Georgia Real Estate, 8e - PowerPoint for Ch 04
advertisement

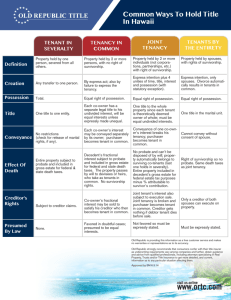
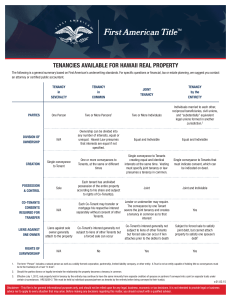
Chapter 4 Georgia Real Estate An Introduction to the Profession Eighth Edition Chapter 4 Forms of Ownership Key Terms • • • • • community property concurrent ownership estate in severalty four unities joint tenancy • • • • right of survivorship tenancy by the entirety tenants in common undivided interest © 2015 OnCourse Learning Sole Ownership When title to property is held by one person, it is called an estate in severalty. Businesses usually hold title to property in severalty. © 2015 OnCourse Learning Tenants in Common When two or more people wish to share the ownership of a single property, they may do so as tenants in common. Each owns an undivided interest in the whole property. © 2015 OnCourse Learning Tenants in Common The interests do not need to be the same. Each owner can independently sell, mortgage, give away or devise an individual interest. Each tenant in common has a separate legal title to an undivided interest. © 2015 OnCourse Learning Tenants in Common One parcel of land; Three owners with unity of possession A B C What happens if C dies? A B © 2015 OnCourse Learning C’s heirs Wording of Conveyance If nothing is said regarding the size of each coowner’s interest in the property, the law presumes that all interests are equal. © 2015 OnCourse Learning Wording of Conveyance In Georgia, unless stated otherwise, when two or more people are named as owners, they are presumed to be tenants in common with an equal ownership interest. © 2015 OnCourse Learning No Right of Survivorship With a tenancy in common, if a co-owner dies, the co-owner’s interest passes to his or her heirs or devisees. There is no right of survivorship. © 2015 OnCourse Learning Co-Owner Responsibilities Income generated by the property belongs to the tenants in common in proportion to the size of their interests. Similarly, each co-owner is responsible for a proportionate share of taxes, repairs, upkeep, etc. © 2015 OnCourse Learning Co-Owner Responsibilities If co-owners cannot agree on a plan for dividing or selling the property, it is possible to request a court-ordered partition. A partition divides the property into portions so that each person can hold their interest in severalty. © 2015 OnCourse Learning Co-Owner Responsibilities If the property cannot be physically divided, the court will order the property sold and the proceeds divided among the co-owners. © 2015 OnCourse Learning Joint Tenancy Joint tenancy is another form of concurrent ownership. Joint tenancy has the right of survivorship. © 2015 OnCourse Learning Joint Tenancy Upon the death of a joint tenant, that interest passes to the surviving joint tenant(s). The interest does not pass to the heirs or by a will. © 2015 OnCourse Learning Joint Tenancy A B C One parcel of land; 3 owners, 4 unities (PITT) C If C dies? A B © 2015 OnCourse Learning Four Unities To create a joint tenancy, the four unities must be present: possession, interest, title and time. Unity of possession means that the joint tenants must enjoy the same undivided possession of the whole property. © 2015 OnCourse Learning Four Unities Unity of interest means that the joint tenants own one interest together. If there are 2 owners, they each own 50%. If there are 3 owners, they each own 33.3% © 2015 OnCourse Learning Four Unities Unity of title means that the joint tenants acquire their interests from the same deed. No matter how many joint tenants there are, there is only one title to the property. © 2015 OnCourse Learning Four Unities Unity of time means that each joint tenant must acquire their ownership interest at the same moment. It is not possible to add new joint tenants later. © 2015 OnCourse Learning Right of Survivorship Upon the death of a joint tenant, that interest in the property is extinguished. Ultimately, the last survivor becomes the sole owner. © 2015 OnCourse Learning Right of Survivorship The right of survivorship has made joint tenancy a popular form of ownership among married couples. Any property held in joint tenancy goes to the surviving spouse without the delay of probate. © 2015 OnCourse Learning “Poor Man’s Will” Because of the survivorship feature, joint tenancy has been labeled a “poor man’s will.” It affects only property held in joint tenancy. As a joint tenant, you cannot will your joint tenancy to someone. © 2015 OnCourse Learning “Poor Man’s Will” Georgia does recognize joint tenancy, but the deed must clearly state that it is a joint tenancy with the right of survivorship. Only a human being can be a joint tenant. A corporation cannot be a joint tenant. © 2015 OnCourse Learning Tenancy by the Entirety Tenancy by the entireties is a form of joint tenancy specifically for married people. A husband and a wife serve as in indivisible legal unit. © 2015 OnCourse Learning Tenancy by the Entirety While both are alive and married to each other, both signatures are required to convey title. © 2015 OnCourse Learning Tenancy by the Entirety A tenancy by the entirety can be terminated only by joint action of husband and wife. Georgia does not recognize tenancy by the entirety. © 2015 OnCourse Learning Effect of Divorce In the event of divorce, the parting spouses become tenants in common. This change is automatic. Tenancy by the entirety can only exist between a husband and a wife. © 2015 OnCourse Learning Community Property Georgia is not a community property state. The concept is that the husband and wife contribute jointly and equally to the marriage and should share equally in any property purchased during the marriage. © 2015 OnCourse Learning Separate Property Property owned before marriage and property acquired after marriage by gift, inheritance or purchased with separate funds can be exempted from the couple’s community property. © 2015 OnCourse Learning Caveat to Agents There may be an occasion when a buyer will ask the real estate agent how to take title. If the agent attempts to respond with a recommendation, the agent is practicing law. A license is required to practice law. Refer the buyers to a lawyer for advice. © 2015 OnCourse Learning