Bio Review Schedule & Resource Links
advertisement
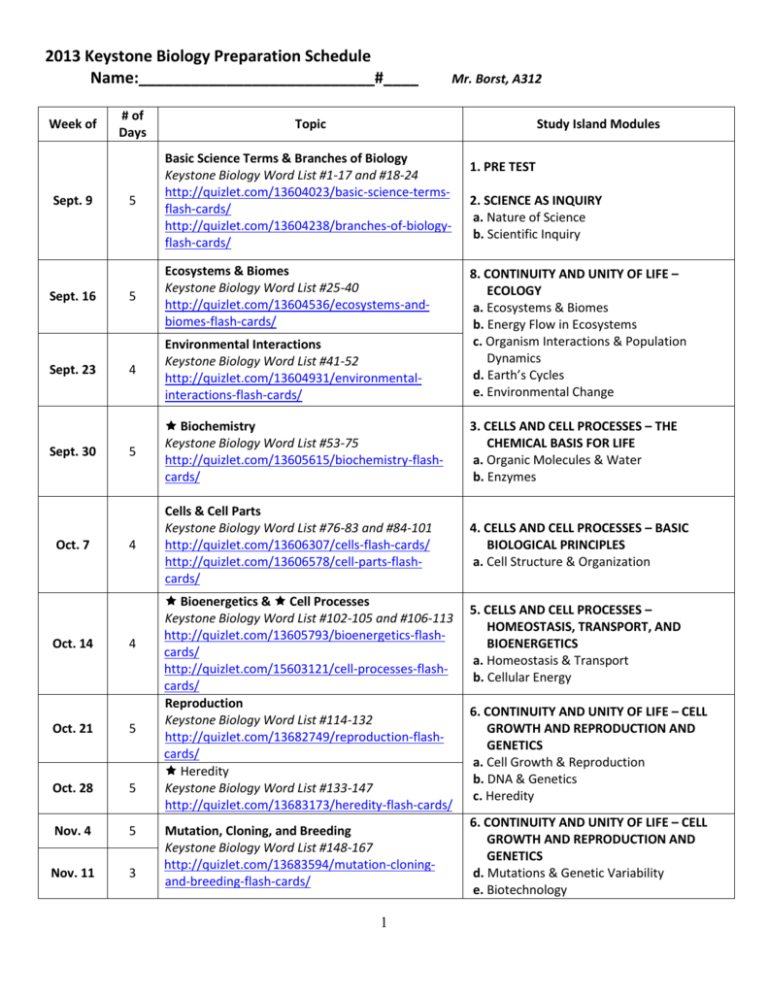
2013 Keystone Biology Preparation Schedule Name:___________________________#____ Week of Sept. 9 Sept. 16 Sept. 23 Sept. 30 Oct. 7 Oct. 14 Mr. Borst, A312 # of Days Topic 5 Basic Science Terms & Branches of Biology Keystone Biology Word List #1-17 and #18-24 http://quizlet.com/13604023/basic-science-termsflash-cards/ http://quizlet.com/13604238/branches-of-biologyflash-cards/ 5 Ecosystems & Biomes Keystone Biology Word List #25-40 http://quizlet.com/13604536/ecosystems-andbiomes-flash-cards/ 4 Environmental Interactions Keystone Biology Word List #41-52 http://quizlet.com/13604931/environmentalinteractions-flash-cards/ 8. CONTINUITY AND UNITY OF LIFE – ECOLOGY a. Ecosystems & Biomes b. Energy Flow in Ecosystems c. Organism Interactions & Population Dynamics d. Earth’s Cycles e. Environmental Change 5 Biochemistry Keystone Biology Word List #53-75 http://quizlet.com/13605615/biochemistry-flashcards/ 3. CELLS AND CELL PROCESSES – THE CHEMICAL BASIS FOR LIFE a. Organic Molecules & Water b. Enzymes 4 Cells & Cell Parts Keystone Biology Word List #76-83 and #84-101 http://quizlet.com/13606307/cells-flash-cards/ http://quizlet.com/13606578/cell-parts-flashcards/ 4. CELLS AND CELL PROCESSES – BASIC BIOLOGICAL PRINCIPLES a. Cell Structure & Organization 4 Oct. 21 5 Oct. 28 5 Nov. 4 5 Nov. 11 3 Study Island Modules Bioenergetics & Cell Processes Keystone Biology Word List #102-105 and #106-113 http://quizlet.com/13605793/bioenergetics-flashcards/ http://quizlet.com/15603121/cell-processes-flashcards/ Reproduction Keystone Biology Word List #114-132 http://quizlet.com/13682749/reproduction-flashcards/ Heredity Keystone Biology Word List #133-147 http://quizlet.com/13683173/heredity-flash-cards/ Mutation, Cloning, and Breeding Keystone Biology Word List #148-167 http://quizlet.com/13683594/mutation-cloningand-breeding-flash-cards/ 1 1. PRE TEST 2. SCIENCE AS INQUIRY a. Nature of Science b. Scientific Inquiry 5. CELLS AND CELL PROCESSES – HOMEOSTASIS, TRANSPORT, AND BIOENERGETICS a. Homeostasis & Transport b. Cellular Energy 6. CONTINUITY AND UNITY OF LIFE – CELL GROWTH AND REPRODUCTION AND GENETICS a. Cell Growth & Reproduction b. DNA & Genetics c. Heredity 6. CONTINUITY AND UNITY OF LIFE – CELL GROWTH AND REPRODUCTION AND GENETICS d. Mutations & Genetic Variability e. Biotechnology 2013 Keystone Biology Preparation Schedule, continued Week of # of Days Nov. 18 5 Nov. 25 3 Topic Study Island Modules Selection and Evolution Keystone Biology Word List #168-194 http://quizlet.com/13729506/selection-andevolution-flash-cards/ 7. CONTINUITY AND UNITY OF LIFE – THEORY OF EVOLUTION a. Theory of Evolution b. Mechanisms of Evolution 9. POST TEST Topics marked with a star in the table above have been identified as focus areas when preparing for the 2013 Keystone Biology Exam. 2 Optional Preparation and Remediation Materials Week of Topic Sept. 9 Basic Science Terms & Branches of Biology Keystone Biology Word List #1-17 and #1824 Sept. 16 Ecosystems & Biomes Keystone Biology Word List #25-40 Sept. 23 Environmental Interactions Keystone Biology Word List #41-52 Sept. 30 Biochemistry Keystone Biology Word List #53-75 Oct. 7 Cells & Cell Parts Keystone Biology Word List #76-83 and #84101 Oct. 14 Bioenergetics & Cell Processes Keystone Biology Word List #102-105 and #106-113 Oct. 21 Reproduction Keystone Biology Word List #114-132 Additional Materials and Resources PSSA Coach Lesson 1: Scientific Theories and Laws PSSA Coach Lesson 6: Experimental Designs and Processes PSSA Coach Lesson 8: Using Data PSSA Coach Lesson 9: Evaluating and Communicating Results Practicing the Scientific Method packet PSSA Coach Lesson 25: Biotic and Abiotic Factors PSSA Coach Lesson 27: Biomes PSSA Coach Lesson 28: Limiting Factors and Population Dynamics Environmental Interactions Words PowerPoint PSSA Coach Lesson 15: Classification PSSA Coach Lesson 26: Interactions of Organisms Biochemistry Words PowerPoint Osmosis & Diffusion The Biomacromolecule Song PSSA Coach Lesson 14: Levels of Organization PSSA Coach Lesson 24: Biological Diversity, Biogeochemical Cycles Online Enzymes tutorial: http://www.wiley.com/college/test/0471787159/biology_b asics/home.html Cell Parts PowerPoint Cell Parts Review worksheet Can You Identify These Cell Structures? Worksheet Cell Parts Mini-Review PSSA Coach Lesson 14: Levels of Organization Bioenergetics & Cells PowerPoint Cell Processes PowerPoint PSSA Coach Lesson 16: Photosynthesis and Respiration Reproduction, Mutation, Cloning, Breeding PowerPoint Reproduction Words (#114-132) worksheet PSSA Coach Lesson 17: DNA Replication and Protein Synthesis PSSA Coach Lesson 22: Mitosis and Meiosis 3 Optional Preparation and Remediation Materials, continued Week of Topic Oct. 28 Heredity Keystone Biology Word List #133-147 Nov. 4 Nov. 11 Mutation, Cloning, and Breeding Keystone Biology Word List #148-167 Nov. 18 Nov. 25 Additional Materials and Resources PSSA Coach Lesson 21: Expressing Genetic Information PSSA Coach Lesson 23: Patterns of Inheritance PSSA Coach pages 17-19: Tongue Rolling Scenario PSSA Coach pages 368-371: Sex-Linked Traits Scenario Bikini Bottom Genetics 1: http://sciencespot.net/Media/gen_spbobgenetics.pdf Bikini Bottom Genetics 2: http://sciencespot.net/Media/gen_spbobgenetics2.pdf Reproduction, Mutation, Cloning, Breeding PowerPoint Mutation, Cloning, and Breeding (#148-167) worksheet Selection and Evolution PowerPoint PSSA Coach Lesson 18: Evidence of Evolution PSSA Coach Lesson 19: Genetic Variation in Populations PSSA Coach Lesson 20: Natural Selection Selection and Evolution Keystone Biology Word List #168-194 4 KEYSTONE BIOLOGY Word List Basic Science Terms http://quizlet.com/13604023/basic-science-terms-flash-cards/ 1. Science – search for understanding of the natural world and technology using systematic inquiry, observation, and experimentation to develop a body of evidence-based knowledge. 