Chapter 5 - Bakersfield College
advertisement

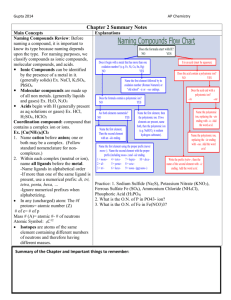
Chemistry B2A Chapter 5 Nomenclature Binary Compounds 1. Ionic compounds (a metal and a nonmetal) 2. Covalent compounds (two nonmetals) Binary Compounds 1. Ionic compounds (a metal and a nonmetal) Metals: lose 1, 2 or 3 e- Cation (Y+) Ions Nonmetals: gain 1, 2 or 3 e- Anion (X-) Number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus remains unchanged. Cation (Y+): Na+ Anion (X-): Cl- Li+ Ca2+ Al3+ F- O-2 1A 2A 3A 4A 5A 6A 7A 8A Transition elements Ionic bonds Metal-Nonmetal Na Na+ + e- Cl + e- Cl- Opposite charges attract each other. Cation Anion Sodium (Na) NaCl Chlorine (Cl) Type I Monatomic Cations Metal has only one type of cation (main group elements) International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) systematic names Name of the metal + “ion” H+ Li+ Hydrogen ion Lithium ion Ca2+ Al3+ Calcium ion Aluminum ion Type II Monatomic Cations Metal has two (or more) type of cations (transition elements) IUPAC or Systematic names Co2+ Co3+ Cobalt(II) ion Cobalt(III) ion Fe2+ Fe3+ Iron(II) ion Iron(III) ion Cu1+ Cu2+ Copper(I) ion Copper(II) ion Hg+ Hg2+ Mercury(I) ion Mercury(II) ion Pb2+ Pb4+ Lead(II) ion Lead(IV) ion Sn2+ Sn4+ Tin(II) ion Tin(IV) ion Type II Monatomic Cations Common name (old name) Name of the metal + “-ous” smaller charge “-ic” larger charge Cu1+ Cu2+ Copper(I) ion Copper(II) ion Hg+ Hg2+ Mercury(I) ion Mercury(II) ion Mercurous ion Mercuric ion Fe2+ Fe3+ Iron(II) ion Iron(III) ion Ferrous ion Ferric ion Sn2+ Sn4+ Tin(II) ion Tin(IV) ion Stannous ion Stannic ion Cuprous ion Cupric ion Naming Monatomic Anions Stem part of name + “-ide” Anion Stem name Anion name F- fluor Fluoride ion Cl- chlor Chloride ion Br- brom Bromide ion I- iod Iodide ion O2- ox Oxide ion S2- sulf Sulfide ion P3- phosph Phosphide ion N3- nitr Nitride ion matter are neutral (uncharged): total number of positive charges = total number of negative charges Na+ Cl- NaCl Ca2+ Cl- CaCl2 Al3+ S2- Al2S3 Ba2+ O2- Ba2O2 Molecule of NaCl BaO Formula of NaCl Naming Binary Ionic compounds Name of metal (cation) + Name of anion NaCl Sodium chloride CaO Calcium oxide Cu2O Copper(I) oxide CuO Copper(II) oxide Cuprous oxide Cupric oxide CsBr Cesium bromide MgS Magnesium sulfide FeCl2 Iron(II) chloride FeCl3 Iron(III) chloride Ferrous chloride Ferric chloride Binary Compounds 1. Ionic compounds (a metal and a nonmetal) 2. Covalent compounds (two nonmetals) Binary Compounds 2. Covalent compounds (two nonmetals) Naming Binary Covalent compounds (type III) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Mono – Di – Tri – Tetra – Penta – Hexa – Hepta – Octa – Nona – Deca prefix and full name of the first element in formula + prefix and the anion name of the second element + “ide” 1. Don’t use “mono” for the 1st element. Rules: 2. Drop the “a” when followed by a vowel. Naming Binary Covalent compounds (type III) NO2 Nitrogen dioxide N2O4 Dinitrogen tetroxide PCl5 Phosphorous pentachloride CCl4 Carbon tetrachloride S2O3 Disulfur trioxide SF6 Sulfur hexafluoride Binary Compounds Yes Metal present? No Type III Use prefixes Yes Does the metal form more than one cation? No Type I Use the element name for the cation Yes Type II Find the charge of the cation Use a Roman number after the element name. Naming Polyatomic Ionic Compounds They contain more than two elements. Naming Polyatomic Ions Cation: NH4+ Ammonium Anion: MnO4- Permanganate CrO42- Chromate OH- Hydroxide Cr2O72- Dichromate NO2- Nitrite CO32- Carbonate NO3- Nitrate HCO3- SO32- Hydrogen Carbonate (bicarbonate) Sulfite PO33- Phosphite SO42- Sulfate PO43- Phosphate HSO3- Hydrogen Sulfite (bisulfite) HPO42- Hydrogen phosphate HSO4- Hydrogen sulfate (bisulfate) H2PO4- Dihydrogen phosphate Oxyanions Polyatomic anions with different numbers of oxygen atoms. When we have two oxyanions in a series: Smaller number of oxygen atoms ends with –ite. Larger number of oxygen atoms ends with –ate. NO2- Nitrite NO3- Nitrate PO33- Phosphite SO32- Sulfite PO43- Phosphate SO42- Sulfate HPO42- Hydrogen phosphate HSO3- Hydrogen Sulfite (bisulfite) H2PO4- Dihydrogen phosphate HSO4- Hydrogen sulfate (bisulfate) Oxyanions When we have more than two oxyanions in a series: (Fewest oxygen atoms) Prefix hypo- (Most oxygen atoms) Prefix per- ClO- hypochlorite ClO2- chlorite ClO3- chlorate ClO4- perchlorate matter are neutral (uncharged): total number of positive charges = total number of negative charges Na+ NO3- NaNO3 Ca2+ CO32- Ca2(CO3)2 Al3+ SO42- Al2(SO4)3 Mg2+ NO2- Mg(NO2)2 Ca(CO3) Naming Polyatomic Ionic compounds Name of metal (cation) + Name of anion NaNO3 Sodium nitrate Ca(CO3) Calcium carbonate Al2(SO4)3 Aluminum sulfate Mg(NO2)2 Magnesium nitrite Naming Polyatomic Ionic compounds Name of metal (cation) + Name of anion FeCO3 Iron(II) carbonate Fe2(CO3)3 Iron(III) carbonate Naming acids Acids: sour They produce H+ (proton) in water. Naming binary acids Hydro + Anion : -ide ion -ic acid HF F-: flouride ion Hydroflouric acid HCl Cl-: chloride ion Hydrochloric acid H2S S2-: sulfuride ion Hydrosulfuric acid Naming Polyatomic Acids Anion: -ite ion -ous acid -ate ion -ic acid HNO2 NO2-: Nitrite ion Nitrous acid HNO3 NO3-: Nitrate ion Nitric acid H2CO3 CO32-: Carbonate ion Carbonic acid H2SO3 SO32-: Sulfurite ion Sulfurous acid