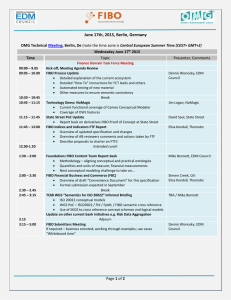
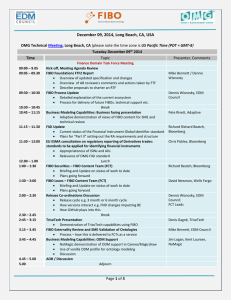
Retail Banking Ontology
advertisement

Retail Banking Ontology Lauren Madar IE 500 Ontological Engineering Dr. Barry Smith & Ron Rudnicki Fall 2014 1 Introduction What is Retail Banking? Banks providing products and services targeted towards consumers and individuals Why is an ontology needed? Communication problems inside the bank Communication and data issues between different banks that must work together Outside parties requesting information from the bank, not knowing what to ask for or terminology But, many organizations face these same issues… 2 So…? How are retail banks different? Retail Banks have additional challenges: Requires massive amounts of recordkeeping Errors and failures cause immediate customer concern Differences in vocabulary from bank to bank Traditional (long-lived) Banks also face: High overhead and infrastructure costs due to ‘brick and mortar’ branches Banking predates modern computers, resulting in residual and outdated processes and data structures Redundant systems and processes due to acquisitions Most traditional banks are not technology-oriented institutions 3 Why does this matter now? Retail Banking competition Easy for smaller companies to offer online banking services without high overhead With more options, customers are less likely to be loyal, and will ‘jump ship’ for a bank that offers services they want Changing customer base More and more people are comfortable with and want online services Branches are an advantage, but overhead costs must be balanced Regulatory Agencies 4 It takes a long time to turn a big ship Old, redundant, and inefficient systems Changes to existing systems require: Massive amounts of research time, and therefore are high cost Lack of documentation of data structures – “I’d have to look at the database” Communication difficulties Easier and cheaper to add new, small, but possibly redundant features and systems than to fix what is already there 5 Look at the database? Subject matter experts on processes and products may not be technically oriented Data structures may have been built by absorbed organizations or by vendors long ago and not improved Barrier to sharing knowledge Contributing to an ontology doesn’t require knowledge of database schemas How it works today vs. what would be most optimal High level mapping of what systems and processes interact doesn’t exist in an easily understood way (picture = 1000 words) 6 Construction & usage Who would help build and use the Retail Banking Ontology? Banks that serve consumers Other financial institutions, government and regulatory agencies 7 Output, other benefits What other benefits could RBO provide? Querying and knowledgebase tools and services Employee training Documentation Opportunity to identify redundant or inefficient processes Drive prioritization of system improvement to align with bank goals 8 In other words… Agility + Desired products & services + Efficient processes = More customers More customers + reduced cost = profit! 9 Relevant work In addition to BFO, two other ontologies were imported. FIBO – Financial Industry Business Ontology http://www.omg.org/hot-topics/finance.htm Beneficial features: Financial terms useful to Retail Banking such as currency, equity, assets Terms regarding organizations such as organizational subunits, agents, legal person 10 FIBO issues Challenges and problems: Structured without BFO Many parent-level terms and definition of many “concepts” that don’t fit well within BFO Issues with numerous FIBO components in Protégé prevented reasoners from running 11 Relevant work - IAO IAO – Information Artifact Ontology https://code.google.com/p/information-artifact-ontology/ Beneficial features: Detailed terms relating to information artifacts Structured to use BFO, making term reuse easy 12 IAO Issues Problem: Complex relationships created issues with reasoners in Protégé 13 Other ontologies Related in subject matter but not imported: FEF: Financial Exchange Framework Ontology http://www.financial-format.com/fef.htm No longer updated, no response to requests for files. Finance Ontology http://www.fadyart.com/ontologies/documentation/finance/index.html Some similarities to FIBO, not BFO-compatible, possible future integration opportunity. Organization Ontology http://www.cs.umd.edu/projects/plus/SHOE/onts/org1.0.html Not based on BFO, focused on physical products, few relationships. FIBO’s organization component was more applicable. 14 Other ontologies Related in subject matter but not imported: REA (Resources, Events, Agents) Ontology http://www.csw.inf.fuberlin.de/vmbo2014/submissions/vmbo2014_submission_24.pdf No links found to ontology, paper discussing incorporating an REA ontology to FIBO, possible future integration opportunity. IFIKR: Islamic Finance Ontology http://ifikr.isra.my/if-knowledge-base Specific to Islamic banks, possible future integration. Interesting ontology map display. 15 IFIKR 16 IFIKR 17 RBO term deep dive Information artifacts Objects & aggregates Specifically dependent continuants Occurrents Individuals Relationships 18 Information artifiacts 19 Information artifacts 20 Information artifiacts - specification 21 Objects 22 Objects – computers 23 Objects – agent and legal person 24 Object aggregates 25 Object aggregate - organization 26 Qualities 27 Qualities 28 Qualities 29 Qualities 30 Qualities 31 Functions 32 Functions – bank account 33 Functions – transfer money 34 Functions - data 35 Roles 36 Roles – employee and customer 37 Roles – security assets and processes 38 Occurrents 39 Occurrents – bank process 40 Occurrents - temporal 41 Occurrents - temporal 42 Individuals 43 Relationships examples ‘has role’ instead of ‘bearer of’ ‘owns’ and ‘is owned by’ bank account, account holder role ‘participates in at some time’ process, role bearers ‘represents’ legal entity, organization ‘manages’ bank technology group, bank systems branch manager, branch 44 Relationships examples ‘is provided by’, ‘constrains’ bank account specification, bank account, bank organization ‘is assigned to’ bank relationship manager, bank account holder ‘has member’, ‘is member of’ bank cost center, organizational sub-unit 45 Relationship examples ‘has person name’ legal person ‘is held by’ real estate, bank organization (eg rent, occupy, uses) 46 Detailed examination Bank Account Relationships between people, organizations and representations of monetary value Bank Organization Banks, employee roles, systems, groups 47 Bank Account 48 Bank Account 49 Bank Organization 50 Bank Organization 51 Project challenges Difficulties fitting FIBO “concepts” into BFO structure Categorizing and defining Account term was a struggle, as it is not just an information artifact and has relationships and qualities Difficulty importing FIBO and IAO components prevented the testing of inference and validation of relationships Scope grew much larger than anticipated 52 Future tasks Resolve issues with FIBO and IAO imports and complete relationships between all currently defined terms Define bank processes to greater level of detail Publish RBO and provide information for other banking organizations to contribute and edit Create a searchable knowledgebase for banking terms (using SparQL or similar) for use by developers and/or vendors to document or find information about complex systems 53 Questions? Thank you! 54