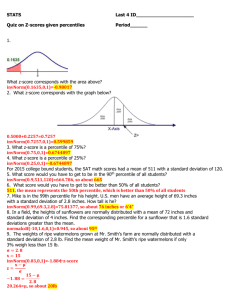
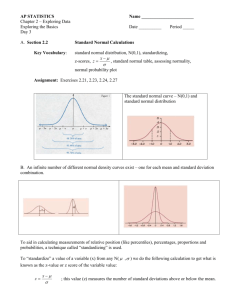
Page 285 4. (a) = binompdf(5, 0.05, 2) = 0.201 (b) = 1 − binomcdf(5
advertisement

Page 285 4. (a) P( X 2) = binompdf(5, 0.05, 2) = 0.201 (b) P( X 2) 1 P( X 2) = 1 − binomcdf(5, 0.05, 2) = 0.001 (c) P ( X 5) binompdf(5, 0.05, 5) = 0.0000003 (d) Since the probability of each event gets less likely the probabilities decrease. 6. The probability of guessing correctly is 1 0.2 . P( X 15) 1 P( X 14) 5 = 1 − binomcdf(20, 0.2, 14) = 0.0000002 This is very unlikely to happen. 8. Note that P(drops out) = 0.103 (a) P ( X 2) = binomcdf(10, .103, 2) = 0.925 (b) If at least six graduate then four or fewer drop out P( X 4) binomcdf(10, 0.103, 4) = 0.998 (c) P(none drop out) = binompdf(10, 0.103, 0) = 0.337 10. Note that P(both work) = 0.521 (a) P( X 0) binompdf(5, 0.521, 0) = 0.025 (b) P( X 3) 1 P( X 3) 1 − binomcdf(5, 0.521, 3) = 0.215 (c) P( X 2) P( X 1) 1 − binomcdf(5, 0.521, 1) = 0.162 12. Note that P(destination wedding) = 0.26 (a) P( X 6) binompdf(12, 0.26,6) = 0.047 (b) P( X 6) 1 P( X 5) = 1 − binomcdf(12, 0.26, 5) = 0.06 (c) P( X 5) P( X 4) = binomcdf(12, 0.26, 4) = 0.821 16. np 10 0.5 5 2 npq 10 0.5 0.5 2.5 2 2.5 1.581 18. Note that p P(use e-mail) 0.83; q 1 p 0.17 np 200 0.83 166 2 npq 200 0.83 0.17 28.22 2 28.22 5.31 24. Note that p P(purchases online) 0.32; q 1 p 0.68 np 200 0.32 64 2 npq 200 0.32 0.68 43.52 Page 310 10. Area right of z 2.01 normalcdf(2.01, 10000) 0.0222 12. Area left of z 0.75 normalcdf( 10000, 0.75) 0.2266 16. Area between z 0.96 and z 0.36 normalcdf( 0.96, 0.36) 0.1909 18. Note when using normalcdf the left hand value must be entered first Area between z 0.24 and z 1.12 normalcdf( 1.12, 0.24) 0.4634 28. P(1.23 z 0) normalcdf( 1.23, 0) 0.3907 40. To find z use invnrom(area left of z). Since the area left of 0 is 0.5 the area z invnorm(0.9066) 1.32 left of z = 0.5 + 0.4066 = 0.9066 Area = 0.48 z invnorm(0.9761) 1.979 42. Area left of z = 1 − 0.0239 = 0.9761. 44. z invnorm(0.9671) 1.840 46. (a) Area left of z = 0.5478. z invnorm(0.5478) 0.12 (b) Area left of z = 0.6985. z invnorm(0.6985) 0.52 (c) Area left of z = 0.8810. z invnorm(0.8810) 1.18 48. The picture is: Area = 0.48 Area = 0.26 Area = 0.26 −z z Area left of z = 0.74. z invnorm(0.74) 0.643 . By symmetry the two values are z 0.643 Page 323 4. The 90th percentile has 90% of the area under the curve to the left of it. The z-score for the 90th percentile is invnorm(0.9) = 1.282. Convert to X using x z 1028 92(1.282) 1146 The z-score for 1200 = 1200 1028 1.870 . Then P( X 1200) P( z 1.870) 92 = normalcdf(1.870, 10000) = 0.0307 8. (a) The z-score for 15000 = 15000 12837 1.442 . Then P( X 15000) P( z 1.442) 1500 = normalcdf(1.442, 10000) = 0.747 13000 12837 0.1087 . 