The Marshall Court and Growing Nationalism: A Cheat Sheet
advertisement

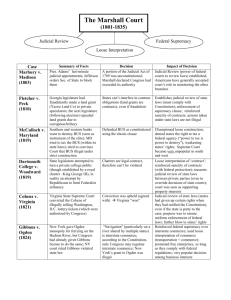
Vinluan Unit 3: The Early Republic The Marshall Court and Growing Nationalism: A Cheat Sheet (originally from Tom Sleet, Thomas Jefferson High School) FLETCHER v. PECK (1810) Issue: Yazoo Land Co./Georgia repeals land grant of previous (corrupt) legislature Ruling:Land grants are contracts/states may not impair the obligations of a contract Result: Georgia may not repeal Yazoo land grant/Court seen as supporting corrupt money interests Precedent: Sanctity of contracts protected/power of the court to overrule decisions of a state legislature when in conflict with the Constitution or federal laws/treaties Court Power: Judicial review of state laws—enforcement of “national supremacy clause” DARTMOUTH COLLEGE v. WOODWARD (1819) Issue: State legislature attempts to create a public college out of a private college established under a royal charter from George III (1769)—Webster argues case for Dartmouth Ruling:Land grants are contracts/states may not impair the obligations of a contract Result: Georgia may not repeal Yazoo land grant/Court seen as supporting corrupt money interests Precedent: Sanctity of contracts protected/power of the court to overrule decisions of a state legislature when in conflict with the Constitution or federal laws/treaties Court Power: Judicial review of state laws—enforcement of “national supremacy clause” MCCULLOCH v. MARYLAND (1819) Issue: Southern/Western states seek to destroy/limit the power of National Bank— Maryland seeks to tax bank business/destroy bank Ruling: Bank constitutional/necessary and proper clause/”power to tax is the power to destroy” Result: Constitutionality of Bank upheld/state tax of federal agency unconstitutional/Court very unpopular in South/West (Panic of 1819) Precedent: Loose interpretation of necessary and proper clause upheld/state cannot tax a federal institution Court Power: Judicial review of state power to tax COHENS v. VIRGINIA (1821) Issue: Virginia courts convicted Cohens for selling lottery tickets illegally. The state supreme court upheld the decision. Decision: Marshall and the court overturned it. Significance: Marshall asserted the right of the Supreme Court to review decisions of the state supreme courts in all questions involving the powers of the federal government. It was a significant blow to states rights and similar to Martin v. Hunter’s Lessee. Vinluan Unit 3: The Early Republic GIBBONS v. OGDEN (1824) Issue: New York gives Ogden a monopoly over Hudson River ferrying/federal Congress gives Gibbons license to ferry same/N. Y. Court rules Gibbons in violation of state law Ruling: “Navigation” is interstate commerce/state monopolies over interstate commerce null and void Result: Free enterprise promoted/state power to grant monopolies limited/popular Court decision makes Republican attacks against Court cease Precedent: Federal supremacy over interstate commerce enforced/loose interpretation of “commerce” established (transportation is commerce) Court Power: Federal government will regulate interstate commerce Questions to consider… 1. What political and economic trends are evident in the rulings of the Marshall Court? 2. What effect do these rulings have on the development and growth of the New Republic?