2. Inquiry – a systematic process in which current knowledge and skills are used to gain and apply new knowledge 3. Hypothesis - A proposed, scientifically testable explanation for an observed phenomenon. 4. Independent variable – the factor that is tested in an experiment; the factor that is intentionally changed by the experimenter. 5. Dependent variable – the factor that is measured in an experiment; it may or may not change as a result of changing the independent variable. 6. Experimental controls – factors that are kept the same in all trials of an experiment to ensure that an experiment is “fair.” 7. Control group – the group or setup of an experiment that is given no special treatment; it is used for comparison. 8. Fact – information that has been objectively verified through direct observation 9. Law – a statement of observed experimental facts that generalizes a body of observations. It has been tested many times and is generally accepted as true. At the time it is made, no exceptions have been found to a law. It explains things but does not describe them; serves as the basis of scientific principles. 10. Principle - A concept based on scientific laws and axioms (rules assumed to be true and valid) where general agreement is present. 11. Theory – An explanation of observable phenomena based on available empirical data and guided by a system of logic that includes scientific laws; provides a system of assumptions, accepted principles, and rules of procedure devised to analyze, predict, or otherwise explain the nature or behavior of a specific set of phenomena. 12. Model – a description or representation of something (physical model, mathematical model, conceptual model, computerized model) that helps us study or understand it better 13. Scientific mechanism - The combination of components and processes that serve a common function. 14. System – A set of interacting or interdependent components, real or abstract, that form an integrated whole. (Ex: a car, a rollercoaster, the human body) 15. Open system – a system that is able to interact with its environment. 16. Closed system – a system that is isolated from its environment. 17. Subsystem – a group of related objects that make up a larger system (examples: a car’s fuel system or sound system; the body’s excretory system or digestive system) Branches of Biology http://quizlet.com/13604238/branches-of-biology-flash-cards/ 18. Biology – The scientific study of life. 19. Ecology - The study of the relationships between organisms and their interactions with the environment. 20. Genetics - The scientific study of inheritance. 21. Embryology - The branch of zoology studying the early development of living things from fertilization to the developed state. 22. Agriculture - The artificial cultivation of food, fiber, and other goods by the systematic growing and harvesting of various organisms. (a.k.a. farming) 5 23. Biotechnology - Any procedure or methodology that uses biological systems or living organisms to develop or modify either products or processes for specific use. This term is commonly associated with genetic engineering, which is one of many applications. 24. Forensics - The science of tests and techniques used during the investigation of crimes. Ecosystems and Biomes http://quizlet.com/13604536/ecosystems-and-biomes-flash-cards/ 25. Habitat - An area that provides an organism with its basic needs for survival. 26. Ecosystem – A system composed of organisms and nonliving components of an environment. 27. Biome - A large area or geographical region with distinct plant and animal groups adapted to that environment. 28. Biosphere - The zone of life on Earth; sum total of all ecosystems on Earth. 29. Succession - A series of predictable and orderly changes within an ecosystem over time. 30. Ecological community - Different populations of organisms interacting in a shared environment. 31. Population - A group of individuals of the same species living in a specific geographical area and reproducing. 32. Population dynamics - The study of short- and long-term changes in the number of individuals for a given population, as affected by birth, death, immigration, and emigration. 33. Nonnative species - A species normally living outside a distribution range that has been introduced through either deliberate or accidental human activity; also known as introduced, invasive, alien, nonindigenous, or exotic. 34. Limiting factor - Chemical or physical factor that limits the existence, growth, abundance, or distribution of an individual organism or a population. 35. Biotic – A term that describes a living or once-living organism in an ecosystem. (Ex: animals, plants, bacteria, manure) 36. Abiotic - a nonliving factor in an ecosystem. (Ex: water, weather) 37. Aquatic - A term that describes an organism associated with a water environment. 38. Terrestrial - A term that describes an organism associated with a land environment. 39. Biogeochemical cycles - The movement of abiotic factors between the living and nonliving components within ecosystems; also known as nutrient cycles (i.e., water cycle, carbon cycle, oxygen cycle, and nitrogen cycle). 