1. Celiac disease causes the destruction of the villi cells. Which of
advertisement
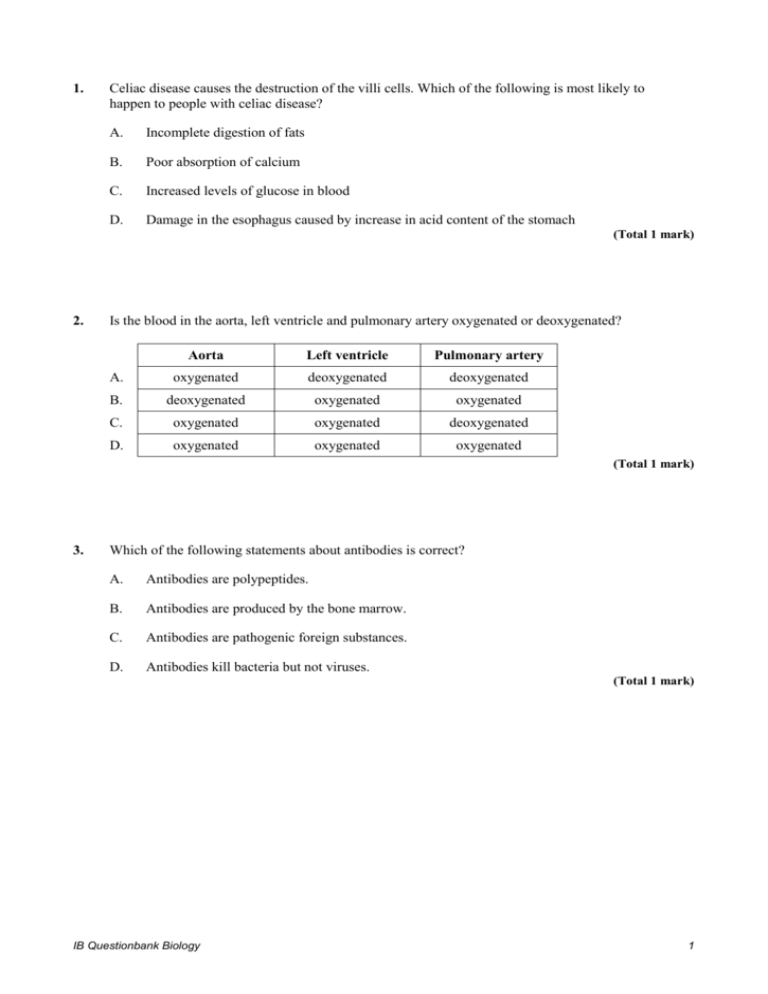
1. Celiac disease causes the destruction of the villi cells. Which of the following is most likely to happen to people with celiac disease? A. Incomplete digestion of fats B. Poor absorption of calcium C. Increased levels of glucose in blood D. Damage in the esophagus caused by increase in acid content of the stomach (Total 1 mark) 2. Is the blood in the aorta, left ventricle and pulmonary artery oxygenated or deoxygenated? Aorta Left ventricle Pulmonary artery A. oxygenated deoxygenated deoxygenated B. deoxygenated oxygenated oxygenated C. oxygenated oxygenated deoxygenated D. oxygenated oxygenated oxygenated (Total 1 mark) 3. Which of the following statements about antibodies is correct? A. Antibodies are polypeptides. B. Antibodies are produced by the bone marrow. C. Antibodies are pathogenic foreign substances. D. Antibodies kill bacteria but not viruses. (Total 1 mark) IB Questionbank Biology 1 4. What normally prevents the membranes of the alveoli from sticking together during expiration? A. The thickness of the single-cell layer of alveoli membranes B. The secretion of fluids in the inner surface of the alveoli C. The pressure within the thoracic cavity D. The dense net of capillaries covering the alveoli (Total 1 mark) 5. Which words from the table below complete the sentence correctly? In the pancreas, ____I____ secrete glucagon, which ____II____ blood glucose levels. I II A. α cells raises B. β cells raises C. α cells lowers D. β cells lowers (Total 1 mark) IB Questionbank Biology 2 6. The diagram below shows the male reproductive system. Which are the epididymis and the seminal vesicle in the diagram? Epididymis Seminal vesicle A. IV I B. III II C. I V D. III I (Total 1 mark) 7. A number of different proteins are involved in nerve function. Which of the following does not require a membrane protein? A. Active transport of sodium B. Diffusion of K+ into the cell C. Diffusion of the neurotransmitter across the synapse D. Binding of the neurotransmitter to the post-synaptic membrane (Total 1 mark) IB Questionbank Biology 3 8. This question refers to the following diagram of the digestive system. Which organs are associated with the transformation of glucose into glycogen? A. 1 and 4 B. 2 and 3 C. 2 and 4 D. 1 and 3 (Total 1 mark) 9. Between which structures do sensory neurons carry nerve impulses? A. From receptors to muscles B. From effectors to the central nervous system (CNS) C. From the central nervous system (CNS) to receptors D. From receptors to the central nervous system (CNS) (Total 1 mark) IB Questionbank Biology 4 10. Rhesus factor is an antigen present on the surface of red blood cells of Rhesus positive individuals. Rhesus positive (Rh+ ) is dominant to Rhesus negative (Rh– ). A mother with Rhesus negative blood gives birth to a baby with Rhesus positive blood and there are concerns that subsequent pregnancies will trigger an immune response. What are the genotypes of the mother and her first baby? Genotype of mother Genotype of first baby A. Rh– Rh– Rh– Rh– B. Rh– Rh– Rh+ Rh– C. Rh– Rh– Rh+ Rh+ D. Rh+ Rh– Rh+ Rh+ (Total 1 mark) 11. Rhesus factor is an antigen present on the surface of red blood cells of Rhesus positive individuals. Rhesus positive (Rh+ ) is dominant to Rhesus negative (Rh– ). A mother with Rhesus negative blood gives birth to a baby with Rhesus positive blood and there are concerns that subsequent pregnancies will trigger an immune response. What is a possible explanation for why subsequent pregnancies could trigger an immune response? A. Exposure to the Rh+ antigen in the first pregnancy triggered the development of antibodies that could attack the blood of a future Rh+ baby. B. Exposure to the Rh+ antigen in the first pregnancy triggered the development of specific phagocytes that could attack the blood of a future Rh+ baby. C. The mother has developed passive immunity to the Rh+ factor. D. The mother’s immune system has been weakened by pregnancy. (Total 1 mark) IB Questionbank Biology 5 12. Which vessel directly supplies the heart muscle with blood? A. The aorta B. The pulmonary artery C. The coronary artery D. The pulmonary vein (Total 1 mark) 13. Which of the following is part of the process of cellular respiration? A. Changes in the volume of the thoracic cavity B. Exchange of gases across the surface of the alveoli C. Exchange of gases across the surface of capillaries D. Glycolysis (Total 1 mark) 14. (a) State the missing source, optimum pH requirement, substrate and product of the human enzymes in the table below. Enzyme Source Optimum pH Amylase Salivary gland 7 Lipase Substrate Products Lipids Fatty acids and glycerol (2) IB Questionbank Biology 6 (b) Explain the need for enzymes in digestion. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (2) (c) Draw a labelled diagram to show the interconnections between the gall bladder, pancreas and small intestine. (3) (Total 7 marks) 15. Up to two additional marks are available for the construction of your answers. (2) (a) Embryos that are produced by in vitro fertilization can be screened for genetic disease. Outline the process of in vitro fertilization, including one example of a situation when it is used. (9) (b) Explain, using an example, how females but not males can be carriers of some recessive alleles. (4) IB Questionbank Biology 7 (c) Explain the causes and consequences of sickle-cell anemia. (5) (Total 20 marks) 16. Tufted ducks (Aythya fuligula) are found in lakes and lagoons throughout Europe. They eat molluscs, insects and plants, sometimes from the surface but mostly by diving under the water. The graph shows how the heart rate of a tufted duck changes when diving under the water. [R Stephenson, P J Butler and A J Woakes. 1986. “Diving behaviour and heart rate in tufted ducks (Aythya fuligula).” J Exp Biol. Vol 126. Pp 341–359.] (a) State the length of time the tufted duck was under the water. ...................................................................................................................................... (1) IB Questionbank Biology 8 (b) Outline the changes in the heart rate during the dive. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (2) (c) Suggest, with a reason, the type of respiration used by the tufted duck during the dive. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (1) IB Questionbank Biology 9 When swimming on the surface, the blood supply to different parts of the body of the tufted duck varies according to whether it is swimming at normal speed or maximum speed. [Source: Butler, PJ, Turner, DL, Al-Wassia, A & Bevan, RM. 1988. “Regional distribution of blood flow during swimming in the tufted duck (Aythya fuligula).” J Exp Biol. Vol 135. Pp 461–472.] (d) Calculate the percentage increase in blood flow to the leg muscles when the tufted duck changes from swimming at normal speed to swimming at maximum speed. ...................................................................................................................................... (1) IB Questionbank Biology 10 (e) Compare the blood flow to the heart muscles with the blood flow to the flight muscles when changing from swimming at normal speed to swimming at maximum speed. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (2) (f) Explain the changes in blood flow that occur when swimming at maximum speed. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (2) (g) Predict, with reference to both graphs, what would happen to the blood flow to the heart muscles when the tufted duck is diving. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (2) (h) State the hormone that affects heart rate. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (1) (Total 12 marks) 17. Up to two additional marks are available for the construction of your answers. (2) IB Questionbank Biology 11 (a) Outline the cause and transmission of AIDS. (5) (b) Describe how phagocytic leucocytes may act as a defence against disease. (4) (c) Explain the principle of homeostasis with reference to the control of body temperature. (9) (Total 20 marks) IB Questionbank Biology 12 18. Vitamin C is an important component of a healthy diet. Because it is water-soluble it cannot be effectively stored and excess vitamin C is released in the urine. In order to investigate the ability of the body to retain different chemical forms of vitamin C, 17 healthy, female university students, between the ages of 18 and 22, were placed on a low vitamin C diet (< 5 mg per day) for three days. The test subjects were divided into two groups and were given an oral vitamin C loading of either ascorbic acid (176 mg) or dehydroascorbic acid (174 mg). Levels of vitamin C in the urine were measured six hours before and at regular intervals over a 24 hour period following vitamin C loading. The negative value indicates time before vitamin C loading. [Masaru Tsujimura, Shizu Higasa, Kazuhiro Nakayama, Yoshiko Yanagisawa, Sadahiko Iwamoto and Yasuo Kagawa. 2008. “Vitamin C activity of dehydroascorbic acid in humans — Association between changes in the blood vitamin c concentration or urinary excretion after oral loading.” J Nutr Sci Vitaminol. Vol 54. Pp 315–320, 1 table.] (a) State the urinary vitamin C content for each of the two study groups six hours before vitamin C loading. Ascorbic acid: .............................................................................................................. Dehyrdoascorbic acid: ................................................................................................. (1) IB Questionbank Biology 13 (b) Calculate the percentage increase in urine levels of vitamin C for the ascorbic acid study group during the first three hours after vitamin C loading. ........................................... % (1) (c) Compare the trends in vitamin C release for the two test groups during the first twelve hours after vitamin C loading. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (2) (d) Large individual differences in the urine level of ascorbic acid and dehydroascorbic acid were recorded between test subjects after 24 hours. Suggest one possible reason for these large individual differences. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (1) IB Questionbank Biology 14 (e) Scurvy is a disease that is due to vitamin C deficiency. Evaluate the importance of this investigation for finding ways to combat vitamin C deficiency. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (2) (Total 7 marks) 19. (a) Body mass index (BMI) can be calculated from the mass (in kg) and height (in m) of an individual. The status of an individual can then be determined from a scale such as the one shown below. (i) BMI / kg m–2 Status < 18.5 Underweight 18.5–24.9 Normal weight 25.0–29.9 Overweight ≥ 30.0 Obese Calculate the BMI for an individual whose mass is 74.0 kg and who has a height of 1.80 m. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (1) (ii) On the basis of the BMI calculated in (a)(i), identify the status of this individual. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (1) IB Questionbank Biology 15 (b) Outline factors that can lead to an individual becoming obese. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (3) (Total 5 marks) 20. (a) State two advantages of breastfeeding over bottle-feeding. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (2) (b) State one symptom of type II diabetes. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (1) IB Questionbank Biology 16 (c) Explain the dietary advice that should be given to a patient who has developed type II diabetes. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (3) (Total 6 marks) 21. Physiological data were collected for a sample of 12 obese subjects across a range of exercise machines. The average age of the subjects was 47 years and the average mass was 101.6 kg. The subjects completed 15-minute trials on each machine at a self-selected, moderate intensity. Mean values and, in some cases, standard deviations, are shown for the collected data. Weight-bearing machines Variable Non weight-bearing machines Treadmill Body Trec Stationary Cycle Airdyne VO2 / cm3 kg–1 min–1 13.5 16.4 10.8 12.5 Heart rate / bpm 110 128 109 118 O2supply / cm3 beat–1 12.3 12.9 10.1 10.9 Ventilation rate / dm3 min–1 30.8 ± 8 39.7 ± 10 29.7 ± 14 31.2 ± 9 Energy expenditure / kJ min–1 27.5 ± 8.8 33.4 ± 8.4 22.2 ± 8.6 26.3 ± 8.4 Blood lactate / mM 2.82 ± 1.33 3.97 ± 1.77 3.35 ± 1.19 3.67 ± 1.63 [Jong-Kyung Kim, Hosung Nho and Mitchell H Whaley. 2008. “Inter-modal comparisons of acute energy expenditure during perceptually based exercise in obese adults.” J Nutr Sci Vitaminol. Vol 54. Pp 39–45.] IB Questionbank Biology 17 (a) Calculate the average O2 supply in cm3 beat–1 for the weight-bearing machines. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (1) (b) Suggest one reason for the higher VO2 recorded for weight-bearing machines, compared to non weight-bearing machines. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (1) (c) Analyse the energy expenditure for the four exercise machines. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (2) (d) Based on these data, discuss the advantages and disadvantages of the body trec for obese subjects undergoing moderate exercise. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (3) (Total 7 marks) IB Questionbank Biology 18 22. The term fitness can be defined as “the physical condition of the body that allows it to perform exercise of a particular type”. Becoming fit requires training a range of muscles and improving the performance of the cardiovascular and pulmonary systems. (a) State two changes in the performance of the cardiovascular system that could occur after a training programme. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (2) (b) Intense exercise during training can lead to a condition called oxygen debt. Outline how oxygen debt is repaid. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (2) (c) Warming up and down routines are often used by athletes as a way of avoiding injuries during training. Outline the importance of warm-up exercises for avoiding injuries. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (2) (Total 6 marks) IB Questionbank Biology 19 23. (a) Draw a labelled diagram of a sarcomere. (3) (b) Explain the role of calcium ions in muscle contraction. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (2) (Total 5 marks) IB Questionbank Biology 20 24. In Australia, a study was undertaken among women to determine the vitamin D levels in their blood. Levels of vitamin D were categorized as sufficient, insufficient and deficient to determine how prevalent each category was. Three locations at three different latitudes and four different seasons were used. A data summary is shown in the graphs below. [Source: Van der Mei, IA, Ponsonby, A-L, Engelsen, O, Pasco, JA, McGrath, JJ et al. 2007. “The high prevalence of vitamin D insufficiency across Australian populations is only partly explained by season and latitude.” Environ Health Perspect. Vol 115, issue 8. DOI:10.1289/ehp.9937.] IB Questionbank Biology 21 (a) (i) Identify the season when the women are least likely to suffer from vitamin D deficiency. ........................................................................................................................... (1) (ii) Using the data from all four seasons, identify the two locations where the patterns of vitamin D are most similar. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (1) (iii) Determine what percentage of women in Geelong have insufficient vitamin D levels in winter. ........................................................................................................................... (1) (b) Compare the deficiency levels of vitamin D at all three locations. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (3) IB Questionbank Biology 22 (c) Location and season were found to account for only a small part of the deficiencies. Suggest, with reasons, how the behaviours of different people could influence the levels of vitamin D in their blood. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (2) (Total 8 marks) 25. (a) Distinguish between the energy content per 100 g of fat, protein and carbohydrate. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (1) (b) Outline consequences of protein deficiency malnutrition. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (2) IB Questionbank Biology 23 (c) Discuss ethical issues concerning the eating of animals and animal products. