Judicial Nationalism and Marshall Court
advertisement

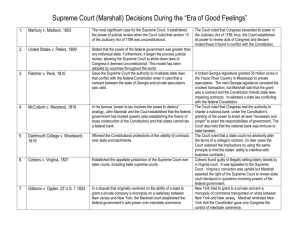
John Marshall and Judicial Nationalism…The Quiz. Write the letter of the best answer on the line provided. _____ 1. Which of the following statements does NOT accurately reflect Marshall’s term on the bench? a. Marshall examined cases from a Federalist philosophy, finding legal precedents to support Madison’s views. b. During the Jacksonian era, his decisions hampered democracy at a time when America was becoming much more democratic. c. His decisions strengthened the union and helped create a stable, nationally uniform environment for business. d. His decisions were another example of checks and balances, specifically against the excesses of popularly elected state legislatures. e. The federal government’s power over the states was greatly increased _____ 2. Which of the following pairs correctly reflects Marshall’s decisions upholding contract law. a. Fletcher v. Peck (1810) and Cohens v. Virginia (1821) b. Dartmouth College v. Woodward (1819) and Gibbons v. Ogden (1824) c. McCulloch v. Maryland (1819) and Fletcher v. Peck (1810) d. Dartmouth College v. Woodward (1819) and Fletcher v. Peck (1810) e. Martin v. Hunter’s Lessee (1816) and Gibbons v. Ogden (1824) _____ 3. The decision in Martin v. Hunter’s Lessee (1816) would be reflected in later controversies, including which one of the following? a. Jackson’s argument for killing the Bank of the United States, partly over the reckless speculation of the “wildcat” state banks. b. The passage of the Force Bill allowing Jackson to use force to collect tariff duties. c. The protection of contract law in Fletcher v. Peck d. Jackson’s ignoring the Supreme Court’s decision in Worcester v. Georgia and proceeding with the removal of Native American tribes from the South. e. Ignoring the Kentucky and Virginia Resolutions following the passage of the Alien and Sedition Acts. _____ 4. The decision in McCulloch v. Maryland (1819) would be rejected in later controversies, including which one of the following? a. Jackson’s argument for killing the Bank of the United States, partly over the reckless speculation of the “wildcat” state banks. b. The passage of the Force Bill allowing Jackson to use force to collect tariff duties. c. The protection of contract law in Fletcher v. Peck d. Jackson’s ignoring the Supreme Court’s decision in Worcester v. Georgia and proceeding with the removal of Native American tribes from the South. e. Ignoring the Kentucky and Virginia Resolutions following the passage of the Alien and Sedition Acts. _____ 5. Which of the following cases reflects a change in the power of the Federal government that was desperately needed during the era of the Articles of Confederation? a. Gibbons v. Ogden b. Cohens. v. Virginia c. Dartmouth College v. Woodward d. Fletcher v. Peck e. Worcester v. Georgia _____ 6. What was the significance in Fletcher v. Peck (1810)? a. The Court ruled the Constitution forbids states from “impairing contracts,” one of the earliest examples of the Court asserting its right to invalidate state laws. b. The Supreme Court rejected “compact theory” and state claims that they were equally sovereign with the federal government. c. It gave “loose construction” theory a major boost and argued the Constitution derived from the consent of the people, thus permitting the government to act for their benefit. d. Marshall ruled the Constitution conferred on Congress alone the right to control interstate commerce. e. While the decision safeguarded business from domination by the states, it set a precedent giving corporations the ability to escape government control. _____ 7. What was the significance of Marshall declaring the Bank of the United States constitutional in the case McCulloch v. Maryland (1819)? a. The Court ruled the Constitution forbids states from “impairing contracts,” one of the earliest examples of the Court asserting its right to invalidate state laws. b. The Supreme Court rejected “compact theory” and state claims that they were equally sovereign with the federal government. c. It gave “loose construction” theory a major boost and argued the Constitution derived from the consent of the people, thus permitting the government to act for their benefit. d. Marshall ruled the Constitution conferred on Congress alone the right to control interstate commerce. e. While the decision safeguarded business from domination by the states, it set a precedent giving corporations the ability to escape government control. _____ 8. What was the significance of the Court’s decision in Dartmouth College v. Woodward (1819)? a. The Court ruled the Constitution forbids states from “impairing contracts,” one of the earliest examples of the Court asserting its right to invalidate state laws. b. The Supreme Court rejected “compact theory” and state claims that they were equally sovereign with the federal government. c. It gave “loose construction” theory a major boost and argued the Constitution derived from the consent of the people, thus permitting the government to act for their benefit. d. Marshall ruled the Constitution conferred on Congress alone the right to control interstate commerce. e. While the decision safeguarded business from domination by the states, it set a precedent giving corporations the ability to escape government control. _____ 9. What was the significance of Gibbons v. Ogden -- 1824 ("steamboat case") (Blow to states' rights)? a. The Court ruled the Constitution forbids states from “impairing contracts,” one of the earliest examples of the Court asserting its right to invalidate state laws. b. The Supreme Court rejected “compact theory” and state claims that they were equally sovereign with the federal government. c. It gave “loose construction” theory a major boost and argued the Constitution derived from the consent of the people, thus permitting the government to act for their benefit. d. Marshall ruled the Constitution conferred on Congress alone the right to control interstate commerce. e. While the decision safeguarded business from domination by the states, it set a precedent giving corporations the ability to escape government control. _____ 10. Which of the following would be valid arguments about the importance of John Marshall’s tenure on the bench? a. Marshall examined cases from a Federalist philosophy, finding legal precedents to support Hamilton’s views. b. During the Jacksonian era, his decisions hampered democracy at a time when America was becoming much more democratic. c. His decisions strengthened the union and helped create a stable, nationally uniform environment for business. d. His decisions were another example of checks and balances, specifically against the excesses of popularly elected state legislatures. e. The federal government’s power over the states was greatly increased