40. Extinction – when a species no longer has any known living individuals. Environmental Interactions http://quizlet.com/13604931/environmental-interactions-flash-cards/ 41. Producer – An organism that uses a primary energy source to produce its own food by conducting photosynthesis or chemosynthesis. 42. Consumer - An organism that obtains energy by feeding on other organisms or their remains. 43. Decomposer - An organism that obtains nutrients by consuming dead and decaying organic matter which allows nutrients to be accessible to other organisms. 44. Food chain - A simplified path illustrating the passing of potential chemical energy (food) from one organism to another organism. 45. Food web - A complex arrangement of interrelated food chains illustrating the flow of energy between interdependent organisms. 46. Trophic level - The position of an organism in relation to the flow of energy and inorganic nutrients through an ecosystem (producer, consumer, and decomposer). 47. Energy pyramid - A model that illustrates the biomass productivity at multiple trophic (food chain) levels in a given ecosystem. 48. Competition - When individuals or groups of organisms compete for similar resources such as territory, mates, water, and food in the same environment. 6 49. Symbiotic relationship - A relationship between two organisms. 50. Mutualism – relationship in which both organisms benefit 51. Parasitism – relationship in which one organism benefits and the other organism is harmed 52. Commensalism - relationship in which one organism benefits and the other organism neither benefits nor is harmed. Biochemistry http://quizlet.com/13605615/biochemistry-flash-cards/ 53. Atom - The smallest unit of an element that retains the chemical and physical properties of that element. 54. Molecule - The smallest particle of a substance that retains the chemical and physical properties of the substance and is composed of two or more atoms held together by chemical forces. 55. Organic molecule - A molecule containing carbon that is a part of or produced by living systems. 56. Macromolecule - A polymer with a high molecular mass. Within organisms there are four main groups: carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. 57. Biological macromolecules - A group of biomacromolecules (large molecules) that interact with biological systems and their environments. 58. Monomer – A molecule of any compound that can react with other molecules of the same or different compound to form a polymer. Each biological macromolecule has characteristic monomers. 59. Carbohydrate - A macromolecule that contains atoms of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in a 1:2:1 ratio (like C6H12O6) and serves as a major source of energy for living organisms (Ex: sugars, starches, and cellulose). 60. Protein - A macromolecule that contains the principal components of organisms: carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen; performs a variety of structural and regulatory functions for cells. 61. Lipids - A group of organic compounds composed mostly of carbon and hydrogen including a proportionately smaller amount of oxygen; insoluble in water, serve as a source of stored energy, and are a component of cell membranes. 62. Temperature - A measure of the average kinetic energy (energy of motion) of particles in a sample of matter. This physical property can determine the rate and extent to which chemical reactions can occur within living systems. It is commonly measured in degrees Celsius (°C) or Fahrenheit (°F). 63. Specific heat - The measure of the heat energy required to increase the temperature of a unit quantity of a substance by a certain temperature interval. (Ex: water has a specific heat of 4186 J/kg°C, which means it takes 4186 Joules of energy to raise the temperature of 1 kilogram of water by 1°C) 64. Freezing point - The temperature at which a liquid changes state to a solid. 65. Catalyst - A substance that changes the rate of a reaction without being changed by the reaction. It may enable a chemical reaction to proceed at a usually faster rate or under different conditions (like at a lower temperature) than otherwise possible. 66. Enzyme - A protein that increases the rate of a chemical reaction without being changed by the reaction; an organic catalyst. 67. Cohesion – The intermolecular attraction between like molecules. Surface tension results from the cohesive properties of water. 68. Adhesion - The intermolecular attraction between unlike molecules. Capillary action results from the adhesive properties of water and the molecules that make up plant cells. 69. Concentration - The measure of the amount or proportion of a given substance when combined with another substance. 70. Concentration Gradient - The graduated difference in concentration of a solute per unit distance through a solution. 7 71. Diffusion - The movement of particles from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration; a natural result of kinetic molecular energy. 72. Facilitated diffusion - A process in which substances are transported across a plasma membrane with the concentration gradient with the aid of carrier (transport) proteins; does not require the use of energy. 73. Impermeable - Not permitting passage of a substance or substances. 74. Osmosis - The movement of water or another solvent through permeable membranes from an area of higher water concentration (dilute) to an area of lower water concentration (concentrated). 