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (4) (Total 7 marks) 26. Describe the causes, consequences and diagnosis of phenylketonuria (PKU). ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ (Total 3 marks) IB Questionbank Biology 24 27. Backflow is the return of blood to the heart. In legs, backflow is enhanced by the pumping action of leg muscles during movement. When this does not occur efficiently, serious health problems can arise. The backflow speed of 40 patients was measured during the application of different therapy methods. The lying position is the control. [Source: Adapted from postdoctoral thesis of Erich Meyer, Medical Faculty of the University of Erlangen-Nürnberg.] (a) (i) State which activity reduces backflow speed in relation to the control. ........................................................................................................................... (1) (ii) Suggest a reason why backflow speed is reduced by the activity stated in (a)(i). ........................................................................................................................... (1) (b) Determine the difference in backflow speed between the lying position and pedal exercise. ...................................................................................................................................... (1) IB Questionbank Biology 25 (c) Discuss the benefits of exercising to promote high backflow speed. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (3) (Total 6 marks) 28. (a) (i) Define the term fitness. ........................................................................................................................... (1) (ii) Outline measures of fitness. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (2) IB Questionbank Biology 26 (b) Explain the effects of training on heart rate and stroke volume during exercise. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (3) (Total 6 marks) 29. What will be happening in a person after eight hours of sleep? A. β cells in the pancreas will be producing insulin. B. Glucose will be converted into glucagon. C. α cells in the pancreas will be producing glucagon. D. Glycogen is being produced and stored in the liver and muscle cells. (Total 1 mark) IB Questionbank Biology 27 30. The diagram below shows the male reproductive system. Which are the epididymis and the seminal vesicle in the diagram? Epididymis Seminal vesicle A. IV I B. III II C. I V D. III I (Total 1 mark) IB Questionbank Biology 28 31. Which is the sequence of events in muscle contraction? I. Use of ATP II. Formation of cross bridges III. Release of calcium ions from the sarcoplasmic reticulum IV. Actin filament moves towards the centre of the sarcomere A. I → II → III → IV B. III → II → IV → I C. IV → I → II → III D. II → IV → I → III (Total 1 mark) IB Questionbank Biology 29 32. The diagram below shows a longitudinal section through a kidney. What is the structure labelled Z and what is its function? Structure Z Function A. cortex osmoregulation B. medulla ultrafiltration C. cortex ultrafiltration D. pelvis osmoregulation (Total 1 mark) 33. During urine production, what happens if the water content of the blood is too low? A. Membrane channels are produced in the cells of the collecting duct. B. The pituitary gland stops secreting ADH. C. The collecting duct becomes less permeable to water. D. Large volumes of dilute urine are formed. (Total 1 mark) 34. A process occurs in which the inside of a neuron develops a net positive charge compared with the IB Questionbank Biology 30 outside. What is the name of this process? A. Resting potential B. Repolarization C. Depolarization D. Hyperpolarization (Total 1 mark) 35. Which of these statements about the human placenta is incorrect? A. The placenta is the site of nutrient and gas exchange between the mother and fetus. B. The placenta produces hormones, such as estrogen. C. The placenta begins to develop after implantation of the blastocyst. D. The mother’s blood and the baby’s blood mix in the placenta. (Total 1 mark) 36. Which of the following is transported by the blood? A. Gametes B. Glycogen C. Heat D. Starch (Total 1 mark) IB Questionbank Biology 31 37. The umbilical artery carries blood from the fetus to the placenta and the umbilical vein carries blood from the placenta to the fetus. How does the composition of the blood in the umbilical artery and the umbilical vein differ? A. Blood in the umbilical artery contains less glucose than blood in the umbilical vein. B. Blood in the umbilical artery contains less carbon dioxide than blood in the umbilical vein. C. Blood in the umbilical vein contains less oxygen than blood in the umbilical artery. D. Blood in the umbilical vein contains more urea than blood in the umbilical artery. (Total 1 mark) 38. What happens when ATP binds to myosin heads during muscle contraction? A. Calcium ions are released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum. B. Calcium ions are taken up by the sarcoplasmic reticulum. C. Cross-bridges between myosin heads and actin filaments are broken. D. Myosin heads form cross-bridges with actin filaments. (Total 1 mark) 39. A blood clot forms around a fibrous network of protein. What is the protein? A. Fibrinogen B. Fibrin C. Thrombin D. Thrombokinase (Total 1 mark) IB Questionbank Biology 32 40. What is a difference between human sperm and human egg cells? A. Sperm have more chromosomes. B. Sperm have a larger surface area to volume ratio. C. Eggs have an acrosome. D. The division of the cytoplasm in sperm production is uneven. (Total 1 mark) 41. Up to two additional marks are available for the construction of your answers. (2) (a) During a period of physical exercise, the rate of urine production falls, but the ventilation rate and the body temperature rise. Explain the mechanisms that are used to cool the body when it is overheated. (5) (b) Explain how the collecting ducts can alter the volume of urine produced by the kidney. (5) (c) Describe the structure of the ventilation system, including the alveoli. (8) (Total 20 marks) 42. Up to two additional marks are available for the construction of your answers. (2) (a) Gametes are produced in humans by spermatogenesis and oogenesis. Compare spermatogenesis and oogenesis. (5) (b) Explain the processes that result in genetic variation in the sperm produced by an adult male. (5) IB Questionbank Biology 33 (c) Outline the process of in vitro fertilization (IVF). (8) (Total 20 marks) 43. (a) Define the term excretion. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (1) (b) Explain the process of ultrafiltration. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (2) IB Questionbank Biology 34 (c) The diagram below shows part of the human kidney. The arrow shows the direction of blood flow. Compare the composition of the fluids found in the regions labelled I and II by giving one difference and one similarity. Difference: ................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... Similarity: .................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (2) (Total 5 marks) 44. Up to two additional marks are available for the construction of your answers. (2) (a) Outline the role of the skin in temperature regulation. (5) (b) Outline the role of hormones in the process of birth in humans. (4) (c) Explain the principles of vaccination. (9) IB Questionbank Biology 35 (Total 20 marks) IB Questionbank Biology 36 45. Helicobacter pylori infection is a cause of stomach ulcers. It affects SLC26A9, which is a membrane protein present in the epithelial lining of the stomach. SLC26A9 takes part in the reversible transport of chloride and hydrogen carbonate ions into and out of the epithelial cells in order to raise the pH at the membrane to neutral levels. Entry of chloride ions into epithelial cells and removal of hydrogen carbonate ions both cause extracellular pH to increase. To assess the function of SLC26A9, this process was reversed by artificially raising the external pH. The rate of change of extracellular pH was measured with normal epithelial cells and with modified cells with extra SLC26A9. The tests were also performed in the presence of DIDS, an inhibitor of SLC26A9. [Reproduced with permission of the American Physiological Society from American Journal of Physiology. J Xu et al. 2005. Cell Physiology. Vol 289. Pp 493–505.] IB Questionbank Biology 37 (a) Calculate the difference in the rate of decrease of pH between the control cells and the modified cells without DIDS. ..................................... pH min–1 (1) (b) State the effect of DIDS on the rate of decrease of the extracellular pH. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (1) (c) Scientists hypothesized that Helicobacter pylori alters the ability to maintain neutral pH at the epithelial cell surface by inhibition of SLC26A9. Evaluate this hypothesis. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (2) (d) In further experiments, scientists observed that the levels of mRNA of SLC26A9 increased in epithelial cells when infected by Helicobacter pylori. Suggest a possible explanation for this increase. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (1) IB Questionbank Biology 38 (e) Predict, with a reason, the effect of DIDS on stomach pH if given to an experimental subject. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (2) (Total 7 marks) 46. (a) Outline how coronary thrombosis can be caused. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (2) IB Questionbank Biology 39 (b) The oxygen dissociation curve is a graph that shows the percentage saturation of hemoglobin at various partial pressures of oxygen. Curve A shows the dissociation at a pH of 7 and curve B shows the dissociation at a different pH. [Used with Permission. From: Basic Skills in Interpreting Laboratory Data, Fourth Edition. Copyright 2009, American Society of Health-System Pharmacists.] (i) State the possible cause of the curve shifting from A to B. ........................................................................................................................... (1) (ii) On the graph, draw the curve for myoglobin. (2) IB Questionbank Biology 40 (c) Describe the breakdown of hemoglobin in the liver. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (2) (Total 7 marks) IB Questionbank Biology 41 47. Explain the control of ADH secretion. ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ (Total 6 marks) IB Questionbank Biology 42 48. Neutrophils are a primary defence against bacterial and fungal infection. This defence involves both phagocytosis and hydrogen peroxide production. If there is an excess production of hydrogen peroxide, tissue damage may occur. In hospitals, intravenous feeding of patients is often necessary and lipids form an essential part of the solutions used. A study was undertaken to measure the impact of two different types of lipid solutions on the activity of neutrophils in blood samples and on their production of hydrogen peroxide. The two lipid solutions were tested at two different concentrations, 0.06 mg cm–3 (Graph A) and 0.6 mg cm–3 (Graph B). The control has no lipid solutions. [Source: Björn Jüttner, Janina Kröplin, Sina M Coldewey, Lars Witt, Wilhelm A Osthaus, Christian Weilbach, Dirk Scheinichen. 2008. “Unsaturated long-chain fatty acids induce the respiratory burst of human neutrophils and monocytes in whole blood.” Nutrition & Metabolism. Vol 5. P 19. © 2008 Jüttner et al; licensee BioMed Central Ltd] (a) Identify the maximum percentage value of neutrophils producing hydrogen peroxide for the LCT-MCT solution at 0.06 mg cm–3. ...................................................................................................................................... (1) IB Questionbank Biology 43 (b) Compare the effects of the two different lipid solutions at the two different concentrations on the percentage of neutrophils producing hydrogen peroxide. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (3) (c) Suggest why the addition of an increasing concentration of lipid into a hydrophilic medium, such as the intravenous feeding solution, may be a problem. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (1) (d) Evaluate the data in terms of decisions for the intravenous feeding of patients. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (3) (Total 8 marks) IB Questionbank Biology 44 49. (a) List the locations of chemosensors that detect changes in CO2 concentrations in the blood. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (2) (b) State the name of the enzyme in red blood cells that converts CO2 to a more soluble form. ...................................................................................................................................... (1) (c) Explain the oxygen dissociation curve of myoglobin. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (3) (Total 6 marks) IB Questionbank Biology 45 50. Outline the roles of gastric acid and Helicobacter pylori in the development of stomach ulcers and stomach cancers. ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ (Total 6 marks) 51. Which of the following is correct for lipase? Substrate Source pH optimum A. triglycerides pancreas pH = 8 B. fatty acids small intestine pH = 7 C. triglycerides small intestine pH = 9 D. fatty acids pancreas pH = 9 (Total 1 mark) IB Questionbank Biology 46 52. What processes occur during assimilation and absorption of lipids? Assimilation Absorption A. lipids are broken down by enzymes lipids are egested B. lipids are incorporated into new membranes lipids pass into the lacteal C. lipids pass into the lacteal lipids are incorporated into new membranes D. lipids are egested lipids are broken down by enzymes (Total 1 mark) IB Questionbank Biology 47 53. The diagram below shows the human heart. What structures are indicated by the labels X, Y and Z? [Source: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Heart_diagram-en.svg. Image by ZooFari] X Y Z A. left atrium aorta semi-lunar valve B. left atrium aorta atrio-ventricular valve C. right atrium pulmonary artery atrio-ventricular valve D. right atrium pulmonary artery semi-lunar valve (Total 1 mark) IB Questionbank Biology 48 54. What are two effects of HIV on the immune system? A. Reduction in antibody production and increase in active lymphocytes B. Increase in antibody production and decrease in red blood cells C. Reduction in antibody production and decrease in active lymphocytes D. Increase in antibody production and increase in red blood cells (Total 1 mark) 55. What is the function of the structure labelled X? [From: www.medical-look.com/human_anatomy/organs/Lungs.html] A. Gas exchange B. Ventilation C. Respiration D. Inspiration (Total 1 mark) IB Questionbank Biology 49 56. What are causes of type I and type II diabetes? Type I Type II A. autoimmune disease leading to reduced insulin secretion decreased responsiveness of the body to insulin B. decreased responsiveness of the body to insulin autoimmune disease leading to reduced insulin secretion C. increased responsiveness of the body to insulin autoimmune disease leading to increased insulin secretion D. autoimmune disease leading to increased insulin secretion increased responsiveness of the body to insulin (Total 1 mark) IB Questionbank Biology 50 57. In the diagram of synaptic transmission below, what is indicated by the letters X and Y? [Source: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Synapse_Illustration2_tweaked.svg. Image by Nrets.] X Y A. neurotransmitter enters synaptic knob Ca2+ ions B. Ca2+ ions diffuse into the synaptic knob neurotransmitter C. K+ ions diffuse into the synaptic knob neurotransmitter D. Na+ ions diffuse into the synaptic knob Ca2+ ions (Total 1 mark) IB Questionbank Biology 51 58. Which of the following is/are a role of testosterone in males? I. Pre-natal development of male genitalia II. Maintenance of sex drive III. Increase in mental development A. II only B. I and II only C. II and III only D. I, II and III (Total 1 mark) 59. The graph below shows the levels of hormones during the menstrual cycle. IB Questionbank Biology 52 (a) Identify hormones I and II. I: .................................................................................................................................. II: ................................................................................................................................. (2) (b) Outline the roles of FSH in the menstrual cycle. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (2) (c) FSH is secreted by the pituitary gland. During pregnancy, FSH secretion is inhibited. Suggest how FSH secretion could be inhibited during pregnancy. