A Guide to Past Tense Verbs
advertisement

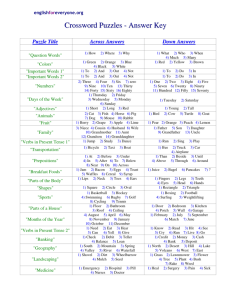
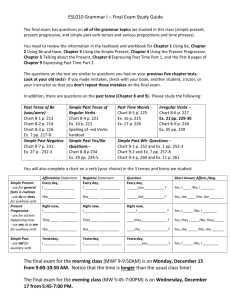
A Guide to Past Tense Verbs Presented By Delora, Kathy, and Clarine The word "tense" comes from Latin tempus, meaning time. In grammar, "tense" refers to the form of the verb itself: • Tense indicates completeness or continuance. If • the event is complete, it's past; if the event isn't complete, it's present. We use past tense (preteritum) to tell about something that happened at a specific time in the past, or to tell about something that happened repeatedly in the past. The simple past tense is one of the most common tenses in English. Its form is the same with all subjects. It is usually formed by adding -ED to the verb. This page will explain the rules for forming the tense with regular verbs. *The simple past tense regular verbs, are created just by adding -D or -ED. However, with some verbs, you need to also change the ending. Here are some examples: • Verb ending in e, Add –D live - lived • Consonant + y Change y to i, then add –ED try - tried • One vowel + one consonant (but NOT w or y) Double the consonant, then add –ED tap tapped commit – committed • [anything else] Add –ED boil – boiled , fill – filled When the verb in the independent clause is the past tense, the verb in the dependent clause is usually in a past tense as well. The past tenses are: the simple past, the past progressive, the past perfect, and the past perfect progressive. When you are writing about a subject, be sure to keep it in the same tense throughout your paper. Do This: • I saw a bear climb a tree, and then I wrote • • • about him. Jenny mixed the cake, while I whipped the frosting. Do Not Do This: I saw a bear climb a tree, and then I write about him. Jenny mixes the cake, while I whipped the frosting. The simple past tense • Last year, I traveled to Japan. • They never went to school; they always skipped. • I finished work, walked to the beach, and found a nice place to swim. In the simple past tense, negative and question forms are made using the auxiliary verb "do" (in its past form, "did") followed by the simple form of the main verb. This page explains the rules. • Simple past statement : I had a car. You ate my toast. • Informal negative : I didn't have a car. You didn't eat my toast. • Formal negative : I did not have a car. You did not eat my toast. The past perfect refers to a time earlier than before now. It is used to make it clear that one event happened before another in the past. It does not matter which event is mentioned first - the tense makes it clear which one happened first. • I had saved my document before the computer crashed. • When they arrived, we had already started cooking. • The train had just left when I arrived at the station. The past progressive tense is commonly used in English for actions which were going on (had not finished) at a particular time in the past. This page will explain the rules for forming the past progressive tense, and how it is used. Subject BE-ING FORM Examples: • • • • • I was singing. You were singing. He was singing. We were singing. They were singing. Definition: The Perfect Progressive tense is used to express the time that has elapsed between two points in time. The Past Perfect Progressive expresses the time elapsed between the beginning of a continuous action that began in the past and another point in time in the past. • The police had been looking for the robber for two months before they finally found him. • Before the budget cuts, the students had been participating in many extracurricular activities. Past Tense Verbs Regular versus Irregular How to Identify Them • • • • • • • • • * REGULAR VERBS: The regular verbs show past tense simply by adding “d” or “ed” such as: care becomes cared and talk becomes talked. This is also true of the past participles for regular verbs as there is no change in their spelling *Examples of regular verbs, (simple past): They played football all day. He pitched a perfect baseball game. Debbie cared for three babies. The children jumped rope until lunchtime. *Examples of regular verbs, (past participles with their helping verbs): They have played football all day. He has pitched a perfect baseball game. Debbie has cared for three babies. The children have jumped rope all day. Irregular Verbs • • • • • • • • • IRREGULAR VERBS: The irregular verbs are verbs that change in spelling to show their past tense. Mastering the spelling of these irregular verbs must be done by repetition and studying. Their past participle is usually another spelling of the verb and needs a helping verb such as: have, having, has or had. The main verb with the helping verb forms a perfect tense. *Examples of irregular verbs, (simple past): More customers ate here today than Saturday. Students spoke at the convention last month. The flowers grew beautifully in the garden. She drank all of the orange juice. *Examples of irregular verbs (past participles) with their helping verbs, (past perfect tense): More customers have eaten here today than Saturday. Students have spoken at the convention in the past. The flowers have grown beautifully in the garden. She has drunk all of the orange juice. Works Cited • Rodrigues, Dawn, and Myron C. Tuman. Writing Essentials. 2nd ed. New York: W. W. • • Norton and Co. Inc., 1999. Aaron, Jane E. The Little, Brown Essential Handbook for Writers. 2nd ed. New York: Addison-Wesley Educational Publishers, Inc., 1997. Boyd, Mark D. Personal interview. September 28, 2005. Works Cited “Past Perfect Progressive.” My English Teacher. 2002. 15 Dec. 2005 <www.myenglishteacher.net/past_perfect_progressive.html>. “Summary of Verb Tenses.” Leo Literacy Education Online. 22 Sept. 2000. 15 Dec. 2005. <http://leo.stcloudstate.edu/grammar/tenses.html>. "Forming the Simple Present Tense." English Language Center Study Zone. 1998-1999. 15 Dec. 2005. <http://web2.uvcs.uvic.ca/elc/studyzone/330/grammar/pres.htm>. Fulwiler ,Toby, Hayakawa, Alan R. The College Writer’s Reference 3rd Ed. 2001 Works Cited • Basic Rules Verbs: Past Tense. 2000. 15 Dec. 2005. <www.stolaf.edu/depts/norwegian/grammar/pasttense.htm>. • "Grammar, Punctuation and Spelling." Online Writing Lab. 2004. 15 Dec. 2005. <http://owl.english.purdue.edu/handouts/grammar/>. • “Online English Grammar.” edufind.com. 2005 15 Dec. 2000. <www.edufind.com/english/grammar/Tenses11.cfm>