75. pH - The measure of acidity or alkalinity (basicity) of an aqueous solution scaling from 1 (highly acidic) to 14 (highly alkaline) with a midpoint of 7 (neutral). Cells http://quizlet.com/13606307/cells-flash-cards/ 76. Cell - The basic unit of structure and function for all living organisms. Cells have three common components: genetic material, cytoplasm, and a cell membrane. Eukaryotic cells also contain specialized organelles. 77. Tissue – An anatomical unit composed of cells organized to perform a similar function. 78. Organ – An anatomical unit composed of tissues serving a common function. 79. Organ system - An anatomical system composed of a group of organs that work together to perform a specific function or task. 80. Organism - A form of life; an animal, plant, fungus, protist or bacterium. 81. Prokaryote – A single‐ celled organism that lacks a membrane‐ bound nucleus and specialized organelles. 82. Eukaryote - A type of organism composed of one or more cells containing a membrane‐ bound nucleus, specialized organelles in the cytoplasm, and a mitotic nuclear division cycle. 83. Endosymbiosis - A theorized process in which early eukaryotic cells were formed from simpler prokaryotes. Cell Parts http://quizlet.com/13606578/cell-parts-flash-cards/ 84. Organelle - A subunit within a cell that has a specialized function. 85. Nucleus - A membrane‐ bound organelle in eukaryotic cells functioning to maintain the integrity of the genetic material and, through the expression of that material, controlling and regulating cellular activities. 86. Mitochondrion - A membrane‐ bound organelle found in most eukaryotic cells; site of cellular respiration. The powerhouse of a cell. 87. Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) – An organelle, containing folded membranes and sacs, responsible for the production, processing, and transportation of materials for use inside and outside a eukaryotic cell. There are two forms of this organelle (rough and smooth). 88. Rough ER –has surface ribosomes and participates in the synthesis of proteins mostly destined for export by the cell 89. Smooth ER – has no ribosomes and participates in the synthesis of lipids and steroids as well as the transport of synthesized macromolecules. 90. Ribosome - A cellular structure composed of RNA and proteins that is the site of protein synthesis in eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells. 91. Golgi Apparatus - An organelle found in eukaryotic cells responsible for the final stages of processing proteins for release by the cell. 92. Plasma membrane - A thin, phospholipid and protein molecule bilayer that encapsulates a cell and controls the movement of materials in and out of the cell through active or passive transport. 8 93. Active transport – The movement of particles from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration that uses energy provided by ATP or a difference in electrical charges across a cell membrane. 94. Passive transport - The transportation of materials across a plasma membrane without using energy. 95. Pumps (ion or molecular) - Any of several molecular mechanisms in which ions or molecules are transported across a cellular membrane requiring the use of an energy source (glucose, sodium [Na+], calcium [Ca+], and potassium [K+]) 96. Choloroplast - An organelle found in plant cells and the cells of other eukaryotic photosynthetic organisms where photosynthesis occurs. 97. Plastids - A group of membrane‐ bound organelles commonly found in photosynthetic organisms and mainly responsible for the synthesis and storage of food. 98. Extracellular - Located outside a cell. 99. Intracellular - Located inside a cell. 100. Multicellular - Made up of more than one cell. 101. Unicellular - Made up of a single cell. Bioenergetics http://quizlet.com/13605793/bioenergetics-flash-cards/ 102. Bioenergetics - The study of energy flow (energy transformations) into and within living systems. 103. Biomass conversion - The changing of organic matter into other chemical forms such as fuels. 104. Energy transformation - A process in which energy changes from one form to another form while some of the energy is lost to the environment. 105. Environment - The total surroundings of an organism or a group of organisms. Cell Processes http://quizlet.com/15603121/cell-processes-flash-cards/ 106. Homeostasis - The regulatory process in which an organism regulates its internal environment. 107. Homeostatic mechanism - A regulatory mechanism that contributes to maintaining a state of equilibrium (e.g., thermoregulation, water regulation, and oxygen regulation). 108. Cellular respiration - A complex set of chemical reactions involving an energy transformation where potential chemical energy in the bonds of “food” molecules is released and partially captured in the bonds of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) molecules. 109. Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) - A molecule that provides energy for cellular reactions and processes. ATP releases energy when one of its high‐ energy bonds is broken to release a phosphate group. 110. Carrier (transport) proteins - Proteins embedded in the plasma membrane involved in the movement of ions, small molecules, and macromolecules into and out of cells; also known as transport proteins. 111. Endocytosis - A process in which a cell engulfs extracellular material through an inward folding of its plasma membrane. 