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (1) (Total 5 marks) 60. Up to two additional marks are available for the construction of your answers. (2) (a) The pumping of blood is a vital process. Explain the roles of the atria and ventricles in the pumping of blood. (4) (b) Explain how the structure of an artery allows it to carry out its function efficiently. (5) (c) Describe the inheritance of ABO blood groups. (9) (Total 20 marks) IB Questionbank Biology 53 61. Up to two additional marks are available for the construction of your answers. (2) (a) Plants are a diverse group of eukaryotic organisms. Describe the different characteristics of the bryophyta, filicinophyta, coniferophyta and angiospermophyta. (9) (b) Plants store carbohydrate in the form of starch. Explain the reasons for starch being digested by the human digestive system. (4) (c) Compare the structure of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. (5) (Total 20 marks) IB Questionbank Biology 54 62. Male Lepidoptera (butterflies and moths) commonly drink from pools of water or from moist soil. This behaviour, called puddling, was investigated in an undisturbed area where male tiger swallowtails, Papilio glaucus, had been seen puddling. Four successive sets of experiments were performed under similar conditions of temperature and humidity. In each set, equal samples of sand were spread out evenly on trays and then treated differently. Except for one dry sample (in the first set), all others were saturated with a different liquid. Results of the observations are given in the table below. [Source: adapted from K Arms et al., “Sodium: Stimulus for Puddling Behaviour by Tiger Swallowtail Butterflies, Papilio glaucus” (1974) Science, 185: 5 (5 July–27 Sept) #4148, pp. 372–374. Reprinted with permission from AAAS] (a) Identify the dissolved element always present in the three samples with most puddling time. ...................................................................................................................................... (1) IB Questionbank Biology 55 (b) Discuss the relationship between sampling visits (V) and puddling time (T) in experiments 1, 2 and 3. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (2) (c) Analyse the results for experiment 4. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (2) IB Questionbank Biology 56 Study of the male moth Gluphisia septentrionis revealed that their puddling behaviour can last for hours. Though drinking results in the uptake of hundreds of gut-loads of fluid, this fluid becomes rapidly expelled from the digestive system through frequent anal ejections. In this experiment, the ion concentration change was calculated by subtracting ions ejected from ions taken in. The following data was collected from males drinking laboratory solutions and from natural puddles. [Source: adapted from SR Smedley and T Eisner “Sodium Uptake by Puddling in a Moth” (1995) Science, 270 (15 Dec) #5243, pp. 1816–1818. Reprinted with permission from AAAS] (d) (i) Identify which ion the moths are retaining in their body from the laboratory solutions. ........................................................................................................................... (1) IB Questionbank Biology 57 (ii) Compare the gain and loss of ions in the male moths which have drunk from laboratory solutions with the changes in those that have drunk from natural puddles. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (3) The diagram below shows the digestive system anatomy of the male and female moth. [Source: adapted from SR Smedley and T Eisner “Sodium Uptake by Puddling in a Moth” (1995) Science, 270 (15 Dec) #5243, pp. 1816–1818. Reprinted with permission from AAAS] IB Questionbank Biology 58 (e) Using the diagram above, evaluate the hypothesis that male moths are better adapted than female moths to benefit from puddling behaviour. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (2) (f) Suggest one reason for puddling behaviour in male Lepidoptera. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (1) (Total 12 marks) 63. (a) State a word equation for anaerobic cell respiration in humans. ...................................................................................................................................... (1) (b) Describe the need for a ventilation system in humans. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (2) IB Questionbank Biology 59 (c) Sketch the hormone changes between days 13 and 28 on the graphs below for a woman in her normal menstrual cycle. [Source: adapted from www.mivf.com.au/ivf/infertility/images/cyclediagram.GIF] (2) (Total 5 marks) 64. Up to two additional marks are available for the construction of your answers. (2) (a) Compare simple diffusion with facilitated diffusion as mechanisms to transport solutes across membranes. (5) (b) Describe the process of endocytosis. (5) (c) Explain how an impulse passes along the membrane of a neuron. (8) (Total 20 marks) IB Questionbank Biology 60 65. A study was made to look at the effect of breastfeeding on infant health. The infants studied were all healthy at birth. They were classified as never breastfed, partially breastfed or only breastfed, based on their feeding status in the first three months of life. The frequency of health care use was assessed for each of these groups, for three illnesses (lower respiratory infection, middle ear infection and gastroenteritis). The table below indicates the frequency of initial and follow-up visits to the doctor, prescription of medication and hospitalizations during the first year of life. Follow-up visits and medication were seldom needed for gastroenteritis. Mean frequency of healthcare use per child in the first year of life Never breastfed Partially breastfed Only breastfed Mean number of visits to doctor 0.46 0.44 0.40 Follow-up visits 0.07 0.01 0.02 Medications 0.27 0.21 0.19 Hospitalization 0.02 0.02 0.01 Mean number of visits to doctor 2.04 1.88 1.51 Follow-up visits 1.02 1.44 0.76 Medications 2.04 1.88 1.51 Mean number of visits to doctor 1.50 0.94 0.45 Hospitalizations 0.11 0.11 0.04 Lower respiratory infection Middle ear infection Gastroenteritis [Source: Thomas M Ball, Anne L Wright. Apr 1, 1999. “Health care costs of formula-feeding in the first year of life”. Pediatrics. Vol 103. Pp 870–876. Copyright © 1999, American Academy of Pediatrics. Reproduced with permission.] (a) Using the data, identify the illness (i) that causes the greatest healthcare use in the first year of life. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (1) (ii) for which breastfeeding causes the greatest reduction in visits to the doctor. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (1) IB Questionbank Biology 61 (b) Compare the health effects of only breastfeeding with partial breastfeeding, using the data in the table. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (2) (c) Suggest how the composition of breast milk and artificial milk may have contributed to these results. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (2) (Total 6 marks) 66. (a) State the energy content of 100 g of carbohydrate, fat and protein. Carbohydrate: .............................................................................................................. Fat: ............................................................................................................................... Protein: ......................................................................................................................... (1) IB Questionbank Biology 62 (b) Explain the possible health consequences of diets rich in fats. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (3) (c) Outline the consequences of protein deficiency malnutrition. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (2) (Total 6 marks) 67. (a) List two dietary sources of vitamin D. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (1) IB Questionbank Biology 63 (b) Discuss exposure to sunlight as a source of vitamin D. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (3) (Total 4 marks) 68. Outline the concept of food miles. ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ (Total 2 marks) IB Questionbank Biology 64 69. A study was carried out to assess the effects of high-intensity interval training on heart rate. Twenty subjects were randomly assigned to two groups: training and control. They underwent a test in which the exercise became harder and harder until they reached the point of exhaustion (progressive incremental test). The training group then performed nine sessions of high intensity interval training on a cycle ergometer during three weeks (1 minute at 130% of maximal aerobic work rate with 1 minute rest intervals until they felt they were at the point of exhaustion).The control group did not do any training. Both groups then repeated the progressive incremental test. The graphs below show the mean heart rate curves during progressive incremental tests before and after training. [Source: Franchetti, L et al. 2007. “Effects of high-intensity interval training on heart rate variability during exercise”. Journal of Exercise Physiology-online. Vol 10, issue 4. Reproduced with permission.] (a) State three factors that would have to be considered when selecting the subjects used in this study. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (1) IB Questionbank Biology 65 (b) Describe the relationship between workload and heart rate shown by the graphs. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (2) (c) (i) Calculate the change in mean heart rate at a workload of 90 W in the training group before and after three weeks of training. ........................................................................................................................... (1) (ii) Deduce the effect of training on heart rate. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (2) (Total 6 marks) IB Questionbank Biology 66 70. (a) The diagram below shows an elbow joint. (i) On the diagram, label a pair of antagonistic muscles. (1) (ii) State the function of the structure labelled A. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (1) IB Questionbank Biology 67 (b) Explain the role of ATP in the contraction of skeletal muscle. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (3) (Total 5 marks) 71. (a) Define tidal volume. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (1) (b) Outline the effects of training on the pulmonary system. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (3) (Total 4 marks) IB Questionbank Biology 68 72. Discuss the need for warm-up routines. ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ (Total 3 marks) 73. Body mass index (BMI) is an important indicator of health. The relationship between a high BMI and percentage risk of developing type II diabetes was studied and the following data presented. [Source: Colditz, G et al. 1995. Annals of Internal Medicine. Vol 122. P 481.] IB Questionbank Biology 69 (a) Describe the effect of increased BMI on the risk of developing type II diabetes. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (2) (b) Identify the risk of developing type II diabetes in men with a BMI of 33 kg m–2. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (1) (c) Determine, by indicating on the graph, the range of age-adjusted relative risk for women who are overweight but not obese. (1) (d) Explain the dietary advice that should be given to a patient who has developed type II diabetes. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (4) (Total 8 marks) IB Questionbank Biology 70 74. (a) Distinguish between the composition of human milk and artificial milk for bottle-feeding babies. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (2) (b) State a main dietary source of carbohydrates in two named ethnic groups. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (2) (c) Explain possible health consequences of diets rich in fats. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (3) (Total 7 marks) 75. (a) State a source of vitamin D in a human diet. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (1) IB Questionbank Biology 71 (b) Discuss exposure to sunlight as a source of vitamin D. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (2) (Total 3 marks) 76. The VO2 max was studied for a person exercising on a treadmill. Data was collected for 13 minutes of progressively faster and steeper running until a peak VO2 was reached. Time / mins VO2 per kg / ml min–1 kg–1 Heart rate / beats min–1 Ventilation rate / breaths min–1 00:47 27.4 126 26.0 02:17 36.6 134 26.0 03:47 40.9 140 26.5 05:17 45.6 149 32.2 06:46 49.2 153 31.1 08:17 53.1 162 34.0 09:47 57.2 167 37.1 11:17 59.2 172 38.4 12:47 62.4 176 41.8 13:17 63.2 177 42.9 [Source: adapted from raw data obtained from sports exhibition at Toronto Science Centre (1989)] (a) State the maximum VO2 per kg for this subject. ...................................................................................................................................... (1) IB Questionbank Biology 72 (b) Determine which has had a greater percentage increase, ventilation rate or heart rate, during the duration of the exercise. Show your working. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (2) (c) The subject weighed 70.0 kg at the time of this exercise. Calculate the VO2 max. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (1) (d) Evaluate the limitations of the data provided by this research. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (2) (Total 6 marks) 77. (a) (i) Define stroke volume. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (1) IB Questionbank Biology 73 (ii) Define cardiac output. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (1) (b) As fitness increases, a person’s heart rate drops. Suggest a reason for this phenomenon. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (1) (c) Describe distribution of blood flow at rest and during exercise. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (3) (Total 6 marks) 78. (a) State two methods of ATP production used by muscles during intense exercise. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (2) IB Questionbank Biology 74 (b) Discuss the ethics of using performance-enhancing substances. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (4) (Total 6 marks) 79. What prevents antibiotics from being effective against viruses? A. Viruses have a high rate of mutation. B. Viruses have no RNA. C. Viruses have no metabolism. D. Viruses have a protein shell that protects them. (Total 1 mark) 80. Which muscles contract to cause air to pass into the lungs through the trachea? A. Internal intercostal muscles and diaphragm B. Internal intercostal muscles and abdomen wall muscles C. External intercostal muscles and diaphragm D. External intercostal muscles and abdomen wall muscles (Total 1 mark) IB Questionbank Biology 75 81. The diagram below shows the changes in membrane potential during an action potential. What occurs at the stages labelled 1 and 2? 