Mitosis Notes
advertisement

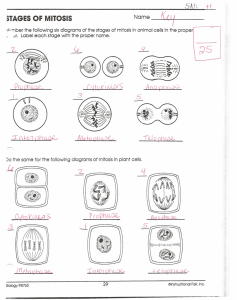
Why do cells divide? Agenda for Friday Dec 19th 1. Go over test 2. Mitosis notes & video 3. Mitosis worksheet Grades on wall Why does a cell divide? • Too large to work efficiently – Smaller the cell = quicker it can work • Transport of Substances • Cellular communication – Ratio of surface area to volume Other reasons for cellular division • Growth • Replace damaged cells The Cell Cycle • Cell reaches max size it stops growing or divides – Cells reproduce by growing and dividing = cell cycle • 3 main stages of cell cycle 1. Interphase – cell grows, replicates DNA 2. Mitosis – nucleus and nuclear material divide 3. Cytokinesis – cytoplasm divides 3 Stages of Interphase Gap 1 (G1) • Right after cell divides, normal functions, prepares to replicate DNA Synthesis (S) • Cell copies DNA (contains genetic material) – Chromatin is the relaxed form of DNA – Chromosomes are the condensed form of DNA Gap 2 (G2) • Cell prepares for mitosis Mitosis • Cell’s DNA separates – Creates 2 identical daughter cells – Same DNA – Same Number of Chromosomes in each cell • 4 Stages – Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase 1. Prophase • Chromatin condenses into chromosomes – X – shaped – Consist of two chromatids – identical copies of DNA – Chromatids are connected at a centromere 1. Prophase • Nuclear membrane disappears • Spindle apparatus appears – Spindle fibers, centrioles, and aster fibers – Helps move chromosomes 2. Metaphase • Chromatids Line up at center of cell 3. Anaphase • Chromatids pull apart 4. Telophase • • • • Chromosomes arrive at the poles Chromosomes unwind (back to chromatin) Two nuclear membranes begin to form Spindle apparatus disappears Cytokinesis • Divides cytoplasm • Animal Cells – Microfilaments constrict/pinch the cytoplasm • Plant Cells – Cell plate forms between two daughter nuclei – Cell walls then form on either side of cell plate Explain what happens in each step of mitosis. Agenda for Monday Jan. 5th 1. Review mitosis (video) 2. Go over HW 3. Mitosis Cell Lab • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=L0kenzoeOM If a cell has 150 chromosomes how many daughter cells are created at the end of mitosis? How many chromosomes are in each cell? Agenda for Tuesday Jan 6th 1. Finish mitosis onion cell lab http://www.sumanasinc.com/webcontent/animations/content/mitosis.html http://highered.mcgrawhill.com/sites/0072495855/student_view0/chapter2/animation__mitosis_and_cytok inesis.html What is cancer? Agenda for Thursday Jan 8th 1. Cancer Notes 2. Cancer worksheet Cancer Vocab • Cancer – uncontrolled growth and spread of abnormal cells • Neoplasm – new growth of tissue that serves no physiological function • Tumor – clumping of neoplasmic cells • Malignant - cancerous • Benign - noncancerous • Biopsy –examination of cell development Skin Cancer • The ABCD’s of melanoma (skin cancer): – – – – A B C D Asymmetry: one half is not like the other Border: the edges are jagged or irregular Color: the color is varied, tan, red, black ect Diameter: the diameter is larger than 8mm (the top of a pencil eraser Cancer • Uncontrolled cell division • Tumors begin with a single cell that reproduces by mitosis – Cells in tumors divide continuously • Metastasis: Process in which cells are invasive and move to other sites in the body How does it happen? • Two classes of genes: Oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes – Proto-oncogenes: control cell division – Tumor suppressor genes turn off cell division G2/M checkpoint 4 Cell division 3 DNA repair 1 Mitosis G2 G1 • Checkpoints in the cell cycle regulate cell division 2 Cell grows, doubles in size S Chromosome duplication G1/S checkpoint Stepped Art p. 181 The Cell Cycle and Cancer • Neoplasm- abnormal growth of cells • Benign neoplasms are not cancerous – Encapsulated; Do not invade neighboring tissue or spread • Malignant neoplasms are cancerous – Not encapsulated; Readily invade neighboring tissues – May also detach and lodge in distant places – metastasis Stages of Cancer • 4 stages, – 1 = not so bad – 4 = really bad • Stage I – localized to one part of the body Stage II - locally advanced • Stage III - also locally advanced • Stage IV - often metastasized, or spread Causes of Cancer • Mutation: change in genetic makeup • A factor which brings about a mutation is called a mutagen. • Any agent that causes cancer is called a carcinogen and is described as carcinogenic. What Causes Cancer? Family History Lifestyle Environment Lifestyle Risks • Smoking • Diet high fat and low in fruits and vegetables • Lack of exercise • Unprotected exposure to the sun, (UV) rays • Obesity Environmental Risks • Second hand smoke • Air pollution • Industrial pollution • Chemical exposures – tar from cigarettes – some foods Inherited Risks • Less than 15% of cancers are inherited • Gene mutations are linked to some inherited cancers • Cancers that may be caused by inherited gene mutations are: – Colon cancer – Breast cancer – Ovarian – Prostate cancer – Skin cancer • Some families are more susceptible to getting certain cancers. – Remember you can’t inherit cancer its just that you maybe more susceptible to getting it. Stress • There is connection between stress, immune system and cancer, that is changing the direction of research – it now appears that cancer cells make proteins that actually tell the immune system to let them alone and even to help them grow. Other ways • Many forms of cancer related to: – Physical surroundings – Personal behavior – Or both • At least 50% of all cancer can be attributed to some type of environmental factor Treatment Chemotherapy treatment • uses medicine to weaken and destroy cancer cells in the body, including cells at the original cancer site and any cancer cells that may have spread to another part of the body. • a systemic therapy, which means it affects the whole body by going through the bloodstream. Treatment Radiation therapy (also called radiotherapy) • high-energy rays are used to damage cancer cells and stop them from growing and dividing. • A specialist in radiation therapy is called a radiation oncologist • Like surgery, radiation therapy is a local treatment; it affects cancer cells only in the treated area Cancer Prevention Healthy lifestyle • Exercise and proper breathing • Balanced diet • Complete rest and sleep • Water • Eating Fruit lab How does one go about getting cancer (name 2 ways)? Agenda for Friday Jan 9th 1. Quiz 2. Cancer lab Mitosis Foldable Go to Page 243 Follow those directions Homework • Page 253 – 257 • Questions 1 – 7 on page 257