112. Exocytosis - A process in which a cell releases substances to the extracellular environment by fusing a vesicular membrane with the plasma membrane, separating the membrane at the point of fusion and allowing the substance to be released. 113. Photosynthesis - A process in which solar radiation is chemically captured by chlorophyll molecules and through a set of controlled chemical reactions resulting in the potential chemical energy in the bonds of carbohydrate molecules. Reproduction 9 http://quizlet.com/13682749/reproduction-flash-cards/ 114. Mitosis - A nuclear division resulting in the production of two somatic cells that are genetically identical to the original cell. 115. Cell cycle - The series of events that take place in a cell leading to its division and duplication. The main phases of the cell cycle are interphase, nuclear division, and cytokinesis. 116. Interphase – The longest‐ lasting phase of the cell cycle in which a cell performs the majority of its functions, such as preparing for nuclear division and cytokinesis. 117. Nuclear division – The phase of the cell cycle in which the nucleus divides. 118. Cytokinesis - The final phase of a cell cycle resulting in the division of the cytoplasm. 119. Meiosis - A two‐ phase nuclear division that results in the eventual production of gametes (sex cells) with half the normal number of chromosomes. 120. Nondisjunction - The process in which sister chromatids fail to separate during and after mitosis or meiosis. 121. Gamete - A specialized cell (egg or sperm) used in sexual reproduction containing half the normal number of chromosomes of a somatic cell. 122. Chromosome - A single piece of coiled DNA and associated proteins found in linear forms in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells and circular forms in the cytoplasm of prokaryotic cells; contains genes that encode traits. Each species has a characteristic number of chromosomes. 123. Nucleic acid - A biological macromolecule (DNA or RNA) composed of the elements C, H, N, O, and P that carries genetic information. 124. Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) – A biological macromolecule that encodes the genetic information for living organisms and is capable of self‐ replication and the synthesis of ribonucleic acid (RNA). 125. DNA Replication - The process in which DNA makes a duplicate copy of itself. 126. Semiconservative replication - The process in which the DNA molecule uncoils and separates into two strands. Each original strand becomes a template on which a new strand is constructed, resulting in two DNA molecules identical to the original DNA molecule. 127. Transcription - The process in which a strand of messenger RNA (mRNA) is synthesized by using the genetic information found on a strand DNA as a template. 128. Translation - The process in which the messenger RNA (mRNA) molecule on a ribosome is decoded to produce a sequence of amino acids for protein synthesis. 129. Protein synthesis - The process in which amino acids are arranged in a linear sequence through the processes of transcription of DNA and to RNA and the translation of RNA to a polypeptide chain. 130. Crossing-over - An exchange of genetic material between homologous chromosomes during anaphase I of meiosis; contributes to the genetic variability in gametes and ultimately in offspring. 131. Translocation - The process in which a segment of a chromosome breaks off and attaches to another chromosome. 132. Gene recombination - A natural process in which a nucleic acid molecule (usually DNA but can be RNA) is broken and then joined to a different molecule; a result of crossing‐ over. HEREDITY http://quizlet.com/13683173/heredity-flash-cards/ 10 133. Gene - A sequence of nucleotides composing a segment of DNA that provides a blueprint for a specific hereditary trait (like hair color, eye color, etc.) 134. Allele - A variation of a gene’s nucleotide sequence (an alternative form of a gene, like blue, brown, black, etc.). 135. Multiple alleles - More than two forms of a gene controlling the expression of a trait. 136. Inheritance - The process in which genetic material is passed from parents to their offspring. 137. Genotype - The genetic composition of an organism with reference to a single trait, a set of traits, or the entire complement of traits of an organism. (Ex: BB, Bb, bb) 138. Homozygous – genotype in which two of the same alleles are present (BB or bb) 139. Heterozygous – genotype in which two different alleles are present (Bb) 140. Phenotype – The observable, physical expression of a genotype. (Ex: brown hair, blonde hair) 141. Gene expression - The process in which a nucleotide sequence of a gene is used to make a functional product such as protein or RNA. 142. Dominant inheritance - A pattern of inheritance in which the phenotypic effect of one allele is completely expressed within a homozygous and heterozygous genotype. 143. Recessive inheritance - A pattern of inheritance in which the phenotypic effect of one allele is only expressed within a homozygous (bb) genotype. In a heterozygous condition with a dominant allele (Bb), the recessive trait is not expressed in the phenotype. 144. Codominance – A pattern of inheritance in which the phenotypic effect of two alleles in a heterozygous genotype express each phenotype of each allele fully and equally; a phenotype which would not be expressed in any other genotypic combination. 145. Incomplete dominance - A pattern of inheritance in which two alleles, inherited from the parents, are neither dominant nor recessive. The resulting offspring have a phenotype that is a blending of the parental traits. 