1 2 A. Na+ ions diffuse in; inside becomes more positive K+ ions diffuse out; inside becomes more negative B. K+ ions diffuse out; inside becomes more negative Na+ ions diffuse in; inside becomes more positive C. Na+ ions diffuse out; inside becomes more negative K+ ions diffuse out; inside becomes more positive D. Na+ ions diffuse in; inside becomes more positive K+ ions diffuse in; inside becomes more negative (Total 1 mark) IB Questionbank Biology 76 82. What are the roles of testosterone in males? A. Stimulation of FSH production and growth in puberty B. Pre-natal development of genitalia and development of secondary sexual characteristics C. Development of genitalia and pre-natal secondary sexual characteristics D. Stimulation of FSH production and pre-natal development of secondary sexual characteristics (Total 1 mark) 83. What occurs during the blood clotting process? A. Prothrombin is converted into thrombin which acts on fibrinogen. B. Prothrombin is converted into thrombin which acts on fibrin. C. Fibrinogen is converted into fibrin which acts on prothrombin. D. Fibrinogen is converted into fibrin which acts on thrombin. (Total 1 mark) IB Questionbank Biology 77 84. What is indicated by the letters X, Y and Z? X Y Z A. sarcomere myosin filaments actin filaments B. sarcomere actin filaments myosin filaments C. dark band myosin filaments actin filaments D. dark band actin filaments myosin filaments (Total 1 mark) IB Questionbank Biology 78 85. The diagram below shows some stages in the production of monoclonal antibodies. What are stages X, Y and Z? [Used with the permission of Access Excellence @ the National Health Museum] X Y Z A. injection of antibody isolation of B-cell fusion between B-cell and tumour cell resulting in plasma cell B. injection of antibody isolation of T-cell fusion between T-cell and tumour cell resulting in plasma cell C. injection of antigen isolation of T-cell fusion between T-cell and tumour cell resulting in hybridoma cell D. injection of antigen isolation of B-cell fusion between B-cell and tumour cell resulting in hybridoma cell (Total 1 mark) IB Questionbank Biology 79 86. In the diagram of the nephron below, what structures are indicated by the letters Y and Z? [Source: adapted from http://ex.susd.org/sjones/SGHL12007 files/image005.jpg] Y Z A. glomerulus collecting duct B. Bowman’s capsule collecting duct C. Bowman’s capsule distal convoluted tubule D. glomerulus distal convoluted tubule (Total 1 mark) IB Questionbank Biology 80 87. What are the roles of the following structures in the production of semen? Epididymis Seminal vesicle Prostate gland A. production of a fluid containing alkaline minerals production of fructose maturation of sperm B. maturation of sperm production of a fluid containing citric acid production of fructose C. maturation of sperm production of fructose production of a fluid containing alkaline minerals D. production of a fluid containing alkaline minerals maturation of sperm production of fructose (Total 1 mark) 88. What is the role of HCG in early pregnancy? A. It prevents the degeneration of the corpus luteum. B. It initiates the development of the uterus lining. C. It inhibits the production of estrogen. D. It stimulates the degeneration of the corpus luteum. (Total 1 mark) 89. What is a role of the pacemaker or sinoatrial node (SAN)? A. To initiate contraction of the ventricle B. To pass the excitation through Purkinje fibres C. To originate excitation in myogenic muscle D. To cause the relaxation of the atria (Total 1 mark) IB Questionbank Biology 81 90. The diagram below shows water in the human body. Where in the digestive system is the largest volume of water absorbed from? A. Colon B. Pancreas C. Small intestine D. Liver (Total 1 mark) IB Questionbank Biology 82 91. How can active immunity be acquired? A. By having the disease B. Injection of antibodies C. Through colostrum D. Via placenta (Total 1 mark) 92. What are fused in the production of monoclonal antibodies? A. Tumour cells and T-cells B. Tumour cells and B-cells C. B-cells and T-cells D. Antibodies and antigens (Total 1 mark) IB Questionbank Biology 83 93. The diagram below shows the side view of the arm joint. Which letter is pointing to the ulna? A. W B. X C. Y D. Z (Total 1 mark) 94. Which of the following best describes what happens in the glomerulus? A. Selective reabsorption of water and molecules by active transport B. Ultrafiltration introduces water and other molecules into the capillaries C. Regulation of salt balance leading to the production of urine D. High blood pressure forces water and other molecules into the nephron (Total 1 mark) IB Questionbank Biology 84 95. Which pair of statements best describes oogenesis and spermatogenesis? Oogenesis Spermatogenesis A. Four eggs are produced per mitosis every 28 days Millions of sperms are produced per mitosis B. Four eggs are produced per meiosis every 28 days One sperm is produced per meiosis C. One egg is produced per mitosis every 28 days Millions of sperms are produced per meiosis D. One egg is produced per meiosis every 28 days Four sperms are produced per meiosis (Total 1 mark) 96. Up to two additional marks are available for the construction of your answers. (2) (a) Blood is a liquid tissue containing glucose, urea, plasma proteins and other components. List the other components of blood. (5) (b) Outline how the human body prevents blood glucose concentration from rising excessively. (5) (c) Blood plasma, glomerular filtrate and urine have different concentrations of solutes, such as glucose, protein and urea. Explain the processes occurring in the kidney that cause differences in the concentrations of these solutes between blood plasma, glomerular filtrate and urine. (8) (Total 20 marks) IB Questionbank Biology 85 97. Migrating birds must refuel along the way in order to continue flying. A field study was conducted among four different species of migrating birds known to stop at high quality and low quality food sites. Two techniques were used to assess food quality in the stopover sites. Birds were captured and weighed at the two sites. Blood samples were taken from the birds to determine nutrient levels in their blood. The two techniques were compared for their effectiveness. The table below shows data collected from the two sites during one season. Site 1 Species Site 2 N (number captured) Mean bird mass / g N (number captured) Mean bird mass / g Hermit thrush 46 29.8 28 28.3 White-throated sparrow 47 27.9 48 27.2 American robin 8 78.3 10 77.6 Magnolia warbler 30 8.4 10 8.2 [Source: adapted from C Guglielmo, et al., (2005), Physiological and Biochemical Zoology, 78(1), pages 116–125] (a) Considering all the birds sampled, identify which species was sampled the most and which was sampled the least. Most: ........................................................................................................................... Least: ........................................................................................................................... (1) (b) Using the data from the table, calculate the percentage difference in mean bird mass for the hermit thrushes refueling at Site 1 compared to those refueling at Site 2. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (1) IB Questionbank Biology 86 A method was used to determine the average mass change in grams per hour (g h–1) during the study. Graph A represents a summary of data collected during one season whereas Graph B represents a summary of data collected over 17 years. [Source: adapted from C Guglielmo, et al., (2005), Physiological and Biochemical Zoology, 78(1), pages 116–125] (c) Compare the 17-year summary data for the hermit thrush and the magnolia warbler. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (2) (d) Evaluate the one season data for the hermit thrush and the American robin with regard to average mass change per hour at Site 1. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (2) Among birds, high triglyceride concentration in blood plasma indicates fat deposition whereas high butyrate concentration in blood plasma indicates fat utilization and fasting. IB Questionbank Biology 87 The following data summarizes triglyceride levels and butyrate levels measured for the same groups of birds. [Source: adapted from C Guglielmo, et al., (2005), Physiological and Biochemical Zoology, 78(1), pages 116–125] (e) Describe, using the triglyceride levels graph, the results at Site 1 and Site 2 for all of the birds. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (2) IB Questionbank Biology 88 (f) Explain the differences in the triglyceride level and butyrate level for the hermit thrush at Site 1 and Site 2. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (2) (g) Scientists have hypothesized that the food quality is better at Site 1 than at Site 2. Evaluate this hypothesis using the data provided. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (2) (h) Suggest one advantage and one disadvantage for blood sampling rather than weighing birds to assess food quality at stopover sites. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (1) (Total 13 marks) 98. Up to two additional marks are available for the construction of your answers. (2) (a) Outline the process of glycolysis. (5) IB Questionbank Biology 89 (b) Describe how pancreatic cells directly affect blood glucose levels. (5) (c) Explain why diabetes could be detected through the analysis of urine. (8) (Total 20 marks) 99. Up to two additional marks are available for the construction of your answers. (2) (a) Draw a labelled diagram of a mature sperm. (5) (b) Outline the formation of chiasmata during crossing over. (5) (c) Explain how an error in meiosis can lead to Down syndrome. (8) (Total 20 marks) IB Questionbank Biology 90 100. Discuss the concept of brain death and how it can be diagnosed. ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ (Total 6 marks) IB Questionbank Biology 91 101. The human body suffers significant physiological changes at extreme altitudes. Extensive scientific information has been obtained from medical research expeditions to Mount Everest (8848 m above sea level). The figure below shows the relationship between the partial pressures of oxygen (Po2) and carbon dioxide (Pco2) in the alveoli as altitude increases from sea level (at top right) to the summit of Mt. Everest (at bottom left). [Source: West, J B. 2006. “Human responses to extreme altitude”. Integrative and Comparative Biology. Vol 46, issue 1. Pp 25–34. By permission of Oxford University Press.] (a) Outline the changes in the partial pressures of carbon dioxide and oxygen as altitude increases. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (2) IB Questionbank Biology 92 The table below shows the data from the field study on the alveolar gas and arterial blood values for a climber at sea level and on the summit of Mt. Everest. Altitude / meters Inspired Pco2 / mm Hg Arterial Pco2 / mm Hg Arterial pH Sea level (0) 2.50 40.0 7.40 Summit (8848) 0.83 7.5 >7.70 [Adapted from West, J B. 2006. “Human responses to extreme altitude”. Integrative and Comparative Biology. Vol 46, issue 1. Pp 25–34. By permission of Oxford University Press.] (b) Predict, with a reason, how the ventilation rate will change as a climber ascends from sea level to the summit of Mt. Everest. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (2) (c) (i) Calculate the percentage change in the arterial partial pressure of carbon dioxide (Pco2) at the summit compared with that at sea level. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (1) (ii) Suggest a reason for the low arterial partial pressure of carbon dioxide at the summit. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (1) IB Questionbank Biology 93 (d) State one adaptation of people who live permanently in high altitude areas. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (1) (Total 7 marks) 102. (a) (i) Define hormones. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (1) (ii) State one type of hormone, giving an example. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (1) (b) Compare gastric juice and pancreatic juice. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (3) IB Questionbank Biology 94 (c) Outline the reason for one named substance found in food not being digested and absorbed by humans. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (2) (Total 7 marks) 103. Explain the role of the SA (sinoatrial) node in the cardiac cycle. ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ (Total 6 marks) IB Questionbank Biology 95 104. A group of non-smoking men and women were studied for the effects of environmental contamination with cadmium, a toxic metal. A study was conducted to see the effect of cadmium exposure on the metabolism of the liver, as measured by the activity of a cytochrome enzyme that metabolizes drugs, and on renal tubular damage in the kidney as indicated by the excretion of a substance, NAG. [Source: Satarug, S et al. 2004. Environmental Health Perspectives. Vol 111, issue 15. Pp 1512–1518. Reproduced with permission from Environmental Health Perspectives.] (a) (i) Identify the highest hepatic cytochrome activity value in women. ........................................................................................................................... (1) (ii) Identify the lowest renal tubular damage value in men. ........................................................................................................................... (1) IB Questionbank Biology 96 (b) Compare the correlation between hepatic and renal functions for men and for women. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (2) (c) The scientists who conducted the study hypothesized that exposure to cadmium causes toxicity in both hepatic and renal functions. Using the data, evaluate the hypothesis. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (2) (Total 6 marks) 105. (a) Distinguish between the mode of action of protein hormones and steroid hormones. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (2) IB Questionbank Biology 97 (b) Label the indicated structures in the micrograph of exocrine gland cells below. [Reproduced with permission of Ed Friedlander (KCUMB)] I. .................................................................................................................................. II. ................................................................................................................................. (2) IB Questionbank Biology 98 (c) Outline the control of the secretion of gastric juice by nerves and hormones. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (4) (Total 8 marks) IB Questionbank Biology 99 106. Explain, with the use of a diagram, the role of the Bohr shift in the supply of oxygen to respiring heart muscle. ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ (Total 6 marks) IB Questionbank Biology 100 107. What does the nucleus of a human lymphocyte contain? A. Only the genes to produce a specific antigen B. Only the genes to produce a range of antibodies C. Only the genes that control the growth and development of a lymphocyte D. The whole genetic information for a human (Total 1 mark) 108. Which chamber of the heart has the thickest walls? A. Left atrium B. Right atrium C. Left ventricle D. Right ventricle (Total 1 mark) 109. What causes air to be breathed out by the lungs? A. The diaphragm relaxes and the ribs fall. B. The ribs rise and the external intercostal muscles relax. C. The internal intercostal muscles contract and the ribs rise. D. The diaphragm contracts and internal intercostal muscles contract. (Total 1 mark) IB Questionbank Biology 101 110. What causes the formation of a nerve impulse on the post-synaptic membrane? A. Ca2+ binding with a receptor site B. K+ leaking into the post-synaptic membrane C. Neurotransmitter binding with receptor sites D. Neurotransmitter being removed from the synapse (Total 1 mark) 111. What is the difference between the origin of type I and type II diabetes? Type I Type II A. caused by an autoimmune reaction target cells fail to respond to insulin B. occurs in adults only starts in childhood C. too much insulin secreted too little insulin secreted D. caused by dietary problems caused by hereditary factors (Total 1 mark) IB Questionbank Biology 102 112. The following diagram shows the human female reproductive system as seen from the side. [This article was published in Jones, R and Lopez, K. 2006. Human Reproductive Biology. Third Edition. Academic Press. P. 52. Copyright Elsevier 2006.] What are the names of the organs labelled I and II? I II A. uterus vagina B. bladder ovary C. urethra oviduct D. clitoris cervix (Total 1 mark) IB Questionbank Biology 103 113. The hormones progesterone and LH were measured in a woman’s blood over 40 days. When did her menstrual bleed start? (Total 1 mark) 114. Up to two additional marks are available for the construction of your answers. (2) (a) State four molecules transported by the blood. (4) (b) Outline the control of the heartbeat. (6) (c) Discuss the cause, transmission and social implications of AIDS. (8) (Total 20 marks) IB Questionbank Biology 104 115. Rickets, caused by a defective vitamin D receptor (VDR), can be prevented by high calcium intake. A series of experiments were performed to test this. The results are shown in the graphs. Graph A shows the change in blood calcium levels after calcium administration in normal mice with and without addition of vitamin D. It also shows the change in blood calcium levels in mutant mice, which lack the vitamin D receptor. Graph B shows the change in blood calcium levels after calcium administration in normal mice after being subjected to one week of low, medium and high calcium diets. [Cromphaut et al. November 6, 2001. “Duodenal calcium absorption in vitamin D receptor–knockout mice: Functional and molecular aspects.” PNAS. Vol 98, issue 23. Copyright (2001) National Academy of Sciences, USA.] IB Questionbank Biology 105 (a) State the change in blood calcium levels in normal mice 10 minutes after the administration of calcium, with and without the addition of vitamin D. With vitamin D: .......................................................................................................... Without vitamin D: ..................................................................................................... (1) (b) Compare the changes in blood calcium levels in normal mice and in mutant mice after the administration of calcium. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (2) (c) Explain, using graph B, the changes in blood calcium levels for the mice with different diets. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (2) IB Questionbank Biology 106 (d) Discuss whether the scientists were able to support their hypothesis that rickets caused by the defective vitamin D receptor can be prevented by the intake of large amounts of calcium. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (2) (Total 7 marks) 116. (a) (i) Outline the function of the appetite control centre in the brain. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (3) (ii) Outline the implications for the health of a person who has a BMI of 16 kg m–2. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (1) IB Questionbank Biology 107 (b) List, by completing the table below, the differences between human milk and artificial milk when feeding babies. Component sugar Human milk Artificial milk lactose protein antibodies soya protein present (3) (Total 7 marks) 117. Discuss the consequences of products with high food miles. ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ (Total 4 marks) IB Questionbank Biology 108 118. Marine biologists tested the possible adaptations in skeletal muscles to maintain aerobic metabolism under hypoxic (low oxygen) conditions. Samples were collected from swimming and non-swimming muscles of the following Pinnipeds: sea lions (Eumetopias jubatus), fur seals (Callorhinus ursinus) and harbour seals (Phoca vitulina). The sampled muscles were measured for concentration of mitochondria. The activity of β-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase (HAD), an enzyme used for the oxidation of fatty acids used in respiration, was assessed at different concentrations of mitochondria. [Source: S B Kanatous et al. 1999. “High aerobic capacities in the skeletal muscles of pinnipeds: adaptations to diving hypoxia.” Journal of American Physiological Society. Vol 8750. Pp 1247–1256. © Am Physiol Soc, used with permission] IB Questionbank Biology 109 (a) State the general relationship between concentration of mitochondria and the activity of HAD. ...................................................................................................................................... (1) (b) Distinguish between the non-swimming muscles of sea lions and the non-swimming muscles of fur seals. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (2) (c) Compare swimming muscles and non-swimming muscles in Pinnipeds. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (2) IB Questionbank Biology 110 (d) Studies of harbour seals led to the hypothesis that stores of fats (triglycerides) may play an important role in ATP production, especially during diving. Discuss this hypothesis using the data provided. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (3) (Total 8 marks) 119. (a) Label the parts of the following micrograph of the striated muscle. [Coen A.C. Ottenheijm, Leo M.A. Heunks and Richard P.N. Dekhuijzen(2008) Diaphragm adaptations in patients with COPD. _Respiratory Research_, 9(12), doi:10.1186/1465-9921-9-12. © 2008 Ottenheijm _et al._; licensee BioMed Central Ltd.] I. .................................................................................................................................. II. ................................................................................................................................. III. ................................................................................................................................ (3) (b) Outline the effect of training on vital capacity. IB Questionbank Biology 111 ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (1) (Total 4 marks) 120. (a) Outline the effects of moderate-intensity exercise and high-intensity exercise on muscle fibres and heart rate. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (2) (b) Evaluate the risks and benefits of using blood transfusions to improve performance in sports. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (4) (Total 6 marks) IB Questionbank Biology 112 121. (a) Label the parts of the reflex arc shown below. (3) (b) Explain how decision-making is influenced by the central nervous system (CNS). ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (3) (Total 6 marks) IB Questionbank Biology 113 122. What are the names of the organs labelled I and II in the diagram below? I II A. pancreas liver B. small intestine large intestine C. gall bladder pancreas D. esophagus stomach (Total 1 mark) 123. Where in a cell are antigens found? A. In the nucleus B. In the cytoplasm C. In the plasma membrane D. On the surface of the Golgi apparatus (Total 1 mark) IB Questionbank Biology 114 124. Which feature maintains a high concentration gradient of gases in the ventilation system? A. Thin-walled alveoli B. Thin-walled capillaries C. A moist lining of the alveoli D. Blood flowing in the capillaries (Total 1 mark) 125. What is the correct sequence of factors involved in blood clotting? A. platelets B. clotting factors → C. platelets D. clotting factors → → clotting factors → platelets fibrin → fibrinogen → fibrinogen → fibrin → clotting factors → fibrinogen → fibrin platelets → fibrin → fibrinogen (Total 1 mark) 126. How do vaccines give immunity to infectious diseases? A. They kill pathogenic microbes. B. They produce an immune response. C. They contain antibodies against pathogens. D. They inhibit the antigen-antibody reaction. (Total 1 mark) IB Questionbank Biology 115 127. What are the names of the two structures labelled I and II in the arm joint diagram below? I II A. biceps radius B. biceps humerus C. triceps humerus D. triceps ulna (Total 1 mark) 128. What does the reabsorption of glucose in the proximal tubules of the kidney require? A. Movement of water by osmosis out of the tubule cells B. Facilitated diffusion of Na+ out of the tubule cells C. Active transport of K+ into the tubule cells D. Active transport of Na+ out of the tubule cells (Total 1 mark) IB Questionbank Biology 116 129. What is the role of FSH in spermatogenesis? A. It stimulates the secretion of testosterone from the Sertoli cells. B. It inhibits the secretion of testosterone from the interstitial cells. C. It stimulates the action of testosterone on the Sertoli cells. D. It stimulates the secretion of LH from the pituitary cells. (Total 1 mark) 130. What is the difference between spermatogenesis and oogenesis? Spermatogenesis Oogenesis A. final cells are a similar size final cells are not all the same size B. cells produced are undifferentiated cells produced are differentiated C. spermatogenesis begins in a boy at birth oogenesis begins in a girl before she is born D. one germinal epithelium cell produces four sperm cells in a testis one germinal epithelium cell produces one oocyte in the ovary (Total 1 mark) 131. (a) Define the term passive immunity. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (1) (b) State one use of monoclonal antibodies in diagnosis. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (1) IB Questionbank Biology 117 (c) Define the term pathogen. ...................................................................................................................................... (1) (d) Outline why antibiotics are effective against bacteria but not against viruses. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (2) (Total 5 marks) 132. Up to two additional marks are available for the construction of your answers. (2) (a) Draw a labelled diagram of a mature sperm cell. (4) (b) Outline the role of hormones in the menstrual cycle. (6) (c) Discuss the cause, transmission and social implications of AIDS. (8) (Total 20 marks) IB Questionbank Biology 118 133. Alcohol is known to increase the risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD). An investigation was undertaken to look at the effects of drinking different amounts of alcohol in men and women. C-reactive protein (CRP), fibrinogen and total white blood cell count (WBC) were measured. These are markers that can be used to measure the risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD). Samples were taken from populations in three different countries and their drinking habits were determined and their blood was analysed. [Imhof, A, Woodward, M, Doering, A, Helbecque, N, Loewel, H, Amouyel, P, Lowe, G D O, and Koenig, W. 2004. “Overall alcohol intake, beer, wine, and systemic markers of inflammation in western Europe: results from three MONICA samples (Augsburg, Glasgow, Lille)”. European Heart Journal. Vol 25. Pp 2092–2100. By permission of Oxford University Press.] IB Questionbank Biology 119 (a) State the overall trend for CRP for men and women over the range of alcohol consumption. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (1) (b) Evaluate, using all the data, whether drinking small amounts of alcohol reduces the risk of CVD. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (3) (c) Deduce which is the best marker to measure the risk of CVD. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (1) (d) Outline atherosclerosis and the causes of CVD. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (2) (Total 7 marks) IB Questionbank Biology 120 134. (a) Label the section of healthy liver tissue below. [Photo by Paul Billiet. Reproduced with permission.] I. .................................................................................................................................. II. ................................................................................................................................. III. ................................................................................................................................ (3) (b) Outline two roles of the liver. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (2) IB Questionbank Biology 121 (c) List two materials that are not absorbed but are egested by the body. 1. .................................................................................................................................. 2. .................................................................................................................................. (1) (d) State an example of a protein hormone. ...................................................................................................................................... (1) (Total 7 marks) 135. Explain the oxygen dissociation curves of adult hemoglobin, fetal hemoglobin and myoglobin. ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ (Total 6 marks) IB Questionbank Biology 122 136. Which of the following parts of the digestive system secrete proteases? Stomach Small Intestine Large Intestine A. Yes Yes Yes B. Yes No Yes C. Yes No No D. No No No (Total 1 mark) 137. Why are antibiotics effective against bacteria but not viruses? A. Viruses can hide inside host cells. B. Bacteria are recognized as pathogens but viruses are not. C. The enzymes of bacteria can be inhibited by antibiotics. D. Viruses are resistant to antibiotics. (Total 1 mark) 138. What feature of alveoli adapts them to efficient gas exchange? A. They have muscles which pump air in and out regularly. B. Their membranes are more permeable to gases than water. C. A constant blood supply flows through them. D. A dense network of capillaries surrounds them. (Total 1 mark) IB Questionbank Biology 123 139. On the diagram of the motor neurone shown below, which label identifies a dendrite? (Total 1 mark) 140. The diagram below represents the homeostatic control of body temperature. What does the part labelled X represent? A. Heart B. Kidney C. Pituitary D. Hypothalamus (Total 1 mark) IB Questionbank Biology 124 141. What is the correct sequence of events used in IVF? A. collection of oocytes and sperms stimulation of ovarian follicles incubation of oocytes and sperms implantation B. stimulation of ovarian follicles collection of oocytes and sperms incubation of oocytes and sperms implantation C. stimulation of ovarian follicles incubation of oocytes and sperms collection of oocytes and sperms implantation D. collection of oocytes and sperms incubation of oocytes and sperms stimulation of ovarian follicles implantation (Total 1 mark) 142. Which structure releases glucagon? A. α cells of the pancreas B. β cells of the pancreas C. Liver cells D. Hypothalamus (Total 1 mark) 143. Which event directly leads to an action potential? A. Fusion of vesicles with the pre-synaptic membrane B. Diffusion of neurotransmitter across the synaptic cleft C. Membrane potential reaches the threshold potential D. Breakdown of the neurotransmitter (Total 1 mark) IB Questionbank Biology 125 144. Which muscle action is associated with an increase in the volume of the thoracic cavity during inspiration? A. The diaphragm contracts. B. The external intercostal muscles relax. C. The internal intercostal muscles contract. D. The abdominal muscles contract. (Total 1 mark) 145. Which term describes a molecule capable of triggering an immune response? A. Antibody B. Antigen C. Pathogen D. Antibiotic (Total 1 mark) 146. What is the main function of the large intestine? A. Absorption of water B. Digestion of fats and proteins C. Absorption of nutrients D. Recycling of digestive enzymes (Total 1 mark) IB Questionbank Biology 126 147. What is placed into the uterus after the process of in vitro fertilization (IVF)? A. Eggs B. Sperm C. Embryos D. Fetuses (Total 1 mark) 148. Distinguish between type I and type II diabetes. ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ (Total 3 marks) 149. Up to two additional marks are available for the construction of your answers. (2) (a) Draw a labelled diagram to show the structure of a membrane. (5) (b) Outline how vesicles are used to transport materials secreted by a cell. (6) (c) Explain how the structure of a villus in the small intestine is related to its function. (7) (Total 20 marks) 150. Up to two additional marks are available for the construction of your answers. (2) IB Questionbank Biology 127 (a) Draw a labelled diagram of the heart showing the chambers, associated blood vessels and valves. (4) (b) Describe the relationship between the structure and function of blood vessels. (6) (c) Explain the mechanisms involved in the ventilation of the lungs. (8) (Total 20 marks) 151. Up to two additional marks are available for the construction of your answers. (2) (a) Draw a labelled diagram of the adult female reproductive system. (4) (b) Describe how natural selection leads to evolution. (6) (c) Explain the consequences of altering a DNA base in the genome of an organism. (8) (Total 20 marks) IB Questionbank Biology 128 152. One recommendation for a healthy diet is to decrease the intake of saturated fatty acids. However, the relative benefit of replacing them with monounsaturated fatty acids, polyunsaturated fatty acids, or carbohydrates is still being debated. Diets with the same energy value, but rich in different fatty acids or carbohydrates, were fed to mice. The table below shows the composition of plasma triglycerides, cholesterol, very low density lipoprotein (VLDL), low density lipoprotein (LDL) and high density lipoprotein (HDL) in the diets. Mean plasma concentration / mg dl–1 Diet rich in: Triglycerides Cholesterol VLDL LDL HDL Saturated fatty acids 221 1014 373 608 90 Monounsaturated fatty acids 346 1834 831 788 84 Polyunsaturated fatty acids 101 801 242 526 89 Carbohydrates 178 1518 672 744 93 [Merkel, M et al. 2001. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. Vol 98. Pp 13 294–13 299. Copyright 2001, National Academy of Sciences, USA.] (a) State which diets increase the levels of cholesterol more than a diet rich in saturated fatty acids. ...................................................................................................................................... (1) (b) Calculate the percentage increase in VLDL when changing from a diet rich in saturated fatty acids to a diet rich in carbohydrates. ...................................................................................................................................... (1) (c) Compare a diet rich in saturated fatty acids and a diet rich in monounsaturated fatty acids. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (2) IB Questionbank Biology 129 (d) Evaluate the hypothesis that changing from a diet rich in saturated fatty acids to a diet rich in polyunsaturated fatty acids is healthy. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (3) (Total 7 marks) 153. (a) State one food source rich in vitamin D. ...................................................................................................................................... (1) (b) Outline how appetite is controlled. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (3) (Total 4 marks) 154. (a) (i) State one cause of type II diabetes. ........................................................................................................................... (1) IB Questionbank Biology 130 (ii) List two symptoms in a patient with type II diabetes. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (2) (b) Explain how a special diet can reduce the consequences of phenylketonuria (PKU). ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (4) (Total 7 marks) IB Questionbank Biology 131 155. At high altitude the optimum oxygen saturation of hemoglobin is harder to achieve due to the decrease in air pressure. The effects of lack of oxygen (hypoxia) and of altitude were studied in a group of men. The arterial lactate concentrations were measured during bicycle exercise under four different conditions. Location / altitude in Copenhagen (0 m at sea level) on Mount Chacaltaya, in Bolivia (5260 m above sea level) Oxygen conditions breathing normal air (normoxia) breathing an air mixture containing low levels of O2 (hypoxia) breathing a gas mixture with high levels of O2, allowing normal hemoglobin saturation (normoxia) after nine weeks of acclimatization breathing normal mountain air (hypoxia) [Adapted from van Hall, G et al. 2001. “The re-establishment of the normal blood lactate response to exercise in humans after prolonged acclimatization to altitude”. Journal of Physiology, Vol 536, issue 3. Pp 963–975. Reproduced with permission from Wiley] (a) State the arterial lactate concentration measured at 0 m (sea level) with normoxia when exercise intensity is high. ...................................................................................................................................... (1) IB Questionbank Biology 132 (b) State the effect of increasing exercise intensity on the arterial lactate concentration. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (1) (c) Explain how altitude and oxygen concentration affect the arterial lactate concentration at high exercise intensity. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (3) (d) Outline the fate of the lactate after the exercise has finished. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (2) (Total 7 marks) 156. (a) Label the parts of the sarcomere indicated below. (2) IB Questionbank Biology 133 (b) (i) Distinguish between fast muscle fibres and slow muscle fibres. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (2) (ii) Discuss the need for warm-up routines. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (3) (Total 7 marks) 157. (a) Define the term vital capacity. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (1) IB Questionbank Biology 134 (b) Evaluate the risks and benefits of using EPO (erythropoietin) to improve performance in sports. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (3) (Total 4 marks) IB Questionbank Biology 135 158. What are the structures labelled I and II on the diagram of the male reproductive system? I II A. Testis Seminal vesicle B. Vas deferens Testis C. Seminal vesicle Epididymis D. Seminal vesicle Prostate gland (Total 1 mark) 159. What is the function of the tRNA activating enzyme? A. It links tRNA to ribosomes. B. It links tRNA to mRNA. C. It links tRNA to a specific amino acid. D. It links an amino acid on one tRNA to an amino acid on another tRNA. (Total 1 mark) IB Questionbank Biology 136 160. What is required to produce monoclonal antibodies? A. T-lymphocytes and oocytes B. T-lymphocytes and early embryo cells C. B-lymphocytes and tumour cells D. B-lymphocytes and stem cells (Total 1 mark) 161. What does label X indicate? A. Sarcolemma B. Sarcomere C. Sarcoplasmic reticulum D. Endoplasmic reticulum (Total 1 mark) IB Questionbank Biology 137 162. Which processes are required for the reabsorption of glucose in the kidney tubules? I. Simple diffusion II. Facilitated diffusion III. Active transport A. I and II only B. II and III only C. I and III only D. I, II and III (Total 1 mark) 163. What is the role of testosterone in spermatogenesis? A. It stimulates interstitial cells. B. It stimulates Sertoli cells. C. It inhibits the germinal epithelium. D. It inhibits the prostate gland. (Total 1 mark) 164. What is the role of HCG in early pregnancy? A. HCG stimulates FSH secretions. B. HCG stimulates the degeneration of the corpus luteum. C. HCG stimulates ovarian estrogen and progesterone secretion. D. HCG stimulates uterine contractions. (Total 1 mark) IB Questionbank Biology 138 165. Which structure releases glucagon? A. α cells of the pancreas B. β cells of the pancreas C. Liver cells D. Hypothalamus (Total 1 mark) 166. When a pathogen is ingested by a phagocyte, which event occurs first? A. T-cell activation B. Memory cell proliferation C. Antigen presentation by the phagocyte D. B-cell activation (Total 1 mark) 167. Which of the following describes arteries? A. They have thick muscular walls. B. They usually contain valves. C. They carry blood towards the heart. D. They carry blood from the lungs. (Total 1 mark) IB Questionbank Biology 139 168. What is the main function of the large intestine? A. Absorption of water B. Digestion of fats and proteins C. Absorption of nutrients D. Recycling of digestive enzymes (Total 1 mark) 169. In the following diagram of the kidney, which structure contains urine? (Total 1 mark) 170. Which structure is acted upon by ADH (vasopressin)? A. Proximal convoluted tubule B. Bowman’s capsule C. Loop of Henle D. Collecting duct (Total 1 mark) IB Questionbank Biology 140 171. Which of the cells labelled in the diagram below provides nourishment for developing sperm cells? [Source: Freeman & Bracegirdle, An Atlas of Histology, (Heinemann: 1976) p. 91, Copyright holder unknown.] (Total 1 mark) 172. What structure within muscle tissue is surround by membrane and has multiple nuclei? A. Muscle bundle B. Muscle fibre C. Myofibril D. Sarcomere (Total 1 mark) 173. (a) Outline a possible cause of Down syndrome. (4) (b) Outline the processes involved in oogenesis within the human ovary. (8) (c) Discuss the ethical issues surrounding IVF. (6) IB Questionbank Biology 141 (Total 18 marks) 174. Up to two additional marks are available for the construction of your answers. (2) (a) Outline how antibiotic resistance in bacteria can arise in response to environmental change. (5) (b) Outline the principle of immunity. (6) (c) Discuss the benefits and dangers of vaccination. (7) (Total 20 marks) 175. Up to two additional marks are available for the construction of your answers. (2) (a) Draw a labelled diagram of the adult female reproductive system. (4) (b) Outline the roles of progesterone and estrogen in the human menstrual cycle. (6) (c) Explain the function and structure of the placenta. (8) (Total 20 marks) IB Questionbank Biology 142 176. Up to two additional marks are available for the construction of your answers. (2) (a) Draw a labelled diagram of the heart showing the chambers, associated blood vessels and valves. (4) (b) Describe the processes involved in blood clotting. (6) (c) Discuss the benefits and risks associated with vaccination programmes. (8) (Total 20 marks) IB Questionbank Biology 143 177. Sixteen women were studied to evaluate blood glucose and blood lactate levels while exercising at sea level and at high altitude, 4300 m above sea level. [Source: Barry Braun et al. 2000. “Women at altitude: carbohydrate utilization during exercise at 4,300 m”. Journal of Applied Physiology. Vol 88, issue 1. Pp 246–256 (Figure 6). © American Physiological Society. Reproduced with permission.] IB Questionbank Biology 144 (a) (i) Calculate the percentage increase in blood lactate concentration after 30 minutes of exercise at 4300 m. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (1) (ii) Suggest a reason for the difference in blood lactate concentration between women exercising at sea level and at high altitude. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (1) (b) Describe the variation in the blood glucose and lactate concentrations in the women at sea level. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (2) (c) Analyse the effect of high altitude on the blood glucose and lactate levels. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (3) (Total 7 marks) IB Questionbank Biology 145 178. (a) Outline mechanisms used by the ileum to absorb amino acids. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (2) (b) State two materials which are not absorbed in the ileum. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (1) (Total 3 marks) 179. (a) Outline factors that affect the incidence of coronary heart disease. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (5) IB Questionbank Biology 146 (b) Discuss the roles of gastric acid and Helicobacter pylori in the development of stomach ulcers and cancers. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (5) (Total 10 marks) IB Questionbank Biology 147 180. The effects of lack of oxygen (hypoxia) and of altitude were studied in a group of men. The group was measured for weight, amount of hemoglobin in the blood, maximum oxygen uptake and maximum power output during bicycle exercise both at sea level and at 5260 m. The conditions at each location are described in the following table. Location / altitude in Copenhagen (0 m at sea level) on Mount Chacaltaya, in Bolivia (5260 m above sea level) Oxygen conditions breathing normal air (normoxia) breathing an air mixture containing low levels of O2 (hypoxia) breathing a gas mixture with high levels of O2, allowing normal hemoglobin saturation (normoxia) after nine weeks of acclimatization breathing normal mountain air (hypoxia) The results of the study are shown in the table below. Copenhagen altitude = 0 m Mount Chacaltaya altitude = 5260 m normoxia hypoxia normoxia hypoxia Hemoglobin / g dl–1 14.3 – – 18.7 Maximum oxygen uptake / l min–1 4.3 2.7 – 2.8 Maximum oxygen uptake per body mass ml min–1/ kg body mass–1 56.0 35.0 – 40.0 Maximum power output / W 339.0 233.0 332.0 245.0 4.6 3.1 4.8 3.6 Maximum power output (W) / kg body mass–1 [Source: van Hall, G, Calbet, J A L, Søndergaard, H, and Saltin, B. 2001. “The re-establishment of the normal blood lactate response to exercise in humans after prolonged acclimatization to altitude”. Journal of Physiology. Vol 536, issue 3. Pp 963–975 (Table 1, p. 965). © Wiley-Blackwell (on behalf of The Physiological Society). Reproduced with permission] (a) Identify which conditions of altitude and oxygen levels permit the least maximum oxygen uptake per minute. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (1) IB Questionbank Biology 148 (b) Calculate the percentage change in maximum oxygen uptake per body mass from conditions of normoxia at 0 m to hypoxia at 5260 m altitude. Show your working. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (2) (c) Analyse the data to determine which conditions permit the greatest power output per kilogram of body mass. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (2) (d) Suggest why the amount of hemoglobin changes under the different conditions. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (1) (e) Explain two adaptations of the body to high altitude conditions other than hemoglobin increase. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (2) (Total 8 marks) IB Questionbank Biology 149 181. (a) Distinguish between the mode of action of steroid hormones and protein hormones. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (2) (b) State the major role of Helicobacter pylori in the development of stomach ulcers. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (1) (Total 3 marks) 182. (a) Outline two factors that affect the incidence of coronary heart disease. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (4) IB Questionbank Biology 150 (b) Explain the liver damage caused by excessive alcohol consumption. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (5) (Total 9 marks) 183. Which part of the brain has a role in the control of the heartbeat and how are messages passed from this part of the brain to the heart? Part of the brain Type of message A. hypothalamus hormone B. hypothalamus nerve C. medulla hormone D. medulla nerve (Total 1 mark) IB Questionbank Biology 151 184. What stimulates the production of antibodies? A. AIDS B. Antibiotics C. Anticodons D. Antigens (Total 1 mark) 185. What change occurs to the pressure and volume of the lungs when the external intercostal muscles contract? A. Both pressure and volume increase. B. Pressure increases and volume decreases. C. Pressure decreases and volume increases. D. Both pressure and volume decrease. (Total 1 mark) IB Questionbank Biology 152 186. The graph below shows changes in membrane potential in an axon during the passage of an action potential. What is causing the decrease in membrane potential at point X? A. Sodium ions entering the axon B. Potassium ions entering the axon C. Sodium ions leaving the axon D. Potassium ions leaving the axon (Total 1 mark) 187. What is a role of the hypothalamus in homeostasis? A. Monitoring body temperature B. Monitoring blood glucose concentration C. Secretion of glucagon D. Secretion of sweat (Total 1 mark) IB Questionbank Biology 153 188. What is the sequence of operations during IVF treatment? A. egg collection → FSH injections → fertilization B. egg collection → fertilization → FSH injections C. FSH injections → egg collection → fertilization D. FSH injections → fertilization → egg collection (Total 1 mark) 189. Researchers extracted an enzyme from the human digestive system and tested its activity at different pH values on proteins extracted from the blood of cows. The results are shown in the graph below. (a) Deduce from where in the human digestive system this enzyme was extracted. ...................................................................................................................................... (1) IB Questionbank Biology 154 (b) Outline the need for enzymes in the digestive system. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (2) (c) State one function of the large intestine. ...................................................................................................................................... (1) (d) Explain how the structure of the villus is adapted for absorption. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (3) (Total 7 marks) IB Questionbank Biology 155 190. The diagram below shows the female reproductive system. (a) Label the diagram above with the letter U to show the uterus. (1) (b) Outline the role of luteinizing hormone (LH) after ovulation. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (1) (c) Explain how sexual reproduction can lead to variation in a species. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (3) (Total 5 marks) 191. Up to two additional marks are available for the construction of your answers. (2) IB Questionbank Biology 156 (a) Draw a labelled diagram to show the human ventilation system. (4) (b) Outline anaerobic cell respiration in plant cells. (5) (c) Explain the concept of homeostasis, using the control of blood sugar as an example. (9) (Total 20 marks) 192. Zinc (Zn) is an important dietary nutrient. More than 200 enzymes that are dependent on zinc have been identified. One consequence of zinc deficiency is suppression of appetite, due to reduced sensitivity to tastes and smells. A recent study compared the presence of zinc in tissue and fluid samples collected from 15 patients with anorexia nervosa to that from 15 control patients. The results are shown in the graphs below. [© Journal of Orthomolecular Medicine http://www.orthomed.org/. Reprinted with permission] IB Questionbank Biology 157 (a) Compare the zinc content of scalp hair of the control group with that of the anorexia nervosa group. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (2) (b) Discuss whether whole blood zinc content of 6 μg g–1 would indicate that a person has anorexia nervosa. