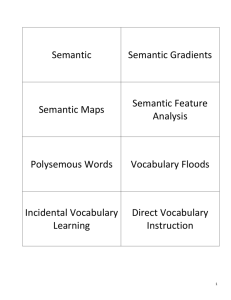
Multiple Meaning Words
advertisement

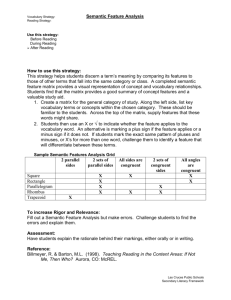
Teaching Vocabulary Meaning Through Semantic-Based Activities Designed by: Brenda Stephenson Mary Helen Gallien Vocabulary How do we teach it ? Teaching Vocabulary Definition-Based Approaches Context-Based Approaches Concept-Based Approaches Semantic Mapping (Schirmer, 2000) Teaching Vocabulary Definition-Based Approaches Definition-Based Approach Two Forms 1st- Students are asked to look up definitions of a list of words in the dictionary, copy them, and write a sentence for each word. 2nd- The teacher briefly discusses the meaning of new words in an upcoming reading selection. Definition Related Technologies Many software programs have dictionaries and other reference tools built into them There are a variety of CDbased dictionaries including picture dictionaries and sign language dictionaries Dictionary and ESL websites are another option Cloze procedure (ex. ClozePro by Crick Software) and other vocabulary software programs (ex. Vocabulary Companion by VISIONS Inc.) can be used to present words in different contexts There are many programs and websites that allow teachers to create materials using their own word lists related to their curriculum Teaching Vocabulary Definition-Based Approaches Context-Based Approaches Concept-Based Approaches Semantic Mapping (Schirmer, 2000) Teaching Vocabulary Context-Based Approaches Context-Based Approach Youngsters ultimately need to encounter a word in context to develop a full sense of its meaning (Gipe, 1980; Gipe & Arnold, 1979). Guessing vocabulary from context is the most frequent way to discover the meaning of new words. Context-Based Approach Students need to be taught to: Look before, at, and after the word. Connect what they know to what the author has written. Predict a possible meaning. Resolve or re-do. Decide if they know enough, should try again, or consult an expert or reference. Blachowicz & Fisher (1996) Context-Based Strategy Technologies There are many commercially available educational software programs that focus on introducing vocabulary within passages (ex. Vocabulary Development by Optimum Resources) Many have pre-test to determine the appropriate level for students Many track student work done so teachers can print reports and keep data on progress Cloze Pro is a program that allows teachers to create Cloze activities Teaching Vocabulary Definition-Based Approaches Context-Based Approaches Concept-Based Approaches Semantic Mapping (Schirmer, 2000) Teaching Vocabulary Concept-Based Approaches Concept-Based Approach New Knowledge Is Gained… from finding new relationships in old knowledge and from relating new information to old knowledge. (Schirmer, 2000) Integration Methods Semantic Maps organize prior knowledge into formal relations provide a basis for understanding Semantic Mapping Prereading Activity used to activate prior knowledge used to introduce key vocabulary words Postreading Activity add words, categories, and new concepts to the original maps to provide understanding Semantic Mapping Vocabulary development activities should consider how a word fits into a student's semantic repertoire rather than how it is used in a particular context. Semantically based activities relate the meaning to the child’s world. Semantic Mapping The teacher writes a word that represents the key concept. The students are asked to think of words that relate to the key word. These words are grouped around the key word in categories. The teacher then presents new words and encourages a discussion about where these words might fit into the map. (Duffelmeyer & Banwart, 1993; Heimlich & Pittelman, 1986; Johnson, Pittelman, &Heimlich, 1986) Semantic map for the solar system: Concept-Based Strategy Technologies There are a variety of semantic mapping software programs, for example Inspiration The maps can be colorcoded, shape-coded, and images can be added to further support students Visual Thesaurus is a web-based “program” that links related words to each other as a semantic map Students can click on related words to more clearly understand meaning and relationships among concepts Hands on Activity (Suggestion: Have students create a semantic map here…) Word Maps A vocabulary word map is a visual organizer engages students with new terms helps students to think about new terms or concepts in several ways Antonyms can go here too. source: http://curry.edschool.virginia.edu/go/readquest/pdf/wordmap_2.pdf We must enhance our students’ knowledge of: Words with Multiple Meanings Figurative Language Idiomatic Meaning of Words Denotation/Connotation Multiple Meaning Video Clip Word of the Day clip Multiple Meanings Run We will have to run to catch the plane. Does the pepper make your nose run? Don’t let the water run. The river will run into the ocean. I have a run in my hose. She will run for class president. How long will the school play run? He will run his father’s business. We run everyday. Multiple Meanings Made I made my bed. I made