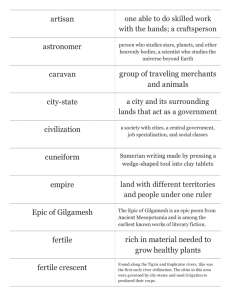
Ch. 3 test review – 6th grade 1. How did Assyrian rulers control an
advertisement

Ch. 3 test review – 6th grade 1. How did Assyrian rulers control an empire that stretched across the Persian Gulf and into Egypt? a. They maintained one unit of government. b. They maintained many units of government. c. They gave up control of some of their territory. d. They limited how far their empire could expand. 2. The ancient city of Babylon, located near present-day _____, became the center of a new Mesopotamian empire under Hammurabi. a. Amman, Jordan c. Tehran, Iran b. Damascus, Syria d. Baghdad, Iraq 3. The Phoenician alphabet was based on a. syllables. c. sounds. b. words. d. vowels. 4. What was an effect of Sargon’s troops moving through the Fertile Crescent? a. Languages were maintained across the region. b. Much of Mesopotamia was divided. c. The Akkadians and Sumerians no longer used the cuneiform system of writing. d. Akkadian and Sumerian cultural traits spread throughout the region. 5. What geographic features(s) was/were extremely important to Sumerian farming? a. Taurus and Zagros mountains c. Sinai Peninsula b. Syrian Desert d. Tigris and Euphrates rivers 6. Which of the following was NOT included in the Ur-Nammu law code, the earliest written code of laws? a. Laws about marriage c. Laws about fighting Babylonia b. Laws about harming others d. Laws about slavery 7. Which of the following was NOT used by the Sumerians? a. Cuneiform c. Alphabet b. Wheeled carts d. Boat sails 8. What was the role of priests in Sumerian civilization? a. Lead the economy c. Communicate with gods b. Introduce new technology d. Run farms 9. What pattern did the laws in Hammurabi’s Code follow? a. Punishment, offense c. Offense, punishment b. Punishment, explanation d. Offense, explanation 10. Which of the following was NOT a reason why the introduction of gold coins helped the Persian empire economy grow? a. Gold coins were accepted currency across the empire. b. Gold coins could only be used by the wealthiest Persians and the king. c. Gold coins assigned a uniform value to goods. d. Gold coins made trade possible in far-off provinces of the empire. 11. How did sailors’ use of the North Star help Phoenician trade? a. The North Star helped sailors earn more money. b. The North Star helped sailors travel across land faster. c. The North Star helped merchants find more customers. d. The North Star helped sailors guide their voyages more accurately. 12. Which of the following is true of Mesopotamia relief sculpture? a. It is flat along the base material. b. It has details that stick out from the base material. c. It is found only on Sumerian seals. d. It is found only on steles. 13. What did Sumerian sculptors create that was different from earlier sculptures? a. Iron pieces c. Hanging gardens b. Realistic statues of humans d. Assyrian-style statues 14. How did the Phoenician alphabet improve upon the cuneiform writing system? a. It took longer to write. c. It involved fewer symbols. b. It required more memorization. d. It did not depend upon sounds. 15. Which body of water do you think was the most important for Phoenician trade routes? a. Atlantic Ocean c. The Adriatic Sea b. Black Sea d. The Mediterranean Sea 16. Which of the following best describes how the geography of the Fertile Crescent helped link the citystates of Sumer? a. The Tigris and Euphrates Rivers served as waterways for the transport of goods between the city-states. b. Due to advances in irrigation and agriculture, the people of the Fertile Crescent were able to grow more crops. c. The waters of the Tigris and Euphrates carried silt from the mountains to improve the farmlands of the plains. d. New technology such as wheeled carts helped make trade more widespread in the Fertile Crescent. 17. One of the laws of Hammurabi’s Code reads “If he break another man’s bone, his bone shall be broken.” Though this might sound cruel by modern standards, why might such laws encourage social order? a. Since there were few doctors who could repair broken bones, people might be unwilling to break laws. b. Social order is only possible under cruel governments. c. People might be less willing to break laws if they see that there are strong consequences for those who do. d. Hammurabi believed that the only way to keep the peace was to have laws that were strict and harsh. 