146. Polygenic trait - A trait in which the phenotype is controlled by two or more genes at different loci on different chromosomes. 147. Sex-linked trait - A trait, associated with a gene that is carried by either the male or female parent (Ex: color blindness, hemophilia, sickle‐ cell anemia). MUTATION, CLONING, AND BREEDING http://quizlet.com/13683594/mutation-cloning-and-breeding-flash-cards/ 148. Mutation - A permanent transmissible change of genetic material (e.g., chromosomal mutations and gene mutations). 149. Point mutation - A single‐ base substitution causing the replacement of a single‐ base nucleotide with another nucleotide 150. Silent mutation – point mutation in which there is no change in an amino acid 151. Missense mutation – point mutation in which there is a different amino acid 152. Nonsense mutation – point mutation in which there is an insertion of a stop codon in the amino acid which stops protein synthesis. 153. Chromosomal mutation – A change in the structure of a chromosome. 154. Deletion – chromosomal mutation due to the loss of a segment of a chromosome and thus the loss of segment containing genes 155. Duplication – chromosomal mutation that occurs when a segment of a chromosome is duplicated and thus displayed more than once on the chromosome 156. Inversion – chromosomal mutation that occurs when a segment of a chromosome breaks off and reattaches in reverse order 157. Translocation – chromosomal mutation that occurs when a segment of one chromosome breaks off and attaches to a nonhomologous chromosome. 158. Frame-shift mutation - The addition (insertion mutation) or removal (deletion mutation) of one or more nucleotides that is not indivisible by three, therefore resulting in a completely different 11 159. 160. 161. 162. 163. 164. 165. 166. 167. amino acid sequence than would be normal. The earlier in the sequence nucleotides are added or removed, the more altered the protein will be. Genetic engineering - A technology that includes the process of manipulating or altering the genetic material of a cell resulting in desirable functions or outcomes that would not occur naturally. Gene splicing - A type of gene recombination in which the DNA is intentionally broken and recombined using laboratory techniques. Gene therapy - The intentional insertion, alteration, or deletion of genes within an individual’s cells and tissues for the purpose of treating a disease. Cloning - A process in which a cell, cell product, or organism is copied from an original source. DNA cloning – the transfer of a DNA fragment from one organism to a self‐ replicating genetic element such as a bacterial plasmid. Reproductive cloning – the transfer of genetic material from the nucleus of a donor adult cell to an egg cell that has had its nucleus removed for the purpose of creating an embryo that can produce an exact genetic copy of the donor organism. Therapeutic cloning – the process of taking undifferentiated embryonic cells [STEM cells] for use in medical research. Genetically Modified Organism (GMO) - An organism whose genetic material has been altered through some genetic engineering technology or technique. Selective breeding - The process of breeding organisms that results in offspring with desired genetic traits. SELECTION & Evolution http://quizlet.com/13729506/selection-and-evolution-flash-cards/ 168. Fossils - The preserved remains or traces of organisms that once lived on Earth. 169. Natural selection - A process in nature in which organisms possessing certain inherited traits are better able to survive and reproduce compared to others of their species. 170. Biological evolution (macroevolution) - a process in which new species develop from preexisting species 171. Species - The lowest taxonomic level of biological classification consisting of organisms capable of reproduction that results in fertile offspring. 172. Speciation - A process typically caused by the genetic isolation from a main population resulting in a new genetically distinct species. 173. Isolating mechanisms - Features of behaviors, morphology, or genetics which serve to prevent mating or breeding between two different species. 174. Temporal isolation – individuals are active at different times of the day, seasons, or mating periods 175. Ecological isolation - individuals only mate in their specific habitat 176. Behavioral isolation – when there are no sexual cues between representatives of the species 177. Mechanical isolation – when there is no sperm transfer during an attempted mating 178. Gametic incompatibility – isolating mechanism that arises when there is sperm transfer without fertilization occurring. 179. Zygotic mortality – one of four factors that prevent hybrid viability when mating can take place between two different species. In this case, there is fertilization but no zygote. 180. Hybrid inviability – one of four factors that prevent hybrid viability when mating can take place between two different species. In this case, the embryo is not viable (it doesn’t survive). 181. Hybrid sterility – one of four factors that prevent hybrid viability when mating can take place between two different species. In this case, the resulting adult is sterile. 12 182. Hybrid breakdown - one of four factors that prevent hybrid viability when mating can take place between two different species. In this case, the first generation is viable (able to survive) but future generations are not. 183. Genetic evolution (microevolution) – a change in the allele frequencies of a population of organisms from generation to generation (genetic evolution or microevolution). 