money. My brother made me do that. The rain made the grass green. I made a present for you. Multiple Meanings Interactive Websites http://www.manatee.k12.fl.us/sites/elementary/palmasola/ps4mm2.htm http://www.quia.com/cb/29778.html (Jeopardy) Develop presentations (ex. PowerPoint) that have multiple meaning words in context Students can sign the words appropriately based on context or draw illustrations to demonstrate the meaning Figurative Language …those forms of language that result in a non-literal meaning. (Easterbrooks & Baker, 2002) Idiomatic expressions Chip off the old block. Similes She looks like an angel. Metaphors My brain is a sieve. Personification Mr. Toothbrush wants you to tickle him. Idiomatic Meanings An idiom is an expression whose meaning is not compositional- that is, whose meaning does not follow from the meaning of the individual words of which it is composed. (Google) - Cut it out - Piece of cake - Hit the hay - Bent out of shape - Kick the bucket Interactive Website: http://www.geocities.com/Athens/Aegean/6720 Denotation/Connotation Denotation (Concrete)- Literal meaning of the word… “dictionary definition.” Connotation (Abstract)- Associations that are connected to a certain word or the emotional suggestions related to that word. The connotative meanings of a word exist together with the denotative meanings. Denotative: “any of numerous scaly, legless, sometimes venomous reptiles having a long, tapering, cylindrical body and found in most tropical settings.” Connotative: Snake meanings of the word snake could include evil or danger. The Fairview Learning Program It provides direct access to ASL and opens a window for hearing and deaf people to begin to think and sign bilingually. (Fairview Learning Network) It is currently being used in 42 states www.fairviewlearning.net The Fairview Learning Program The Bridge Lists English phrases requiring ASL translation for understanding. ‘Down the street’ requires multiple sign concepts, depending on the context. “A ball was hit down the street” “A man walked down the street.” The Fairview Learning Program The Bridging Process allows the conceptual signing of phrases, rather than the word for word signing required by most sign codes. “Put out the fire.” Word by word, one is literally signing, “Pick up the fire and put it outside.” Bridging provides the visual translation of the phase’s true meaning, “Extinguish the fire.” (Fairview Learning Network) The Fairview Learning Program Adapted Dolch Words Dolch words: commonly used words found in most basal readers Deaf children and hearing children do not learn Dolch words in the same way Most hearing children acquire the various meanings effortlessly through their sense of hearing. (Fairview Learning Network) Helpful Tips for Vocabulary Development: Promote Natural Growth in Meaning Vocabulary Promote Lifelong Vocabulary Learning through Indirect Vocabulary Instruction Promote Learning of Specific Words through Direct Vocabulary Instruction (Schirmer, 2000) Additional Technologies to Assist with Vocabulary Development Image-to-Text programs can be used to develop vocabulary study cards or learning activities (ex. Picture It, Signing Exact English Interactive, etc.) Image-to-Text programs can be used to make “rebus” passages with images matched with text (ex. The above and Clicker 5, Writing with Symbols) Many programs have settings for images to be shown or not so phrases rather than individual words can have a picture prompt or after a period of time the image can set not to show for specific words Additional Technologies to Assist with Vocabulary Development Some software programs allow for the development of class or personal digital dictionaries (ex. Wordbar or Clicker 5 by Crick Software) Grids that contain cells with words or phrases are located below the word processing portion of the screen to assist students in selecting appropriate vocabulary Grids can be custom made related to units of study Students can develop their own grids as references for their subject areas Wordbar includes only text and Clicker can contain an image as well as text Additional Technologies to Assist with Vocabulary Development Specialized sign videotapes and DVDs are available for free to deaf individuals and people who work with deaf/hh individuals Captioned Media Program PEPNet These videotapes can help students (and others) learn specialized vocabulary for content and career areas in both sign and English Bibliography Easterbrooks, Susan R. & Baker, Sharon (2002). Language Learning in Children Who Are Deaf and Hard of Hearing. Boston, MA: Allyn and Bacon Schirmer, Barbara, R. (2000). Language and Literacy Development in Children Who Are Deaf. Needham Heights, MA: Allyn & Bacon http://www.manatee.k12.fl.us/sites/elementary/palmasola/ps4mm2.htm http://www.quia.com/cb/29778.html http://www.geocities.com/Athens/Aegean/6720 http://www.fairviewlearning.net/deaf-overview.php



![Word Study [1 class hour]](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/007905774_2-53b71d303720cf6608aea934a43e9f05-300x300.png)