Viruses 2 - Iowa State University
advertisement

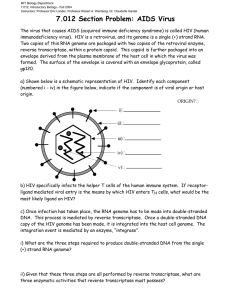
Leader: Course: Instructor: Date: Viruses 2! Supplemental Instruction Iowa State University Tiffany Biol 212 (1) Powell-Coffman 03/06/2011 CONNECT 4 QUESTIONS 1. What type of genome do influenza viruses have? 2. What is a glycoprotein? 3. What are the names of the two surface glycoproteins that influenza viruses have? 4. How can viruses evolve over time? 5. What kind of genomic changes would give a virus a selective advantage? 6. H1N1 is a strain of what type of influenza? 7. What type of virus is HIV (human immunodeficiency virus)? 8. What type of genome does HIV have? 9. What type of host cells does HIV infect? 10. How can HIV be debilitating for a host? 11. What is the first step of HIV’s replication cycle? How does HIV trick the host cell? 12. After HIV proteins and genome enter the cell, what role does reverse transcriptase play? 13. In HIV replication, how is the DNA copy of the viral genome inserted into the host chromosomal DNA? 14. How are telomerase reverse transcriptase and retrovirus reverse transcriptase similar? 15. After the DNA copy of the HIV genome is inserted into the host chromosomal DNA, what is the next step? 16. What are some recommended treatments for HIV? 17. What should a successful anti-viral drug do? 18. For an anti-viral drug, there should be a ________________ _______________ at which the virus is defeated and the ________________ _______________ should be minimal. 19. What do some of the most effective anti-viral drugs do? 20. What is an example of an effective antiviral drug that inhibits nucleic acid synthesis? Supplemental Instruction 1060 Hixson-Lied Student Success Center 294-6624 www.si.iastate.edu Viruses 2! Supplemental Instruction Iowa State University Leader: Course: Instructor: Date: Tiffany Biol 212 (1) Powell-Coffman 03/06/2011 21. What is a nucleotide analog? 22. What is the purpose of an antibiotic? 23. What are two examples of targets of antibiotics? 24. How does tetracycline inhibit the growth of bacterial pathogens? 25. What changes to the bacterial genome would allow a bacterial pathogen to become resistant to tetracycline? Review questions from the last few lectures… 26. What is the difference between junctions between 2 animal cells and 2 plant cells? 27. What is a juxtracrine signal? 28. What is an endocrine signal? 29. What is a paracrine signal? 30. What does a kinase do? 31. What second messenger binds to a channel in the ER and causes calcium levels in the cytoplasm to increase? 32. What is mitosis? 33. What is meiosis? 34. What is polyspermy? 35. What sex invests more energy per gamete? 36. What is somatic nuclear transfer? 37. Where do animal cells concentrate calcium? 38. What gamete is specialized for motility? 39. What are the two characteristics of every virus? 40. Why are viruses referred to as hijackers? 41. What type of genome do phages have? 42. describe the difference between the lytic and lysogenic cycle