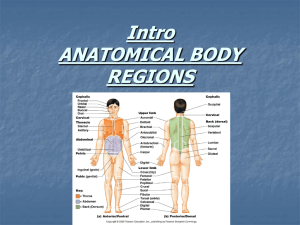
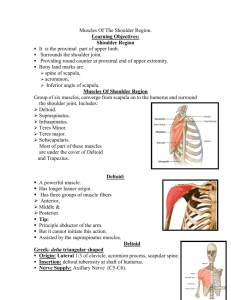
A Review of the Shoulder Muscles and Their Actions
advertisement

A Review of the Shoulder Muscles and Their Actions Questions • • • • • • • • What muscle works closely with the anterior deltoid? Pectoralis major What muscle is involved in any lifting movements? Deltoid What is the major (strongest) extensor muscle? Latissimus Dorsi Name the four rotator cuff muscles. Subscapularis, Supraspinatus, Infraspinatus, and Teres minor. • What muscle works closely with the infraspinatus? • Teres minor Practice • Name the muscles for Horizontal Adduction • Pect Major (both) • Corachobrachialis • Deltoid (anterior) • Name the muscles for Horizontal Abduction • Deltoid (post) • Infraspinatus • Teres minor • Lats Practice • List the muscles that do flexion of the shoulder • Coracobrachialis • Pectoralis major (upper to 60°) • Anterior Deltoid • List the muscles that do extension of the shoulder • Latissimus dorsi • Teres major • Posterior deltoid • Pectoralis major (lower fibers to neutral) Practice • List the muscles that do adduction of the shoulder • Pectoralis major (lower and upper below 90°) • Coracobrachialis • Latissimus dorsi • Teres major List the muscles that do abduction of the shoulder • Deltoid (all sections) • Supraspinatus • Pectoralis major (upper past 90°) Practice • List the muscles that do internal rotation of the shoulder • Subscapularis • Latissimus dorsi • Teres major • Anterior deltoid • Pect. major • List the muscles that do external rotation of the shoulder • Infraspinatus • Teres minor • Posterior deltoid Name the muscle. Coracobrachialis Name the action Adduction of the shoulder Also, flexion and hor. add. Name the muscle. Pectoralis Major Name the muscle. Subscapularis Name the action Internal rotation of the shoulder Name the muscle. Deltoid Name the action Abduction of shoulder Name the muscle. Infraspinatus Name the action External rotation Name the muscle. Name the action Teres Major Adduction of scapula Name the muscle. Teres Minor Name the action if the humerus move directly to the posterior Extension of the shoulder Name the muscle. Supraspinatus Name the action Abduction of the shoulder Coracobrachialis Subscapularis Pect. Major Deltoid Supraspinatus Teres Major Infraspinatus Teres Minor What position are her shoulders in? Flexion What position is his right shoulder in? Horizontal Abduction and External Rotation What rotation action is his shoulder performing as he continues to through the ball? Internal Rotation What position are her shoulders in? Flexion What position are his shoulders in? Horizontal abduction or Extension Position of their shoulders? 1. Flexion 2. Extension What is the position of shoulders? Extension Shoulder Muscle Exercises Major Muscles of the Shoulder • Pectoralis major – – – – – Push-ups Pull-ups Bench press Throwing Tennis serve • Latissimus dorsi – – – – – – Chinning Robe climb Dips on parallel bars Pullover exercises Pulldown exercises Rowing Shoulder action = ? Shoulder muscle(s) = ? Abduction Deltoid Supraspinatus Shoulder action = ? Shoulder muscle(s) = ? Flexion Ant Deltoid Upper Pect Major Coracobrach. Shoulder action = ? Shoulder muscle(s) = ? Horizontal Add. Ant. Deltoid Pect. Major (both) Coracobrachialis Shoulder action = ? Shoulder muscle(s) = ? Horizontal Abduction Latissimus Dorsi Post. Deltoid Teres Minor Infraspinatus Shoulder action = ? Shoulder muscle(s) = ? Adduction Pect. Major (both) Coracobrachialis Latissimus Dorsi Teres Major Shoulder action = ? Shoulder muscle(s) = ? Horizontal Add Ant. Deltoid Pect. Major (both) Coracobrachialis Shoulder action = ? Shoulder muscle(s) = ? Extension Lats Post. Deltoid Infraspinatus Teres Major Pectoralis Major (lower) Teres minor Shoulder action = ? Shoulder muscle(s) = ? External Rotation Infrspinatus Teres Minor Post. Deltoid Name a shoulder muscle isolated with the following exercises. • • • • • • Side arm dumbbell raises Deltoid Push-ups Pectoralis major Rowing and pull-overs Latissimus dorsi What is the action to the left? What muscles perform that action? Internal Rotation External Rotation Internal Rotation Subscapularis, Ant. Deltoid, Pect, Major, Lats. And Teres Major Rotator Cuff Exercises External Rotation Internal Rotation External Rotation Abduction (to work the supraspinatus) Shoulder Related Injuries • The shoulder is built for motion, not stability • Injury rate depends on… – Shallowness of glenoid fossa – Laxity of ligaments – Strength of muscles • Shoulder subluxation – Incomplete or partial dislocation • Shoulder dislocation – Complete dislocation of the GH joint – Most common anteriorly and inferiorly • Shoulder separation – Complete dislocation of the AC joint Shoulder Dislocation Impingement Syndrome Impingement Syndrome • A condition that decreases the subacromial space – Acromion process – Coracoacromial ligament • Causes – Swelling – Bone spurs – Anatomical structure Impingement Syndrome Rotator Cuff Tears Rotator cuff • • • • Subscapularis Supraspinatus Infraspinatus Teres minor Movement of RC Muscles • Subscapularis is an internal rotator of the arm. • Supraspinatus assists the deltoid in abducting the arm, with its greatest contribution being the initiation of abduction. • Infraspinatus and teres minor muscles both externally rotate the arm. Rotator Cuff Injury • The throwing motion has been divided into five phases: wind-up, cocking, acceleration, and follow-through. • Cocking phase – Subscapularis fires in late cocking phase to decelerate the shoulder's external rotation. Also, it is stretched during the cocking phase. Rotator Cuff Injury • Follow-through (muscles fire most intensely) – Subscapularis internally rotates the shoulder, – The infraspinatus and teres minor contract eccentrically to decelerate the arm and are stretched. • During this repetitive eccentric loading, the rotator cuff is prone to overload, fatigue, tendinitis, and even a partial undersurface tear. Note: Surgery needs to be performed within 3 months or the supraspinatus muscle will atrophy and be too short to reattach Glenoid Labrum Labral Tear • The glenoid cavity makes up the “socket” of the shoulder joint. • The labrum acts sort of like a gasket, turning the flat surface of the glenoid into a deeper socket that molds to the head of the humerus for a better fit. • A tear of labrum can cause pain and a catching sensation with movement of the shoulder. Labral Tear • Most labral tears are probably the result of an injury to the shoulder, such as falling on an outstretched hand. • There is reason to believe that the excess motion of the humerus moving around on the glenoid may cause damage to the labrum over time. • An unstable shoulder may also cause injury to the labrum, if it repeatedly dislocates out of the glenoid.