Blood Typing
advertisement

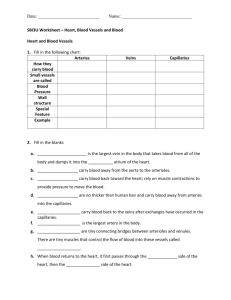
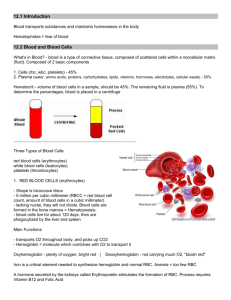
Week 6, Day Three HW # 23- Cornell notes- due Tuesday from the book CH 14, section 1 p. 552-561 from the end of this power point Warm up Review your levers packet. Warm up Response See Homework Response/Check Share two things that you learned from yesterday’s lab activity • Quiz • Bill Nye • Read/Do Blood Bean Demo Cornell Notes The Body’s Transport System Circulatory System Consists of… • Blood Vessels • Blood • Heart Circulatory System -Carries needed substances to cells -Carries waste products away -Blood has cells that fight disease 7 Circulatory System BLOOD VESSELS Two Pathways • Pulmonary Circulation – Carries blood to lungs and back • Systemic Circulation – Carries blood to body and back Capillaries of head and arms Superior vena cava Aorta Pulmonary artery Pulmonary vein Capillaries of right lung Capillaries of left lung Inferior vena cava Capillaries of abdominal organs and legs Your Blood Vessels: Pathway of Circulation • 3 types of vessels – Arteries – Capillaries – Veins Arteries: carries blood Away from heart – – – – Large Thick-walled, Muscular Elastic Oxygenated blood • Exception Pulmonary Artery – Carried under great pressure – Steady pulsating Arterioles: smaller vessels, enter tissue Capillaries – – – – Smallest vessel Microscopic Walls one cell thick Nutrients and gases diffuse here Veins: Carries blood to heart – Carries blood that contains waste and CO2 • – – Exception pulmonary vein Blood not under much pressure Valves to prevent much gravity pull Venules: larger than capillaries Varicose Veins Damaged Valves in Veins Contractions of the heart = blood pressure Valves in the heart prevent backflow of blood 18 Structure of Heart • Four chambers – Two upper (Atria) • Walls thinner • Less muscular – Two lower (Ventricles) • Walls thicker • More muscular • Do more work Circulatory System •BLOOD What is Blood? • Blood Simulation The Blood • Body contains 4-6 L • Consists of – – – – Water Red Blood Cells Plasma White blood cells and platelets Plasma Platelets White blood cells Red blood cells Whole Blood Sample Sample Placed in Centrifuge Blood Sample That Has Been Centrifuged Plasma Platelets White blood cells Red blood cells Whole Blood Sample Sample Placed in Centrifuge Blood Sample That Has Been Centrifuged Plasma Platelets White blood cells Red blood cells Whole Blood Sample Sample Placed in Centrifuge Blood Sample That Has Been Centrifuged Parts of the Blood Oxygen in the Blood • Hemoglobin, iron containing molecule • Loosely picks up oxygen in the lungs • Loses oxygen in areas low in oxygen (diffuses) Carbon Dioxide in the Blood • Hemoglobin carries CO2 also • CO2 is a waste product of cellular work • 70% of CO2 combines with water • The rest travels to the lungs What does blood contain? • • • • 50% Water 45% Erythrocytes 4% Plasma with Substances 1% Leukocytes + Platelets Erythrocytes (RBC) (optional info) • Transporters of – Oxygen – Carbon Dioxide • RBC – Lack a nucleus – Contain hemoglobin – Disk-shaped • RBC are produced in red bone marrow of – – – – ribs, humerus, femur, sternum, and other long bones • Lives for 120 days • Old RBC are destroyed in liver and spleen Leukocytes (WBC) (optional info) • WBC fight infection – • • • Less abundant Large cells Some live for months – • • Attack foreign substances Most just a few days Several types ALL contain nuclei Platelets • • • • • PLATELETS are for CLOTTING blood Cell fragments Produced in bone marrow Short life span (1 week) Fibrin (sticky network of protein fibers) – Form a web trapping blood cells Blood Clotting Break in Capillary Wall Clumping of Platelets Clot Forms Blood vessels injured. Platelets clump at the site and release thromboplastin. Thromboplastin converts prothrombin into thrombin.. Thrombin converts fibrinogen into fibrin, which causes a clot. The clot prevents further loss of blood.. Elaboration • Blood Typing: To Clump or Not to Clump? Blood Types • Massive loss of blood requires a transfusion • Four Types –A –B – AB –O • Inherited from your parents Blood Types What happens when you mix blood types? • Plasma contains proteins that correspond to the shape of the different antigens • If you mix one type with the wrong one, you get CLUMPING • Type O is the universal donor • Type AB is the universal acceptor What Makes Our Blood Type? Blood Transfusions Blood Type of Donor Blood Type of Recipient A B AB O A B AB O Unsuccessful transfusion Successful transfusion Rh Factor • Rhesus factor (Rh), also inherited – Rh+ (have antigen) – Rh- (NO antigen) • Can cause complications in pregnancies – mother Rh- 1st baby Rh+ : blood mixes with mother; mother’s body makes anti-Rh+ antibodies – 2nd Rh + body attacks baby – Now have medicine to prevent antibody formation Bloods Path Through the Heart • Both Atria fill at same time – Rt atrium receives oxygen POOR blood from body from vena cava – Left atrium receives oxygen RICH blood from lungs through four pulmonary veins • After filled with blood atria contract, pushing blood into ventricle Both ventricles contract Right ventricle contracts and pushes oxygen-poor blood toward lungs, • against gravity, • through pulmonary arteries Bloods Path Through the Heart (cont) Left ventricle contracts and forces oxygen rich blood • out of heart through • aorta (largest vessel) Control of the Heart (Nervous System) (optional information) • Medulla oblongata regulates rate • Sensory cells stretch when too fast • Pressure drops when beat is too low Heartbeat Regulation • Force of blood from left ventricle into arteries (pulse) • Pacemaker (SA Node), group of cells at top of right atrium • Electrical impulse, signals BOTH atria to contract • Triggers 2nd set of cells (AV Node)-base of the right atrium to send message to ventricles, they contract • EkG – record of electrical changes in the heart Your Blood: Fluid Transport (optional information) • a Tissue • 50% water • 4% dissolved substances Liquid Portion Carries Blood cells – Erythrocytes (RBC - red blood cells) – Leucocytes (WBC - white blood cells) Platelets (non cellular particles) Proteins – Enzymes – Hormones – Endocrine System Nutrients - Digestive System Gases - Respiratory System Inorganic salts