FADS
advertisement
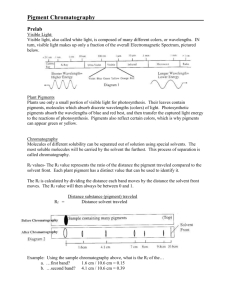
Flawed Scientific Theories • Alchemy: Pb -> Au • Photosynthesis: Light -> Sugar What Is Photosynthesis? • Photosynthesis is an endergonic (∆G + 686 kcal/mol) reaction in which carbon dioxide and hydrogen (derived from water) are fused to make glucose (C6H12O6). • To power this reaction, radiant energy from the sun excites electrons in pigments. The boost in energy is used to recharge ATP, which is used to “pay” for the synthesis of glucose. • 6CO2 + 6H2O + light ---- C6H12O6 + 6O2 How Does The Form Of Autotrophs Allow For The Function of Photosynthesis? Wavelength and Energy • Wavelength of electromagnetic radiation (λ) is inversely related to the amount of energy it possesses Accessory Pigments • Accessory pigments absorb the other wavelengths of light not absorbed by chlorophyll (GBIV) • The excited electrons of the accessory pigments are passed on to chlorophyll, exciting its electrons • Examples: – Beta Carotene (reflects orange) – Anthocyanin (reflects red) – Xanthophyll (reflects yellow) Why don’t most plants have pigments that reflect the color blue? BIV Absorption • Blue, indigo and violet have the shortest wavelengths • Shortest wavelengths produce the greatest excitation of electrons • More excited electrons = more ATP • Plants can’t afford NOT to absorb blue If red is low energy light, why do almost all pigments absorb it? RED LIGHT • If light is not immediately absorbed by the chloroplast, it is reflected by other objects in the environment • When light “bounces back”, it does so at a longer wavelength (red) • The amount of reflected red light is plentiful • Excessive absorption would also cause plant to overheat and lose water LAB: Identification of Photosynthetic Pigments via Paper Chromatography • Purpose: – To isolate and view the various photosynthetic pigments present in several different types of leaves. – To determine if said photosynthetic pigments are unique to each species or if common pigment molecules are shared between species • Method: Paper chromatography Paper Chromatography • Pigments are removed from leaf tissue using a non-polar solvent • Pigment extract is applied to a paper chromatogram and a solvent is passed through the paper • The pigments dissolve into the solvent and move up the chromatogram using adhesion and capillary action • Based upon their size, weight and polarity, different molecules move different distances up a paper chromatogram Rf Values & Pigment Identification • As each unique pigment molecule has different size, weight and polarity, each pigment moves a different % of the total distance on the chromatogram. • This % of the chromatogram traveled by the pigment is its Rate of Flow (Rf). • Unknown pigments can be identified or known pigments compared by using this value. Hypothesis • How will the pigments in three species of leaves differ (or will they)? Do all species have their own unique pigments or are they shared across species? – Spinichia oleracea – Daucus carota – Brassica cephalacea • Will there be a difference between the chromatograms of pigments derived from fresh vs. canned S. oleracea? Steps 1-5: Isolation of Pigments • Put on goggles and aprons • Each member of your group will work with a different species/preparation – – – – Spinichia oleracea (fresh) Spinichia oleracea (canned) Daucus carota Brassica acephalea • Obtain 0.5g of leaf tissue and 0.5g of MgSO4 and grind in mortar & pestle (no sand) • Add powder to small test tube with 2mL acetone solvent (A). Stopper, shake and let stand for 5-10 min. Steps 6-10: Preparation of Chromatogram • Fill the chromatography chamber (large tube) to depth of 0.5cm with chromatography solvent (CS) • Each member should obtain a blank chromatogram • Mark a pencil line 1cm from the bottom and cut bottom to a point • Dip a fresh capillary tube into the small test tube of pigment extract and transfer to the 1cm line of the chromatogram. • Let dry and repeat. • Using a paperclip, hang the chromatogram in the chamber with the tip of the chromatogram immersed in the solvent. DO NOT PLACE THE PIGMENTS DIRECTLY IN THE SOLVENT! • Let stand for 15-20 min Steps 11-12: Marking the Chromatogram • Remove the chromatogram from the chamber, dispose of the solvent into the waste container. • Mark the furthest point the solvent traveled immediately (this is the solvent front) • Identify each of the pigment bands and calculate the Rf value for each band using the formula in your lab Photosynthesis Is Comprised Of Two Main Metabolic Pathways • PHOTOLYSIS • • • • • • THE CALVIN CYCLE aka The Light Dependent • aka The Light Reactions Independent/Dark Occurs in grana of Reactions chloroplast • Occurs in stroma Depend upon light energy to • Do not require light accelerate electrons of pigments • Using the ATP from the photolysis, the Calvin ATP is produced to power 2nd set of reactions Cycle “fixes” Carbon Dioxide by combining it Water replaces electrons lost with hydrogen to make by chlorophyll. This causes water to split, releasing glucose oxygen gas. • Leftover hydrogen is used to build glucose