1500 14000 12837 0.7753 . The z-score for 13000 = 1500 (b) The z-score for 13000 = Then P(1300 X 14000) P(0.1087 z 0.7753) = normalcdf(0.1087, 0.7753) = 0.2376 10. (a) The z-score for 30 = 30 25 0.8197 . Then P( X 30) P( z 0.8197) 6.1 = normalcdf(0.8197, 10000) = 0.206 (b) The z-score for 18 = 18 25 1.1475 . Then P( X 18) P( z 1.1475) 6.1 = normalcdf(−10000, −1.1475) = 0.1256 14. The z-score for 384 = 384 225 3.5333 . Then P( X 384) P( z 3.5333) 45 = normalcdf(3.5333, 10000) = 0.0002 18. The picture is: Area = 0.5 Area = 0.25 Area = 0.25 z −z Area left of z = 0.75. z invnorm(0.75) 0.6745 . By symmetry the two values are z 0.6745 The lower value is X z 792 103(0.6745) 722.52 The upper value is X z 792 103(0.6745) 861.47 Answer: $722.52 and $861.47 20. The picture is: Area = 0.8 Area = 0.1 Area = 0.1 −z z Area left of z = 0.75. z invnorm(0.9) 1.282 . By symmetry the two values are z 1.282 The lower value is X z 246300 15000(1.282) 227070 The upper value is X z 246300 15000(1.282) 265530 Answer: $227,070 to $265,530 26. The picture is: For second part For first part Area = 0.3 Area = 0.1 z2 z1 Area left of z1 = 0.9. z invnorm(0.9) 1.282 . This one is sneaky: You are given the variance so take a square root to get the standard deviation Then x z 4.8 2.1(1.282) 6.658 Then 10% of hospital stays last longer than 6.658 days Area left of z2 = 0.3. z invnorm(0.3) .5244 . Then x z 4.8 2.1(0.5244) 4.404 Then 30% of hospital stays last less than 4.404 days 30. The picture is: Area = 0.2 z Area left of z = 0.8. z invnorm(0.8) 0.8416 . Then x z 64 9(0.8416) 71.6 Assuming scores are whole numbers the cut off score is 72 Page 330 x 45000 37764 1.4188 5100 Then P( X 45000) P( z 1.4188) normalcdf(1.4188, 10000) = 0.0778 12. (a) z (b) For sample means the mean is the population mean and the standard deviation is x 38000 37764 0.4007 5100 n 75 Then P( x 38000) P( z 0.4007) normalcdf(0.4007, 10000) = 0.3443 z 16. The standard deviation for samples of size 33 is x n 2.6 33 23.8 24.3 1.104 2.6 n 33 Then P( x 23.8) P( z 1.1047) normalcdf(10000, 1.1047) = 0.1346 z 20. The standard deviation for samples of size 34 is n 4850 34 First part: x 50000 51803 2.1677 4850 n 34 Then P( x 50000) P( z 2.1677) normalcdf(2.1677, 10000) = 0.9849 z Second part: x 48000 51803 4.5721 4850 n 34 Then P( x 48000) P( z 4.5721) normalcdf(10000, 4.5721) = .000002 z 22. (a) Use 120 for and 5.6 for . Then P(120 x 121.8) 120 120 121.8 120 P( z ) 5.6 5.6 P(0 z .3214) = normalcdf(0, .3214) = 0.126 (b) Use 120 for and 5.6 30 for . Then n