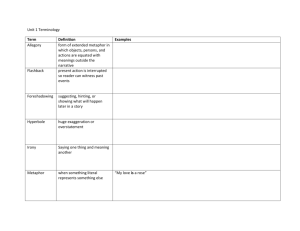
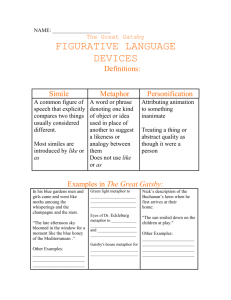
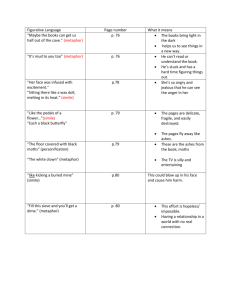
Literary Devices Chart
advertisement

Definitions for Review Table plot exposition rising action climax falling action denouement simile metaphor analogy personification onomatopoeia dead metaphor implied metaphor mixed metaphor extended metaphor PLOT - Series of events that make up a story. PLOT - Series of events that make up a story. EXPOSITION - Background information to a story; introduces characters and setting PLOT - Series of events that make up a story. EXPOSITION - Background information to a story; introduces characters and setting RISING ACTION - The events of a plot that lead up to the climax; builds suspense PLOT - Series of events that make up a story. EXPOSITION - Background information to a story; introduces characters and setting RISING ACTION - The events of a plot that lead up to the climax; builds suspense CLIMAX - The highest, most intense point of conflict in a story PLOT - Series of events that make up a story. EXPOSITION - Background information to a story; introduces characters and setting RISING ACTION - The events of a plot that lead up to the climax; builds suspense CLIMAX - The highest, most intense point of conflict in a story FALLING ACTION - The events of a dramatic or narrative plot following the conflict PLOT - Series of events that make up a story. EXPOSITION - Background information to a story; introduces characters and setting RISING ACTION - The events of a plot that lead up to the climax; builds suspense CLIMAX - The highest, most intense point of conflict in a story FALLING ACTION - The events of a dramatic or narrative plot following the conflict DENOUEMENT - Resolution of the plot SIMILE - Comparing two unlike things using “like” or “as” SIMILE - Comparing two unlike things using “like” or “as” METAPHOR - Comparing two unlike things SIMILE - Comparing two unlike things using “like” or “as” METAPHOR - Comparing two unlike things ANALOGY - Resembling relations; comparing groups to show relationships SIMILE - Comparing two unlike things using “like” or “as” METAPHOR - Comparing two unlike things ANALOGY - Resembling relations; comparing groups to show relationships PERSONIFICATION - Giving human qualities or characteristics to nonliving things SIMILE - Comparing two unlike things using “like” or “as” METAPHOR - Comparing two unlike things ANALOGY - Resembling relations; comparing groups to show relationships PERSONIFICATION - Giving human qualities or characteristics to nonliving things ONOMOTOPOEIA - Use of a word whose sound often imitates its meaning DEAD METAPHOR - An overused metaphor that has gained a new meaning DEAD METAPHOR - An overused metaphor that has gained a new meaning IMPLIED METAPHOR - A more subtle use of a metaphor DEAD METAPHOR - An overused metaphor that has gained a new meaning IMPLIED METAPHOR - A more subtle use of a metaphor MIXED METAPHOR - Two or more metaphors used together that appear illogical DEAD METAPHOR - An overused metaphor that has gained a new meaning IMPLIED METAPHOR - A more subtle use of a metaphor MIXED METAPHOR - Two or more metaphors used together that appear illogical EXTENDED METAPHOR - Metaphor that continues throughout the entire text anachronism allusion protagonist antagonist foil flat character round character static character dynamic character symbolism imagery flashback foreshadow theme tone mood ANACHRONISM - Something that is not in its correct historical time period ANACHRONISM - Something that is not in its correct historical time period ALLUSION - An implied or direct reference to another text, person, thing, or event ANACHRONISM - Something that is not in its correct historical time period ALLUSION - An implied or direct reference to another text, person, thing, or event PROTAGONIST - Main character of a story ANACHRONISM - Something that is not in its correct historical time period ALLUSION - An implied or direct reference to another text, person, thing, or event PROTAGONIST - Main character of a story ANTAGONIST - The character who opposes the main character ANACHRONISM - Something that is not in its correct historical time period ALLUSION - An implied or direct reference to another text, person, thing, or event PROTAGONIST - Main character of a story ANTAGONIST - The character who opposes the main character FOIL - Character who contrasts protagonist to enhance qualities FLAT CHARACTER - A one-dimensional character FLAT CHARACTER - A one-dimensional character ROUND CHARACTER - A fully developed character FLAT CHARACTER - A one-dimensional character ROUND CHARACTER - A fully developed character STATIC CHARACTER - A character that stays the same throughout the story FLAT CHARACTER - A onedimensional character ROUND CHARACTER - A fully developed character STATIC CHARACTER - A character who stays the same throughout the story DYNAMIC CHARACTER – Character who changes permanently throughout the story SYMBOLISM - Representations of things to others by means of symbols SYMBOLISM - Representations of things to others by means of symbols IMAGERY - Descriptive text; creating mental images for the reader SYMBOLISM - Representations of things to others by means of symbols IMAGERY - Descriptive text; creating mental images for the reader FLASHBACK - When the text refers back to previous events SYMBOLISM - Representations of things to others by means of symbols IMAGERY - Descriptive text; creating mental images for the reader FLASHBACK - When the text refers back to previous events FORESHADOW - To give a hint to what will happen later in the text THEME - Author’s message to the reader; underlying meaning of a story THEME - Author’s message to the reader; underlying meaning of a story TONE - Attitude of the writer toward a subject - Author’s message to the reader; underlying meaning of a story TONE - Attitude of the writer toward a subject MOOD - Feeling the reader gets from a story THEME allegory internal conflict external conflict denotation connotation parallelism alliteration parody satire irony situational irony dramatic irony verbal irony hyperbole understatement ALLEGORY - Symbolic representations of abstract or spiritual ideas ALLEGORY - Symbolic representations of abstract or spiritual ideas INTERNAL CONFLICT - Conflict within a character; man vs. self ALLEGORY - Symbolic representations of abstract or spiritual ideas INTERNAL CONFLICT - Conflict within a character; man vs. self EXTERNAL CONFLICT - Conflict outside of a character; man vs. man, man vs. society, man vs. nature, etc. ALLEGORY - Symbolic representations of abstract or spiritual ideas INTERNAL CONFLICT - Conflict within a character; man vs. self EXTERNAL CONFLICT - Conflict outside of a character; man vs. man, man vs. society, man vs. nature, etc. DENOTATION - Basic dictionary definition of a word ALLEGORY - Symbolic representations of abstract or spiritual ideas INTERNAL CONFLICT - Conflict within a character; man vs. self EXTERNAL CONFLICT - Conflict outside of a character; man vs. man, man vs. society, man vs. nature, etc. DENOTATION - Basic dictionary definition of a word CONNOTATION - The implied meaning or attributes given to a word PARALLELISM - The use of identical phrases, clauses, and structures within a sentence PARALLELISM - The use of identical phrases, clauses, and structures within a sentence ALLITERATION - Repetition of same sounds at the beginning of words PARALLELISM - The use of identical phrases, clauses, and structures within a sentence ALLITERATION - Repetition of same sounds at the beginning of words PARODY - Humorous imitations of a piece of text PARALLELISM - The use of identical phrases, clauses, and structures within a sentence ALLITERATION - Repetition of same sounds at the beginning of words PARODY - Humorous imitations of a piece of text SATIRE - A text that mocks social conventions; ridicules serious situations IRONY - Contrast between expectations and reality IRONY - Contrast between expectations and reality SITUATIONAL IRONY - Expecting one thing to happen but something entirely different taking place IRONY - Contrast between expectations and reality SITUATIONAL IRONY - Expecting one thing to happen but something entirely different taking place DRAMATIC IRONY - Contrast between what the character knows and what the reader knows IRONY - Contrast between expectations and reality SITUATIONAL IRONY - Expecting one thing to happen but something entirely different taking place DRAMATIC IRONY - Contrast between what the character knows and what the reader knows VERBAL IRONY - When someone says something but means another (often called “sarcasm”) HYPERBOLE - Extreme exaggeration HYPERBOLE - Extreme exaggeration UNDERSTATEMENT Statement less strong or striking than facts would show paradox oxymoron pun idiom assonance dissonance dialect jargon slang iambic pentameter soliloquy monologue propaganda stereotype PARADOX - A seemingly contradictory or absurd statement that may suggest truth PARADOX - A seemingly contradictory or absurd statement that may suggest truth OXYMORON - Two seemingly contradictory words used together for effect PARADOX - A seemingly contradictory or absurd statement that may suggest truth OXYMORON - Two seemingly contradictory words used together for effect PUN - Humorous use of words; a play on words PARADOX - A seemingly contradictory or absurd statement that may suggest truth OXYMORON - Two seemingly contradictory words used together for effect PUN - Humorous use of words; a play on words IDIOM - Expressions; meaning of expression is not true to words ASSONANCE - Resemblance of sounds; vowel rhyme ASSONANCE - Resemblance of sounds; vowel rhyme DISSONANCE - Harsh, disagreeable sounds; discord ASSONANCE - Resemblance of sounds; vowel rhyme DISSONANCE - Harsh, disagreeable sounds; discord DIALECT - A provincial, rural, or socially distinct variety of language ASSONANCE - Resemblance of sounds; vowel rhyme DISSONANCE - Harsh, disagreeable sounds; discord DIALECT - A provincial, rural, or socially distinct variety of language JARGON - “jibberish”; words associated with a specific subject or profession ASSONANCE - Resemblance of sounds; vowel rhyme DISSONANCE - Harsh, disagreeable sounds; discord DIALECT - A provincial, rural, or socially distinct variety of language JARGON - “jibberish”; words associated with a specific subject or profession SLANG - Informal language IAMBIC PENTAMETER - Verse consisting of 5 meters alternating stressed and unstressed syllables IAMBIC PENTAMETER - Verse consisting of 5 meters alternating stressed and unstressed syllables SOLILOQUY - Speaking to oneself oblivious to people hearing; reveals inner thoughts IAMBIC PENTAMETER - Verse consisting of 5 meters alternating stressed and unstressed syllables SOLILOQUY - Speaking to oneself oblivious to people hearing; reveals inner thoughts MONOLOGUE - An extended period of time in which one character speaks PROPAGANDA - The persuasion of others to buy a product, believe something, etc. PROPAGANDA - The persuasion of others to buy a product, believe something, etc. STEREOTYPE - Simple and often inaccurate categorizing of a group of people PROPAGANDA - The persuasion of others to buy a product, believe something, etc. STEREOTYPE - Simple and often inaccurate categorizing of a group of people BIAS – having a pre-existing preference for something (onesided) ALL DEFINITIONS 15 SLIDES PLOT - Series of events that make up a story. EXPOSITION - Background information to a story; introduces characters and setting RISING ACTION - The events of a plot that lead up to the climax; builds suspense CLIMAX - The highest, most intense point of conflict in a story FALLING ACTION - The events of a dramatic or narrative plot following the conflict DENOUEMENT - Resolution of the plot SIMILE - Comparing two unlike things using “like” or “as” METAPHOR - Comparing two unlike things ANALOGY - Resembling relations; comparing groups to show relationships PERSONIFICATION - Giving human qualities or characteristics to nonliving things ONOMOTOPOEIA - Use of a word whose sound often imitates its meaning DEAD METAPHOR - An overused metaphor that has gained a new meaning IMPLIED METAPHOR - A more subtle use of a metaphor MIXED METAPHOR - Two or more metaphors used together that appear illogical EXTENDED METAPHOR - Metaphor that continues throughout the entire text ANACHRONISM - Something that is not in its correct historical time period ALLUSION - An implied or direct reference to another text, person, thing, or event PROTAGONIST - Main character of a story ANTAGONIST - The character who opposes the main character FOIL - Character who contrasts protagonist to enhance qualities FLAT CHARACTER - A onedimensional character ROUND CHARACTER - A fully developed character STATIC CHARACTER - A character who stays the same throughout the story DYNAMIC CHARACTER – Character who changes permanently throughout the story SYMBOLISM - Representations of things to others by means of symbols IMAGERY - Descriptive text; creating mental images for the reader FLASHBACK - When the text refers back to previous events FORESHADOW - To give a hint to what will happen later in the text - Author’s message to the reader; underlying meaning of a story TONE - Attitude of the writer toward a subject MOOD - Feeling the reader gets from a story THEME ALLEGORY - Symbolic representations of abstract or spiritual ideas INTERNAL CONFLICT - Conflict within a character; man vs. self EXTERNAL CONFLICT - Conflict outside of a character; man vs. man, man vs. society, man vs. nature, etc. DENOTATION - Basic dictionary definition of a word CONNOTATION - The implied meaning or attributes given to a word PARALLELISM - The use of identical phrases, clauses, and structures within a sentence ALLITERATION - Repetition of same sounds at the beginning of words PARODY - Humorous imitations of a piece of text SATIRE - A text that mocks social conventions; ridicules serious situations IRONY - Contrast between expectations and reality SITUATIONAL IRONY - Expecting one thing to happen but something entirely different taking place DRAMATIC IRONY - Contrast between what the character knows and what the reader knows VERBAL IRONY - When someone says something but means another (often called “sarcasm”) HYPERBOLE - Extreme exaggeration UNDERSTATEMENT Statement less strong or striking than facts would show PARADOX - A seemingly contradictory or absurd statement that may suggest truth OXYMORON - Two seemingly contradictory words used together for effect PUN - Humorous use of words; a play on words IDIOM - Expressions; meaning of expression is not true to words ASSONANCE - Resemblance of sounds; vowel rhyme DISSONANCE - Harsh, disagreeable sounds; discord DIALECT - A provincial, rural, or socially distinct variety of language JARGON - “jibberish”; words associated with a specific subject or profession SLANG - Informal language IAMBIC PENTAMETER - Verse consisting of 5 meters alternating stressed and unstressed syllables SOLILOQUY - Speaking to oneself oblivious to people hearing; reveals inner thoughts MONOLOGUE - An extended period of time in which one character speaks PROPAGANDA - The persuasion of others to buy a product, believe something, etc. STEREOTYPE - Simple and often inaccurate categorizing of a group of people BIAS – having a pre-existing preference for something (onesided)