Senses and Ear Flashcards
advertisement
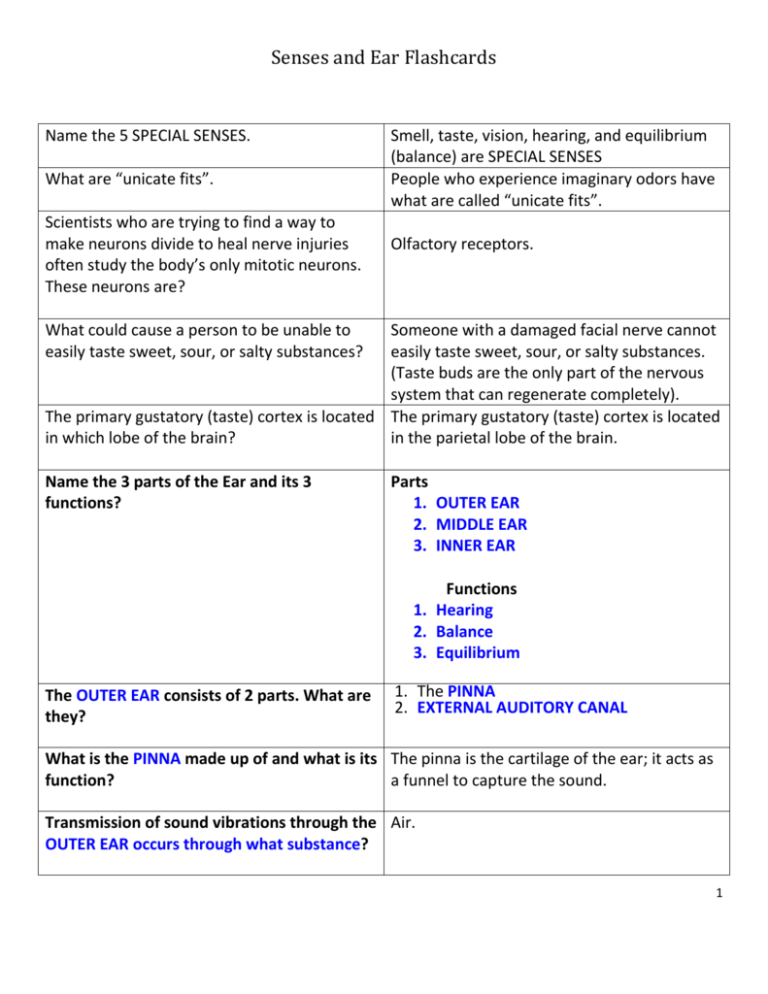
Senses and Ear Flashcards Name the 5 SPECIAL SENSES. What are “unicate fits”. Scientists who are trying to find a way to make neurons divide to heal nerve injuries often study the body’s only mitotic neurons. These neurons are? Smell, taste, vision, hearing, and equilibrium (balance) are SPECIAL SENSES People who experience imaginary odors have what are called “unicate fits”. Olfactory receptors. What could cause a person to be unable to easily taste sweet, sour, or salty substances? Someone with a damaged facial nerve cannot easily taste sweet, sour, or salty substances. (Taste buds are the only part of the nervous system that can regenerate completely). The primary gustatory (taste) cortex is located The primary gustatory (taste) cortex is located in which lobe of the brain? in the parietal lobe of the brain. Name the 3 parts of the Ear and its 3 functions? Parts 1. OUTER EAR 2. MIDDLE EAR 3. INNER EAR Functions 1. Hearing 2. Balance 3. Equilibrium The OUTER EAR consists of 2 parts. What are they? 1. The PINNA 2. EXTERNAL AUDITORY CANAL What is the PINNA made up of and what is its The pinna is the cartilage of the ear; it acts as function? a funnel to capture the sound. Transmission of sound vibrations through the Air. OUTER EAR occurs through what substance? 1 Senses and Ear Flashcards What is the middle ear normally filled with? Air. The middle ear is open to the nasopharynx by way of what structure and what is its function? AUDITORY TUBE The function of the auditory tube is to equalize the pressure of the middle ear and the outside air, so the ear bones can vibrate. What 3 bones are attached to the tympanic membrane and what is their function? 1. MALLEUS (hammer). The malleus vibrates the incus 2. INCUS (anvil). Vibrates the stapes 3. STAPES (stirrup). Their function is to amplify sound vibrations. The INNER EAR is in what portion of the skull? Bony Labyrinth is filled with what fluid? The temporal bone (petrious portion). What fluid is in the MEMBRANOUS LABYRINTH? What structure contains receptors for hearing? ENDOLYMPH. What 3 structures are responsible for balance? 1. Semicircular Canals 2. Utricle 3. Saccule Bony Labyrinth is filled with PERILYMPH COCHLEA 2 Senses and Ear Flashcards A F G H B B C E Answer key located to the right for the above picture shown A. B. C. D. E. F. G. H. D Semicircular Canals Superior Posterior Lateral Stapes Cochlea Vestibulocochle ar nerve Saccule Utricle Where are hair cells found? Cochlea and Semicircular Canals Hair cells are receptor cells for what 2 things? What cranial nerve carries information for hearing? What is the stapes is attached to? What structure determines movement in three planes? Hearing and equilibrium CN VIII VESTIBULAR COCHLEAR NERVE OVAL WINDOW SEMI-CIRCULAR CANALS 3 Senses and Ear Flashcards What are the two joined structures attached to the semi-circular canals? What type of fluid and what receptors are within each semi-circular canal? What are calcium deposits in the inner ear called? They are an essential part of the utricle and saccule for what purpose? How is the Otoliths play an essential process in stimulating the hair cells? What is VERTIGO or LABYRINTHITIS? UTRICLE and the SACCULE. Endolymph and hair cells. OTOLITHS (“ear rocks”). Equilibrium It allows the hair cells in this region to act as receptors by telling you what position your head is in and provide you a sense of equilibrium. Inflammation of the semi-circular canals that give a sense of motion when you’re not moving. This can be debilitating. 4