P(120 x 121.8) 120 120 121.8 120 P( z ) 5.6 5.6 30 30 P(0 z 1.7605) = normalcdf(0, 1.7605) = .4608 (c) Means are less variable than individual data. 24. (a) Use 36.2 for and 3.7 for . Then P(36 x 37.5) 36 36.2 37.5 36.2 z ) 3.7 3.7 P(.0541 z 0.3514) P( = normalcdf(0.0541, 0.3514) = 0.1589 (b) Use 36.2 for and 3.7 for . Then 15 P(36 x 37.5) 36 36.2 37.5 36.2 z ) 3.7 3.7 15 15 P(.2094 z 1.3607) P( = normalcdf(0.2094, 1.3607) = .4961 Page 364 10. From the TI83+ you find x 346.25 . For 92% confidence z 1.751 using invnorm(.96). [The 2 area to right of z is 0.04, so the area to the left is 0.96.] Then 2 x z x z 2 n n 165.1 165.1 346.25 1.751( ) 346.25 1.751( ) 32 32 295.1 397.4 2 14. (a) A point estimate is what you get from one sample: 7.2 jobs (b) For 95% confidence z 1.960 from the last line of the t-table or using invnorm(0.975) 2 x z x z 2 n n 2.1 2.1 7.2 1.960( ) 7.2 1.960( ) 50 50 6.62 7.78 2 (c) For 99% confidence z 2.576 from the last line of the t-table or using invnorm(0.995) 2 x z x z 2 n n 2.1 2.1 7.2 2.576( ) 7.2 2.576( ) 50 50 6.43 7.97 2 (d) To make it more likely that the interval contains the mean the interval must be wider. 18. For 90% confidence z 1.645 from the last line of the t-table or using invnorm(0.95) 2 x z x z n 630 2 3987 1.645( n 2 ) 3987 1.645( 50 $3840 $4134 630 ) 50 As a start up your pricing needs to be competitive so charge $3,800 20. For 95% confidence z 1.960 from the last line of the t-table or using invnorm(0.975) 2 x z 2 190.7 1.960( x z n 54.2 2 n ) 190.7 1.960( 35 172.7 208.7 54.2 ) 35 22. . For 90% confidence z 1.645 from the last line of the t-table or using invnorm(0.95) 2 x z 2 58.0 1.645( Page 372 n 4.8 x z 2 n ) 58.0 1.645( 171 57.40 58.60 4.8 ) 171 6. From the TI83+ the sample standard deviation s 17.487 and the sample mean x 217.7 Since n =10 you have d.f. = n – 1 = 9. From the t-table t 2.262 2 s s x t 2 2 n n 17.487 17.487 217.7 2.262( ) 217.7 2.262( ) 10 10 205.2 230.2 x t 12. Since n =13 you have d.f. = n – 1 = 12. From the t-table t 3.055 2 s s x t x t 2 2 n n 1.7 1.7 15 3.055( ) 15 3.055( ) 13 13 13.6 16.4 If you were to issue a warning to make sure people had enough time to get out of the way you would use the highest speed of 16.4 mph. 14. Since n =8 you have d.f. = n – 1 = 72. From the t-table t 2.365 2 s s x t 2 2 n n 4.1 4.1 13.1 2.365( ) 13.1 2.365( ) 8 8 9.7 16.5 x t 16. Since n =8 you have d.f. = n – 1 = 72. From the t-table t 2.365 2 s s x t 2 2 n n 4.1 4.1 13.1 2.365( ) 13.1 2.365( ) 8 8 9.7 16.5 x t 20. Since n =24 you have d.f. = n – 1 = 23. From the t-table t 2.069 2 s s x t 2 2 n n 7.5 7.5 46.1 2.069( ) 41.6 2.069( ) 24 24 38.4 44.8 x t