184. Gradualism - A proposed explanation in evolutionary biology stating that new species arise from the result of slight modifications (mutations and resulting phenotypic changes) over many generations. 185. Punctuated equilibrium - A proposed explanation in evolutionary biology stating that species are generally stable over long periods of time. Occasionally there are rapid changes that affect some species which can quickly result in a new species. 186. Allele frequency - The measure of the relative frequency of an allele at a genetic locus in a population; expressed as a proportion or percentage. 187. Genetic migration - The permanent movement of genes into or out of a population resulting in a change in allele frequencies. 188. Genetic drift - A change in the allele frequency of a population as a result of chance events rather than natural selection. 189. Homologous structure - A physical characteristic in different organisms that is similar because it was inherited from a common ancestor. (Ex: bones in whale fins, chimpanzee arms, and human arms are considered divergent structures) 190. Analogous structure - A physical structure, present in multiple species, that is similar in function but different in form and inheritance. These structures evolved independently. (Ex: butterfly wings, bird wings, bat wings are considered convergent structures) 191. Vestigial structure - A physical characteristic in organisms that appears to have lost its original function as a species has changed over time. (Ex: human appendix, tail bone) 192. Endemic species - A species that is found in its originating location and is generally restricted to that geographic area. 193. Founder Effect - A decrease in genetic variation caused by the formation of a new population by a small number of individuals from a larger population. 194. Keystone Biology Exam – a test given by the state of Pennsylvania that you are now prepared to dominate. Following Pages: Extra Review Materials Name Period 13 Date OSMOSIS & DIFFUSION ISOTONIC Solute Outside Concentration Inside the Cell HYPOTONIC Solute Outside Concentration Inside the Cell HYPERTONIC Solute Outside Concentration Inside the Cell Iso means __________________ Hypo means ________________ Hyper means _______________ ______ movement of water! Water moves _______ the cell. Water moves _______ the cell. Like your ________________ Cherry Kool Aid Like your ________________ Cherry Kool Aid Like your ________________ Cherry Kool Aid 1. Use the terms hypotonic and hypertonic to explain why your fingers get wrinkly in the swimming pool. 2. Putting salt on a snail is putting the snail in a ____________________________ environment. 3. What happens when you put salt on your French fries? Explain why using science words! 4. Restaurants put out peanuts and popcorn to make you thirsty. Why does this make you thirsty? Explain using science words! 5. You can smell a cooking Thanksgiving turkey because of the process of _____________________. 6. If a plant cell and a red blood cell are put into a hypotonic environment, the red blood cell bursts but the plant does not. Why? The Biomacromolecule Song (To the Tune of “B-I-N-G-O”) A carbohydrate has C, H, O, 14 In a 1 to 2 to 1 ratio. 1 C, 2 H, and 1 O, 1 C, 2 H, and 1 O, 1 C, 2 H, and 1 O, Is the carbohydrate ratio. WHAT THEY DO CARBOHYDRATES Lipids have C, H, and O, In no specific ratio. C and H and much less O, C and H and much less O, C and H and much less O, If it’s a lipid that’s how you’ll know. LIPIDS Proteins have C, H, and O, With Nitrogen thrown in also. PROTEINS C and H, N and O, C and H, N and O, C and H, N and O, Proteins have Nitrogen also. 15 EXAMPLES Cell Parts Review Part A: Cells and Cell Parts 1. What is an organelle? 2. What are three differences between prokaryotes and eukaryotes? 3. Identify a structural difference between prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells that is directly related to their difference in size. 4. Describe one similarity between prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells that is independent of size. 5. List each organelle under the part of the cell where it is found. On the Cell Membrane In the Cytoplasm In the Nucleus Part B: Cell City The cell can be compared to a major city. Listed below are some of the parts of the cell and their function. What part of a city would be comparable to the function performed by each organelle in the cell? Be prepared to explain your choice. 1. Energy is produced in the MITOCHONDRIA. 2. The CELL MEMBRANE allows certain chemicals to enter and not others. 3. CHROMOSOMES contain all of the information about what the cell is like and instructions for what it is supposed to do. 4. The NUCLEUS is in charge of all cell activity. 5. RNA carries messages to different parts of the cell. 6. CYTOPLASM is the “stuff” inside the cell where all of the organelles are found. 7. RIBOSOMES make protein for the cell 8. ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM carries materials around the cell. 9. The GOLGI APPARATUS gets proteins ready to send out of the cell. 10. Plants have a CELL WALL that enables them to maintain a rigid structure. 