cleavage •Deuterostomes (Blastopore becomes anus) •Development of true coeloem •Usually slow moving or sessile •Usually are radially symmetrical •Body parts usually radiate from center (frequently as 5 spokes) •Possess a thick calcium plate endoskeleton surrounded by a thin skin layer •Possess a unique Water Vascular System, which continues throughout animal and extends into extensions called Tube Feet. •Functions for locomotion, feeding, & gas exchange. •Reproduce sexually or through regeneration. Class Asteroidea Include sea stars Usually have 5 (or multiple of 5) arms radiating from central disk Tube feet located underneath each arm used for locomotion & grasping prey. Operate by hydraulic principles. Anatomy of a Sea Star Feeding Feed on mollusks by pulling shells apart and extending stomach outside the mouth into the bivalve. The bivalve is digested within it's shell. The sea star than re-ingests its stomach Reproduction Can reproduce sexually by releasing sperm and egg. Can reproduce by regeneration Sea Stars Class Ophiuroidea Include Brittle Stars Distinct central disks with long tube-like arms Lack suckers Move by serpentine motion of their arms Brittle Star Class Echinoidea Include Sea urchins & sand dollars Lack arms, but possess tube feet Many species of urchins possess poisonous spines used for defense Echinoideans Sand Dollar Sea Urchin Class Holothuroidea Include Sea cucumbers Are elongated along oralanal axis Lack spines and have reduced endoskeleton. Do possess tube feet and water vascular system Sea Cucumber Class Crinoidia Ancient class of animals Include sea lilies Filter feeders with arms radiating from mouth Most are sessile, but some can move Crinoids