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (2) (c) Discuss whether dietary zinc supplementation would be an effective treatment for anorexia nervosa. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (2) IB Questionbank Biology 158 (d) Zinc is a mineral. Distinguish between a mineral and a vitamin. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (1) (e) State the body mass index (BMI) below which a person is considered to be underweight. ...................................................................................................................................... (1) (Total 8 marks) 193. (a) State one consequence of protein deficiency malnutrition. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (1) (b) Outline the reasons for increasing rates of clinical obesity in some countries. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (3) IB Questionbank Biology 159 (c) Discuss whether consumers should choose foods to minimize food miles. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (3) (Total 7 marks) 194. Outline the variation in the structure of fatty acids. ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ (Total 3 marks) IB Questionbank Biology 160 195. A build-up of hydrogen ions (H+) in muscles causes a condition known as acidosis. Anaerobic cell respiration of glucose in the muscles leads to the production of lactate and H+. One molecule of glucose is converted into two lactate ions and two H+ (a 1:1 ratio of lactate to H+). The development of acidosis during intense exercise has traditionally been explained by the increased production of lactate and H+ from the breakdown of glucose. This hypothesis has led to the interpretation that anaerobic cell respiration causes acidosis which leads to muscle fatigue during intense exercise. The graph below shows the quantities of H+ and lactate released from contracting muscles during vigorous exercise. [Source: Juel, C. 2004. “Effect of high-intensity intermittent training on lactate and H+ release from human skeletal muscle”. American Journal of Physiology – Endocrinology and Metabolism. Vol 286. Pp 245–251.] (a) Compare the rate of release of lactate with the rate of release of H+ in contracting muscles during vigorous exercise. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (2) IB Questionbank Biology 161 (b) Evaluate the hypothesis that acidosis in muscles is due entirely to H+ production as a result of anaerobic glucose breakdown. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (2) (c) Predict the results if the data had been collected beyond 12 minutes. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (2) (Total 6 marks) 196. (a) Draw a labelled diagram to show the structure of a skeletal muscle sarcomere. (3) IB Questionbank Biology 162 (b) Outline the role of myoglobin in muscle fibres. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (2) (Total 5 marks) 197. (a) Outline the relationship between the intensity of exercise and the proportions of carbohydrate and fat used in respiration. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (2) IB Questionbank Biology 163 (b) Compare the distribution of blood flow at rest and during exercise. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (2) (c) Discuss speed and stamina as measures of fitness. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (3) (Total 7 marks) IB Questionbank Biology 164 198. The diagram below shows parts of the human digestive system. Which points are linked by the small intestine? A. I and III B. II and III C. II and IV D. III and IV (Total 1 mark) 199. What is the consequence of insufficient secretion of FSH in women? A. Embryo implantation fails because the uterus lining is too thin. B. Mature eggs (oocytes) are not produced. C. Menstruation starts before embryo implantation occurs. D. Progesterone secretion is inhibited. (Total 1 mark) IB Questionbank Biology 165 200. Which cells activate helper T-cells by antigen presentation? A. B-cells B. Bacteria C. Macrophages D. Plasma cells (Total 1 mark) 201. What happens during muscle contraction? A. The number of light bands is reduced. B. The width of the dark bands is reduced. C. The lengths of the sarcomeres are reduced. D. Actin and myosin filaments coil up. (Total 1 mark) 202. The Bowman’s capsule is a cup-shaped structure that is part of the nephron. What is the source of glucose in the fluid in the Bowman’s capsule? A. Blood in the glomerulus B. Urine in the renal pelvis C. Filtrate in the distal convoluted tubule D. Interstitial fluid in the medulla (Total 1 mark) IB Questionbank Biology 166 203. The diagram below shows a human egg. What are the structures labelled I, II and III? I II III A. acrosomes zona pellucida follicle cells B. acrosomes cell wall sperm C. cortical granules cell wall sperm D. cortical granules zona pellucida follicle cells (Total 1 mark) IB Questionbank Biology 167 204. Type II diabetes is having an impact on the health of many individuals worldwide. The condition is characterized by elevated levels of both insulin and glucose in the bloodstream. Some animals produce an insulin-degrading enzyme (IDE) which breaks down the insulin molecule. In an attempt to develop a model of type II diabetes, genetically modified mice have been developed. In these mice, both copies of the IDE gene have been removed (IDE – / –) and the enzyme is not produced. The bar chart below shows the mean concentration of insulin in the bloodstream of IDE – / – mice and that of control mice (IDE + / +). [Source: Wesley Farris et al. 2003. “Insulin-degrading enzyme regulates the levels of insulin, amyloid B-protein, and the B-amyloid precursor protein intracellular domain in vivo”. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. Vol 100, issue 7. Pp 4162–4167. Copyright 2003 National Academy of Sciences, USA.] (a) Calculate the percentage increase between mean blood insulin levels in IDE + / + mice and those in IDE – / – mice. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (1) (b) Explain the difference in blood insulin concentrations between the two groups of mice. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (2) IB Questionbank Biology 168 In another experiment, groups of IDE – / – and IDE + / + mice were injected with a fixed amount of glucose. The levels of blood glucose were measured at various time intervals following glucose injection. The data are shown in the graph below. [Source: Wesley Farris et al. 2003. “Insulin-degrading enzyme regulates the levels of insulin, amyloid B-protein, and the B-amyloid precursor protein intracellular domain in vivo”. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. Vol 100, issue 7. Pp 4162–4167. Copyright 2003 National Academy of Sciences, USA.] (c) Distinguish between the response of the two groups of mice to the injection of glucose. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (2) IB Questionbank Biology 169 (d) Deduce, with a reason, whether transgenic IDE – / – mice are an appropriate model of type II diabetes. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (2) In animals that do not have type II diabetes, insulin stimulates glucose uptake into skeletal muscle. Glucose uptake into skeletal muscle is also stimulated when skeletal muscle is exercised. Genetically modified mice have been developed in which the insulin receptor is not produced in skeletal muscle and these are known as MIRKO mice. In another experiment, the effect of insulin and exercise on glucose uptake in skeletal muscle from control and MIRKO mice was examined. The results are shown in the bar chart below. [Republished with permission of the American Society for Clinical Investigation, from Jørgen F P Wojtaszewski, Yasuki Higaki, Michael F Hirshman, M Dodson Michael, Scott D Dufresne, C Ronald Kahn and Laurie J Goodyear. 1999. “Exercise modulates postreceptor insulin signaling and glucose transport in muscle-specific insulin receptor knockout mice”. Journal of Clinical Investigation. Vol 104, issue 9. Pp 1257–1264. Permission conveyed through Copyright Clearance Center, Inc.] (e) Explain the reason for the differences in insulin-stimulated glucose uptake between control mice and MIRKO mice. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (2) (f) Distinguish between the effects of insulin alone and exercise alone on glucose uptake in skeletal muscle of MIRKO mice. IB Questionbank Biology 170 ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (1) (g) Evaluate, using the data, whether exercise would be an appropriate therapy for human patients with type II diabetes. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (3) (h) State which cells secrete insulin and the organ in which they are located. Cells: ........................................................................................................................... Organ: ......................................................................................................................... (2) (i) State the name of one hormone other than insulin involved in the regulation of blood glucose. ...................................................................................................................................... (1) (Total 16 marks) IB Questionbank Biology 171 205. HIV was discovered in 1981 and is now one of the most serious causes of disease in the world. It causes the immune system to fail, leaving the patient vulnerable to other infections. (a) Distinguish between active immunity and passive immunity as a defence against disease. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (2) (b) Outline how monoclonal antibodies are produced. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (2) (c) Discuss how the HIV virus is transmitted. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (2) (d) Explain why antibiotics are ineffective against viruses. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (2) (Total 8 marks) IB Questionbank Biology 172 206. Up to two additional marks are available for the construction of your answers. (2) (a) Draw a labelled diagram to show the structure of a sarcomere. (4) (b) Outline how skeletal muscle contracts. (5) (c) Explain how nerve impulses are transmitted along and between neurons. (9) (Total 20 marks) 207. Up to two additional marks are available for the construction of your answers. (2) (a) Draw a labelled sigmoid population growth curve. (4) (b) Outline the process of spermatogenesis in humans. (5) (c) Explain the structure and function of the placenta during pregnancy. (9) (Total 20 marks) 208. Up to two additional marks are available for the construction of your answers. (2) (a) Outline the thermal, cohesive and solvent properties of water. (5) (b) Outline adaptations of xerophytes. (4) IB Questionbank Biology 173 (c) Explain the role of the kidney in maintaining water balance in humans. (9) (Total 20 marks) IB Questionbank Biology 174 209. Helicobacter pylori is able to live inside the stomach wall of humans. This bacterium can cause inflammation of the stomach wall (gastritis). There may be a link between H. pylori and the development of stomach cancer. The graph below shows the blood levels of antibodies resulting from H. pylori infection for a control group without stomach cancer and a group with stomach cancer. The solid lines show the median concentrations for the control group and the group with stomach cancer. Antibody concentrations above 10 μg ml–1 indicate that there has been infection with H. pylori. [Source: Forman, D. 1991. “Association between infection with Helicobacter pylori and risk of gastric cancer: evidence from a prospective investigation”. British Medical Journal. Vol 302. Pp 1302–1305.] IB Questionbank Biology 175 (a) 47 % of the control group had been infected with H. pylori. Calculate the percentage of the group with stomach cancer that had been infected. Show your working. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (2) (b) Using all of the data, evaluate the hypothesis that H. pylori causes stomach cancer. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (3) (c) A study in gerbils indicated that infection with H. pylori leads to a decrease in the secretion of hydrochloric acid. Discuss the consequences of this finding for the digestion of proteins in the stomach in humans. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (2) (Total 7 marks) IB Questionbank Biology 176 210. The electron micrograph below shows cells from the intestine. [Source: C Candalh, Inserm, magnification ×10 000] (a) In the electron micrograph above, state the name of the (i) structure labelled X. ........................................................................................................................... (1) (ii) type of cells labelled Y. ........................................................................................................................... (1) IB Questionbank Biology 177 (b) Define hormone. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (2) (c) Outline the circulation of blood through liver tissue. ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... (3) (Total 7 marks) IB Questionbank Biology 178 211. Explain how and why ventilation rate varies with exercise. ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ ................................................................................................................................................ (Total 6 marks) 212. What does the digestion of starch by amylase produce? A. Lactose B. Sucrose C. Galactose D. Maltose (Total 1 mark) IB Questionbank Biology 179 213. Which vessel carries deoxygenated blood? A. The coronary artery B. The pulmonary artery C. The aorta D. The pulmonary vein (Total 1 mark) 214. William Harvey discovered that blood flows away from the heart in arteries and back to the heart in veins. What hypothesis could be developed from this discovery? A. The human body contains both arteries and veins. B. Blood vessels link up arteries to veins. C. How blood moves from arteries into veins. D. Veins are connected to the left side of the heart and arteries to the right side. (Total 1 mark) 215. Which factors related to mucous membranes protect the body against microbes? I. Production of lysozyme II. Secretion of alkaline solutions III. Trapping of microbes A. I and II only B. II and III only C. I and III only D. I, II and III (Total 1 mark) IB Questionbank Biology 180 216. Capillaries surround the alveoli in the lungs. Which pair of statements correctly describes the concentrations of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the lungs? Oxygen Carbon dioxide A. Higher in the capillaries Higher in the alveoli B. Lower in the capillaries Higher in the alveoli C. Lower in the alveoli Higher in the capillaries D. Higher in the alveoli Higher in the capillaries (Total 1 mark) 217. What causes a resting potential to develop in a neuron? A. Diffusion of sodium and potassium ions B. Active transport of sodium and potassium ions C. Active transport of sodium and diffusion of chloride ions D. Active transport of potassium and diffusion of chloride ions (Total 1 mark) 218. What are the levels of the hormones estrogen, progesterone, LH and FSH during the menstrual cycle at the time of ovulation? Estrogen Progesterone LH FSH A. High Low High High B. High High Low High C. Low High High Low D. Low Low Low Low (Total 1 mark) IB Questionbank Biology 181 219. (a) List two roles of testosterone in males. 1. .......................................................................................................................... 2. .......................................................................................................................... (1) (b) A boy inherited red-green colour-blindness from one of his grandfathers. Deduce, giving your reasons, which of his two grandfathers was also colour-blind. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (3) (Total 4 marks) 220. Up to two additional marks are available for the construction of your answers. (2) (a) Draw and label a diagram of the digestive system. (4) (b) Discuss factors that affect enzyme activity. (9) (c) Outline one industrial use of lactase. (5) (Total 20 marks) IB Questionbank Biology 182 221. A study was conducted to investigate dietary changes in European Atlantic coast countries, USA and a broader group of 15 European nations. The graphs below show the dietary intake from plant and animal sources in 1961 and 2000. Dietary energy intake from Plant and Animal Origin, Total Availability – Year 1961 graph 1 Portugal Spain Belgium Norway Netherlands Denmark France UK Iceland USA 15 European Nations 0 2000 4000 6000 8000 kJ / person day–1 Key: Plant sources 10 000 12 000 14 000 Animal sources Dietary energy intake from Plant and Animal Origin, Total Availability – Year 2000 graph 2 Portugal Spain Belgium Norway Netherlands Denmark France UK Iceland USA 15 European Nations 0 2000 4000 6000 8000 10 000 12 000 14 000 kJ / person day–1 16 000 [Source: FAO, Global Perspectives Studies Group, ESDG, 2003] IB Questionbank Biology 183 (a) A commonly recommended daily intake of energy is 10 500 kJ day–1. Identify one country that did not reach this target in 1961. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (1) (b) State the country whose total dietary energy intake changed the least over the study period. ..................................................................................................................................... (1) (c) Compare dietary changes in the USA with the dietary changes that occurred in the group of 15 European nations. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (2) (d) Discuss why the incidence of coronary heart disease and obesity may be on the rise in the European Atlantic coast countries. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (3) (Total 7 marks) IB Questionbank Biology 184 222. (a) Distinguish between minerals and vitamins in terms of their chemical nature. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (2) (b) Explain the benefits of artificial supplementation of iodine in the diet. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (3) (Total 5 marks) 223. (a) Compare the energy content of carbohydrate, protein and fat. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (2) IB Questionbank Biology 185 (b) Outline the causes and symptoms of type II diabetes. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (4) (Total 6 marks) 224. As intensity of exercise increases, humans respond to the increased need for gas exchange in two ways: varying ventilation rate and varying tidal volume. Experimental data for a runner on a treadmill are shown below. 80 2.8 Tidal volume 2.6 Ventilation rate 70 2.2 60 2.0 50 1.8 40 1.6 Tidal Volume / litres Ventilation rate / min –1 2.4 1.4 30 1.2 1.0 16 .5 0 18 .0 0 .0 0 15 13 .5 0 .0 0 12 .5 0 10 9. 00 7. 50 20 Treadmill speed / km h –1 [Source: www.home.hia.no/~stephens/ventphys.htm] (a) Outline the relationship between treadmill speed and tidal volume. IB Questionbank Biology 186 (i) up to 14 km h–1 .......................................................................................................................... .......................................................................................................................... (1) (ii) above 14 km h–1 .......................................................................................................................... .......................................................................................................................... (1) (b) Compare the trend in ventilation rate with the trend in tidal volume at a high treadmill speed. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (1) (c) Calculate the total volume of air inhaled per minute when the treadmill speed is 15 km h–1. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (2) IB Questionbank Biology 187 (d) Suggest how the ventilation rate and tidal volume might alter if treadmill speed were increased even further. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (2) (Total 7 marks) 225. (a) Outline the functions of the (i) synovial fluid ........................................................................................................................... (1) (ii) joint capsule ........................................................................................................................... (1) (b) State the name of the structure that links muscle to bone. ..................................................................................................................................... (1) (c) Describe the injuries involved in a sprain. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (2) (Total 5 marks) IB Questionbank Biology 188 226. (a) Outline the role of ATP in muscle contraction. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (2) (b) Evaluate the effectiveness of dietary supplements containing creatine phosphate in enchancing performance in sports. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (4) (Total 6 marks) 227. (a) List two types of human sensory receptors. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (1) (b) Define the term contra lateral processing. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (1) (c) Outline the role of hair cells in the cochlea in the processing of sound. ..................................................................................................................................... IB Questionbank Biology 189 ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (3) (Total 5 marks) 228. (a) (i) List two examples of excitatory psychoactive drugs. 1. ....................................................................................................................... 2. ....................................................................................................................... (1) (ii) State one behavioural effect of THC (Tetrahydrocannabinol). ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (1) (b) Discuss the role of genetic predisposition and dopamine secretion in addiction. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (4) (Total 6 marks) 229. The diagrams show the death rate in January from influenza in Canada and the United Kingdom (UK). Canada is a very large, sparsely populated country. The United Kingdom is a densely populated island. IB Questionbank Biology 190 Death rate from infuenza per 100 000 inhabitants Canada 20 15 10 5 0 Jan 1951 Jan 1953 Jan 1955 Jan 1957 Jan 1959 Jan 1961 Jan 1963 Jan 1965 Jan 1967 Jan 1969 Jan 1971 Winter season Death rate from infuenza per 100 000 inhabitants United Kingdom 80 60 40 20 0 Jan 1951 Jan 1953 Jan 1955 Jan 1957 Jan 1959 Jan 1961 Jan 1963 Jan 1965 Jan 1967 Jan 1969 Jan 1971 Winter season [Source: G Vihoud, et al., (2006), Emerging Infectious Diseases, 12, (4), pages 661668] (a) (i) Identify the year in which there were no observed deaths from influenza in either country. ........................................................................................................................... (1) (ii) Calculate the total number of deaths from influenza in 1968 in Canada assuming the population size was 19.8 million. ........................................................................................................................... (1) (b) Compare the death rates between Canada and the United Kingdom between 1953 and 1963. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (3) (c) Influenza is caused by a virus. Outline the diversity of structure in viruses. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... IB Questionbank Biology 191 ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (2) (Total 7 marks) 230. What name is given to the molecules that bind to foreign proteins that enter the body? A. Antigens B. Antibodies C. Allergens D. Antibiotics (Total 1 mark) 231. Which muscles contract to cause air to pass out from the lungs through the bronchioles? A. Internal intercostal muscles and diaphragm B. Internal intercostal muscles and abdomen wall muscles C. External intercostal muscles and diaphragm D. External intercostal muscles and abdomen wall muscles (Total 1 mark) IB Questionbank Biology 192 232. The levels of hormones vary during the menstrual cycle in women. Each hormone reaches its maximum level at a different time in the cycle. In what sequence do the hormones reach their maximum level, if the cycle begins at the start of menstruation? A. LH, progesterone, FSH, estrogen B. FSH, progesterone, LH, estrogen C. LH, estrogen, FSH, progesterone D. FSH, estrogen, LH, progesterone (Total 1 mark) 233. How is in vitro fertilization different from natural fertilization in humans? A. In vitro fertilization involves artificial injection of sperm into the uterus B. In vitro fertilization only involves one parent C. In vitro fertilization happens outside the body D. In vitro fertilization uses stem cells instead of eggs (Total 1 mark) IB Questionbank Biology 193 234. Antibiotic peptides occur naturally on the surface of human skin. One of these peptides, called LL-37, and three other similar synthetic peptides were investigated to assess both their antibiotic properties and effect on human cells. The graphs show the antibiotic effect of the peptides against two microbes, S. aureus and C. albicans. The technique involves measuring the inhibition of growth of the microbes. S. aureus Amount of inhibition / arbitrary units 10 8 8 6 6 4 4 2 2 5 20 40 100 Key for peptides: C. albicans 10 LLG GKE FKR LL-37 5 Peptide concentration / mol dm 20 40 100 –3 [Source: T Sigurdardottir, et al., (2006), Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, 50 (9), pages 29832989] (a) Describe the effect of the FKR on C. albicans. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (2) (b) Compare the effects of the peptide LLG on S. aureus and C. albicans. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (2) IB Questionbank Biology 194 (c) Evaluate the effectiveness of LL-37 against the two microbes. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (3) DNA fragmentation / x-fold increase over control There is concern that the peptides could damage living human cells. One form of damage is fragmentation of DNA. Human cells were incubated for 16 hours with each peptide at varying concentrations. The amount of DNA fragmentation was measured. 25 20 15 10 5 0 2 6 20 80 LL-37 2 6 20 80 LLG 2 6 20 80 GKE 2 6 20 80 FKR Peptide concentration / mol dm–3 [Source: T Sigurdardottir, et al, (2006), Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, 50 (9), pages 29832989] (d) State which peptide causes the least damage to DNA. ..................................................................................................................................... (1) (e) Calculate the percentage increase in DNA damage that results when the concentration of LL-37 increases from 2 mol dm–3 to 6 mol dm–3. Show your working. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (2) (f) Discuss the hypothesis that synthetic peptides are most suitable for controlling S. aureus IB Questionbank Biology 195 infection inside the human body. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (4) The shape of the secondary structure of a peptide can be predicted from its amino acid composition. The figure shows the theoretical likelihood of the peptide LL-37 forming an -helix, based on the properties and position of its 37 amino acids. Possibility of forming α-helix / arbitrary units 15 10 5 0 10 20 30 Number of amino acids [Source: T Sigurdardottir, et al., (2006), Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, 50 (9), pages 2983–2989] (g) In addition to the -helix, state a type of shape commonly formed as the secondary structure of proteins. ..................................................................................................................................... (1) IB Questionbank Biology 196 (h) Analyse the data to determine the region of LL-37 most likely to form a helical shape. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (2) (i) Draw and label the structure of a peptide bond between two amino acids. (2) (Total 19 marks) 235. Up to two additional marks are available for the construction of your answers. (2) (a) Draw a labelled diagram showing the structure of a motor neurone. (4) (b) Outline how heartbeat is controlled as the body goes from rest to hard exercise. (6) (c) Explain how skeletal muscle contracts. (8) (Total 20 marks) 236. Up to two additional marks are available for the construction of your answers. (2) (a) Draw a labelled diagram showing the structure of the digestive system. (4) (b) Outline the need for enzymatic hydrolysis in the digestive process. (6) (c) Explain how the kidney prevents the body from losing important materials absorbed from the digestive system. (8) (Total 20 marks) IB Questionbank Biology 197 237. (a) Label the diagram of the human ear shown below. [Source: www.msjensen.gen.umn.edu/webanatomy_archive/wa_nervous/wa_ear_1.html] A : .................................................................... B : .................................................................... C : .................................................................... D : .................................................................... (2) (b) Define the term stimulus. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (1) IB Questionbank Biology 198 (c) Outline the sympathetic and parasympathetic control of the heart rate. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (4) (Total 7 marks) 238. The diagrams show the death rate in January from influenza in Canada and the United Kingdom (UK). Canada is a very large, sparsely populated country. The United Kingdom is a densely populated island. Death rate from infuenza per 100 000 inhabitants Canada 20 15 10 5 0 Jan 1951 Jan 1953 Jan 1955 Jan 1957 Jan 1959 Jan 1961 Jan 1963 Jan 1965 Jan 1967 Jan 1969 Jan 1971 Winter season Death rate from infuenza per 100 000 inhabitants United Kingdom 80 60 40 20 0 Jan 1951 Jan 1953 Jan 1955 Jan 1957 Jan 1959 Jan 1961 Jan 1963 Jan 1965 Jan 1967 Jan 1969 Jan 1971 Winter season [Source: G Vihoud, et al., (2006), Emerging Infectious Diseases, 12, (4), pages 661668] IB Questionbank Biology 199 (a) (i) Identify the year in which there were no observed deaths from influenza in either country. ........................................................................................................................... (1) (ii) Calculate the total number of deaths from influenza in 1968 in Canada assuming the population size was 19.8 million. ........................................................................................................................... (1) (b) Compare the death rates between Canada and the United Kingdom between 1953 and 1963. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (3) (c) Suggest two reasons for the differences in observed death rates in 1951 between Canada and the United Kingdom. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (2) (Total 7 marks) IB Questionbank Biology 200 239. (a) Describe the transmission of malaria. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (2) (b) Discuss the prion hypothesis. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (5) (Total 7 marks) IB Questionbank Biology 201 240. In North America normal diets are traditionally low in fibre. Scientists have proposed the hypothesis that people with diabetes benefit from a high fibre diet. The diagrams show the effect on blood glucose and blood insulin concentrations of a group of diabetic patients fed on a high fibre diet compared to a group of diabetic patients fed on a normal diet. The bars indicate standard error. [Source: M Chandalia, et al., The New England Journal of Medicine, (2000), 342, pages 13921398] (a) (i) Deduce, with a reason, what occurred at the times indicated by the arrows. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (1) IB Questionbank Biology 202 (ii) State the lowest blood glucose concentration in the normal diet. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (1) (b) Compare the variation, over a 24 hour period, in both the blood glucose and insulin concentrations in the high fibre group. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (2) (c) Evaluate the effect of the high fibre diet on lowering blood glucose and insulin levels in the two groups. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (3) (Total 7 marks) 241. (a) List three of the materials that are egested. ..................................................................................................................................... (1) IB Questionbank Biology 203 (b) Describe the process of erythrocyte and hemoglobin breakdown in the liver. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (4) (Total 5 marks) 242. (a) Distinguish between the mode of action of steroid and protein hormones. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (2) IB Questionbank Biology 204 (b) Explain the events of the cardiac cycle including systole, diastole and heart sounds. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (6) (Total 8 marks) IB Questionbank Biology 205