16 Name Period Date Can You Identify These Cell Structures? Read each description and then identify the cell structure. Write your answer on the line. 1. I’m a real “powerhouse.” That’s plain to see. I break down food To release energy. What am I? 2. I’m strong and stiff Getting through me is tough. I’m found only in plants, But I guess that’s enough. What am I? 3. My name means “colored bodies,” And I contain DNA. I pass on traits to new cells In a systematic way. What am I? 4. I’m the “brain” of the cell Or so they say. I regulate activities From day to day. What am I? 5. Found only in plant cells, I’m green as can be. I make food for the plant Using the sun’s energy. What am I? 6. I’m a series of tubes Found throughout the cell. I transport proteins And other things as well. What am I? 7. I’m a full of holes. Flexible, and thin. I control what gets out As well as what comes in. What am I? 8. Proteins are made here Even though I’m quite small. You can find me in the cytoplasm Or attached to E.R.’s wall. What am I? 9. I’ve been call a “storage tank” By those with little taste I’m a sac filled with water, Food, enzymes, or waste. What am I? 10. Since I contain many enzymes, I can digest an injured cell; And can break down a large molecule Into a smaller one as well. What am I? WORD BANK Vacuole Lysosome Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) membrane Cell Mitochondria Nucleus Cell wall Chloroplast 17 Ribosome Chromosome Cell Parts Mini-Review Locate the following on the diagram below: Cell Parts Mini-Review 1. What’s the difference between extracellular and intracellular? 2. What’s the difference between unicellular and multicellular? 3. What are organelles? 4. What is the plasma membrane made of? 5. What is the plasma membrane’s purpose? 6. ___________ are the powerhouse of a cell. 7. What does the nucleus do? 8. ___________ is folded membranes and sacs. 9. Rough endoplasmic reticulum has ________. 10. What do ribosomes make? 11. What does rough ER make? 12. What does smooth ER make? 13. The ________ _________ grabs proteins and gets them ready to transport out of the cell. 14. What happens in chloroplasts? 15. What kind of cells have chloroplasts? 16. Describe in detail the difference between passive and active transport. 17. What are pumps for? 18. Challenge: What kind of cell (skin, bone, muscle, etc.) in the human body would need the most mitochondria? Nucleus Mitochondria Plasma membrane 18 Smooth ER Rough ER Golgi apparatus Reproduction WORDS (#114-132) MITOSIS MEIOSIS - ___________________ cell division. - Produces _________ cells - The cell splits into _________ cells that are - Sex cells ( ________________ ) each have identical to the parent cell. half as many chromosomes as the parent. CELL CYCLE _________________________ - the longest phase of the cell cycle, when the cell prepares for nuclear division and cytokinesis. _________________________________________ when the nucleus divides (shocking). _________________________ - the final phase of the cell cycle, this occurs when the cytoplasm divides. Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) - Shaped like a double ________________. Provides the blueprint for life! Base-pair rule for DNA: T = __________________ A = __________________ C = __________________ G = __________________ TRANSCRIPTION mRNA is _____________________ during transcription. It is synthesized using DNA as a template. This occurs in the ______________, which makes sense because that’s where DNA is found. TRANSLATION TRANSLOCATION mRNA is _____________________ during translation. This translated information is used to produce amino acids (proteins). Translocation occurs when a piece of a chromosome breaks off and attaches to another chromosome. This occurs on a _______________, which makes sense because that’s where proteins are made. It changes ____________. 19 MUTATION, CLONING, and BREEDING (#148-167) POINT MUTATION – A single-base substitution that causes a single base nucleotide to be replaced with another nucleotide. This occurs at one point on the chain and can have 3 possible results. ______________________________ mutation Results in NO CHANGE in an amino acid. ______________________________ mutation Occurs when a DIFFERENT AMINO ACID results. ______________________________ mutation A STOP CODON is inserted, stopping protein synthesis. CHROMOSOMAL MUTATION – A change in the structure of a chromosome. This can result from… The loss of a segment of a chromosome (and the genes it contained). When a segment of a chromosome is displayed more than once on the chromosome. When a segment of a chromosome breaks off and reattaches in reverse (upside down) order. FRAME-SHIFT MUTATION – the insertion or deletion of one or more nucleotides that is not divisible by 3. When the nucleotides are then put together in groups of three to be decoded, this results in a completely different amino acid sequence and alters the protein produced in the ribosomes. CLONING – When a cell, cell product, or organism is copied from an original source. _________ cloning The transfer of a DNA fragment from one organism to a selfreplicating genetic element like a bacterial plasmid. _______________________ cloning Transferring genetic material from the nucleus of a donor adult to an egg cell with the nucleus removed to create an embryo that can produce an exact genetic copy of the donor. _______________________ cloning Taking undifferentiated (i.e. they haven’t been assigned a task yet) embryonic cells a.k.a. STEM cells for use in medical research or therapeutic uses (curing diseases). SELECTIVE BREEDING happens all the time when it comes to ___________, ___________, and ___________. 20