Chapter 10 Part 1 Overview
advertisement

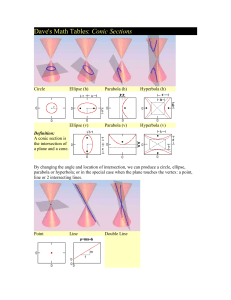
MTH253 Calculus III Chapter 10, Part I (sections 10.1 – 10.3) Conic Sections Conics The intersection of a right circular cone and a plane will produce one of four curves: • Parabola • Ellipse • Circle • Hyperbola Ax Bxy Cy Dx Ey F 0 2 2 Conics Ax Bxy Cy Dx Ey F 0 2 2 Not rotated ◦B=0 ◦ Lines of symmetry are horizontal or vertical Not translated ◦ Parabola: C, D, & F = 0 or A, E, & F = 0 Vertex at the origin ◦ Ellipse & Hyperbola: D = 0 & E = 0 “Centered” at the origin Ax Ey 0 2 The Parabola Vertical Axis of Symmetry x0 i.e. the y-axis x 4 py 2 e 1 (0, p) (2p,p) (0,0) y p Note: If p < 0, then just flip this upside-down. The Parabola - Example 2 x 11y 0 2 e 1 The Parabola - Example Find the equation of the parabola with its vertex at the origin and directrix the equation y = –5 Cy Dx 0 2 The Parabola Horizontal Axis of Symmetry y 0 i.e. the x-axis y 4 px 2 x p (p,2p) e 1 (p,0) (0,0) Note: If p < 0, then just flip this to the right. Ax Cy F 0 2 The Ellipse 2 AC 0 Horizontal Major Axis a b x2 y 2 2 2 2 2 1 , c a b 2 a b (0,b) a a2 x e c (c,0) (a,0) c e a The Ellipse - Example 4 x 9 y 36 0 2 2 e The Ellipse - Example Find the equation of the ellipse with its foci at (2,0) and eccentricity of 0.25. Ax Cy F 0 2 The Ellipse Vertical Major Axis 2 AC 0 a b x2 y 2 2 2 2 2 1 , c a b 2 b a a a2 y e c (0,a) (0,c) (b,0) c e a Ax Cy F 0 2 The Circle 2 AC 0 2 x y 2 1 2 r r 2 or x y r 2 2 2 (0,r) e0 (0,0) (r,0) Ax Cy F 0 2 The Hyperbola 2 AC 0 Horizontal Focal Axis x2 y 2 2 2 2 2 1 , c a b 2 a b b y x a (0,b) (a,0) (c,0) c e a a a2 x e c The Hyperbola - Example 4 x 9 y 36 0 2 2 e The Hyperbola - Example Find the equation of the hyperbola with its vertices at (3,0) and a directrix x = 2. Ax Cy F 0 2 The Hyperbola 2 AC 0 Vertical Focal Axis y 2 x2 2 2 2 2 1 , c a b 2 a b (0,c) a y x b (0,a) (b,0) c e a a a2 y e c PF = e * PD D P D F P F e<1 e>1 P F D e=1 Translations To move the center of an ellipse or hyperbola or the vertex of a parabola to the point (h, k), replace x with x-h and y with y-k. Treat (h, k) as if it was the origin. x h x h 2 4p y k a 2 x h a 2 2 y k 2 y k 2 b 2 b 1 2 2 1 Translations – “Complete the Square” Ax Cy Dx Ey F 0 2 2 Examples: x 3 y 6 x 12 y 1 0 2 2 x 10 x 2 y 5 0 2 Rotations – The “Cross Product Term” Ax Bxy Cy Dx Ey F 0 2 2 Angle of Rotation B 0 tan or 45 AC 1 2 1 Substitutions x x ' cos y 'sin y x 'sin y ' cos Note: Use the rotations calculator! The Descriminant B 4 AC 2 Ax Bxy Cy Dx Ey F 0 2 2 B 2 4 AC 0 Parabola B 4 AC 0 Ellipse B 2 4 AC 0 Hyperbola 2