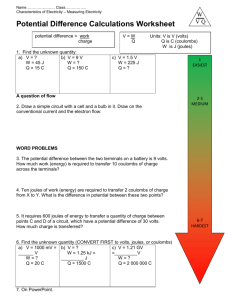
HW 3 Electric Potential Name: Class: ______ 1. Contrast electric
advertisement

HW 3 ELECTRIC POTENTIAL NAME: ___________________ CLASS: __________ 1. Contrast electric potential energy, electric potential, and potential difference. 2. Moving an electron within an electric field would change the ____ the electron. a. mass of b. amount of charge on c. potential energy of 3. If an electrical circuit were analogous to a water circuit at a water park, then the battery voltage would be comparable to _____. a. the rate at which water flows through the circuit b. the speed at which water flows through the circuit c. the distance that water flows through the circuit d. the water pressure between the top and bottom of the circuit e. the hindrance caused by obstacle in the path of the moving water 4. If the electrical circuit in your Walkman were analogous to a water circuit at a water park, then the battery would be comparable to _____. a. the people that slide from the elevated positions to the ground b. the obstacles that stand in the path of the moving water c. the pump that moves water from the ground to the elevated positions d. the pipes through which water flows e. the distance that water flows through the circuit 5. Use your understanding of the mathematical relationship between work, potential energy, charge and electric potential difference to complete the following statements: a. b. A 9-volt battery will increase the potential energy of 1 coulomb of charge by ____ joules. A 9-volt battery will increase the potential energy of 2 coulombs of charge by ____ joules. c. A 9-volt battery will increase the potential energy of 0.5 coulombs of charge by ____ joules. d. A ___-volt battery will increase the potential energy of 3 coulombs of charge by 18 joules. e. A ___-volt battery will increase the potential energy of 2 coulombs of charge by 3 joules. f. A 1.5-volt battery will increase the potential energy of ____ coulombs of charge by 0.75 joules. g. A 12-volt battery will increase the potential energy of ____ coulombs of charge by 6 joules. 6. When an electron is brought near a negatively charged sphere, its potential energy increases. The reason this happens is that a. b. c. d. negative charges repel each other. work was done to bring the charges together. two like charges go from a position far apart to a position close together. none of the above 7. You use 10 J of work to push a 1-C charge into an electric field, its voltage with respect to its starting position is a. less than 10 V. b. 10 V. c. more then 10 V. 8. A 2-C charge is located near a positively charged sphere so that it has 40 J of electric potential energy. Its electric potential is a. 80 V. b. 40 V. c. 20 V. d. 10 V. e. 2 V. 9. When a positive charge moves because of a force, what happens to the electrical potential energy associated with the charge’s position in the system? a. It increases. c. It remains the same. b. It decreases. d. It sharply increases, and then decreases.