18. Which of the following is NOT an example of how the Persian empire encouraged local self-government? a. Leaders of provinces were allowed much independence. b. Persian rulers forced people to follow the same customs and obey the same laws. c. Local laws were allowed and not replaced with Persian laws. d. People could practice their own traditions, as they had for years. Study the map above. What do you notice about the geography of Mesopotamia? a. The cities form a ring of defense against invading armies. b. The location of the cities made it easy for trade merchants to reach the Mediterranean Sea. c. The plain between the rivers seemed ideal for the development of communities. d. The mountains and deserts made trade between the cities difficult. 20. In the Persian empire, who controlled the central government and who controlled the local governments? a. Military leaders controlled the central government and the Persian ruler controlled the local governments. b. The Persian ruler controlled the central government and military leaders controlled the local governments. c. Local leaders controlled the central government and the Persian ruler controlled the local governments. d. The Persian ruler controlled the central government and local leaders controlled the local governments. 21. What led to the conquest of Sumer? a. The unification of city-states c. The fighting among city-states b. The peace among city-states d. The wealth of city-states 22. Choose the correct pairing of Fertile Crescent leader and his accomplishment. a. Cyrus the Great and the conquest of Babylon b. Gilgamesh and the invasion of Kush c. King Sargon and the building of Nineveh d. Hammurabi and the founding of Zoroastrianism 23. How did a steady food supply affect the development of Sumerian cities? a. It allowed people to stay in one place. b. It made it more difficult for people to travel. c. It ruined the quality of the land. d. It made living in cities unnecessary. 24. Phoenicia did not have its own supply of ivory, so it traded for ivory with other regions, which meant that, for the Phoenicians, ivory was a(n) a. import. c. natural resource. b. export. d. impossibility. 25. How did the Sumerians’ development of bronze help them as a society? a. It allowed them to make stronger weapons. b. It allowed them to irrigate. c. It allowed them to move away from the Fertile Crescent. d. It helped them free themselves of priests and kings. 26. How did Cyrus the Great’s treatment of the Jews of Jerusalem differ from that of Nebuchadnezzar? a. Cyrus believed in only local government, while Nebuchadnezzar did not. b. Cyrus allowed the Jews to live in Jerusalem, while Nebuchadnezzar banished them. c. Cyrus believed in only central government, while Nebuchadnezzar did not. d. Cyrus banished the Jews from Jerusalem, while Nebuchadnezzar allowed them to stay. 27. Which word characterizes the soil of the Fertile Crescent? a. Unproductive c. Dry b. Rich d. Rocky 28. What city became the center of Hammurabi’s Mesopotamian empire? a. Babylon c. Ur b. Lagash d. Umma 29. Who were the first kings in Sumerian civilization? a. Priests c. Scribes b. Farmers d. Military leaders 30. Why did Assyrians become so skilled at fighting after the fall of Babylonia? a. They had to protect Babylon. c. They had to fight many invaders. b. They had to battle the Persians. d. They had to expand their empire. 31. Phoenicians in search of natural resources not found in their homeland sometimes moved to the civilization’s faraway ________. 32. The Epic of Gilgamesh was written entirely in _________ on clay tablets. 33. _________ increased the amount of farmland in the Fertile Crescent by bringing water to fields. 34. Assyrians used __________ to build stronger weapons. 35. The spread of the Phoenician alphabet to Greece and eventually Rome is an example of _______________. 36. Mesopotamian relief sculpture is often found on a standing, carved stone slab or pillar, called a(n) ___________. 37. The idea that everyone must obey the law, including powerful politicians, is found in Hammurabi’s Code and is known as the ___________. 38. Sargon conquered and controlled Sumerian city-states, gradually creating a(n) ______. 39. How did the Phoenicians’ willingness to travel far for trade eventually lead to the spread of their civilization? 40. Compare and contrast the role that geography played in the development of the Sumerian and Phoenician civilizations. In your answer, be sure to consider natural resources, trade, and the value of land to other people