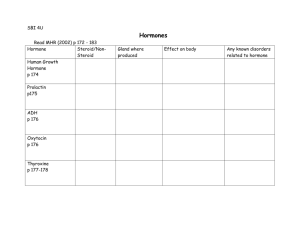
Endocrine System
advertisement
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Garrett Friedman and Will Froelich Overview 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) 7) 8) Function of the system Endocrine vs. Exocrine glands Hormones Major endocrine glands Hormone regulation Nervous system involvement Steroid vs. nonsteroid hormones Negative feedback systems (1) Function of the System Maintain homeostasis Metabolism Growth and development Reproduction Nutrient balances/concentrations Regulates the body using hormones (2)Endocrine Vs. Exocrine Endocrine glands secrete their products into tissue or blood. Paracrine secretions are local Autocrine secretions are within the cell Exocrine glands secret their products into ducts that in turn go to the surface. (3) Hormones Hormone: a (chemical) substance secreted by an endocrine gland and transported in the blood Types of Hormones: Steroid Nonsteroid Amines Peptides Proteins Prostaglandins (3) Hormones (3) Hormones They influence target cells Rely on receptors, which can be Proteins Glycoproteins Change protein production in the nucleus Trigger second messengers in the cytoplasm (4)Major Endocrine Glands (4)Pituitary Gland The pituitary gland has two lobes, is located at the base of the brain, and controls other glands. Anterior Growth Hormone Prolactin Thyroid-stimulating hormone Thyrotropin-releasing hormone Adrenocorticotropic hormone Follicle-stimulating hormone Luteinizing hormone Posterior Antidiuretic hormone Oxytocin (4)Anterior Pituitary Hormones (4)Thyroid Gland The thyroid gland is located below the larynx, and secretes Thyroxine, Tyiidothronine, and Calcitonin. (4)Parathyroid Glands Four small glands on the posterior of the thyroid that secrete parathyroid hormone. (4)Adrenal Glands The adrenal glands are located atop the kidneys, and they include the outer adrenal cortex, and the inner adrenal medulla. Adrenal Medulla: Epinephrine Norepinephrine Adrenal Cortex: Aldosterone Cortisol (4) Pancreas The pancreas, posterior to the stomach, secretes exocrine digestive juice and endocrine hormones. Glucagon Insulin (4)Pancreatic Feedback System (4) Pineal Gland The pineal gland secretes melatonin, which regulates circadian rhythms. (4)Thymus Gland The thymus gland is beneath the sternum and plays an important role in immunity. (5) Hormone Regulation There are 3 mechanisms for controlling hormones: 1. 2. 3. Hypothalamus and anterior pituitary gland Nervous system Change in internal environment All are limited by negative feedback (5) Hormone Regulation (6)Nervous System Control The hypothalamus controls the anterior pituitary gland which in turn controls the secretion of other glands. The nervous system stimulates some glands directly and the adrenal medulla releases hormones in response. (7) Activating Target Cells Steroid Hormones Nonsteroid Hormones (8) Negative Feedback Systems Diabetes Type 1 Type 1 Diabetes is insulin dependent and appears commonly before the age of 20. It is a autoimmune disease which destroys beta cells of the immune system. The cause is that the pancreas stops producing insulin and with the beta cells destroyed people with it can no longer produce insulin. Diabetes Type 1 Treatments Several options are available including rapid acting, regular acting, intermediate, and long acting insulin shots. Insulin pumps are available as well implanted in the body. Diabetes Type 2 Type 2 is where the beta cells produce the insulin but the body cells lose the ability to recognize it. Has more mild symptoms than type 1 and oral drugs are a option for it as well. Symptoms can be delayed by treatment early. Works Cited "Med-Health.net." Pineal Gland Calcification. N.p., n.d. Web. 25 Mar. 2015. <http:// www.med-health.net/Pineal-Gland-Calcification.html>. "Endocrine System." Know Your Endocrine System. N.p., n.d. Web. 25 Mar. 2015. <http:// www.medindia.net/know_ur_body/anatomy-of-endocrine-system.asp>. "Beyond the Pancreas: Researchers Targeting Immune-System Creation Gland." The Pancreas Thymus: Who's to Blame for Diabetes? N.p., n.d. Web. 25 Mar. 2015. <http:// www.healthline.com/diabetesmine/beyond-the-pancreas-researchers-targetingsystem-creation-gland>. or The "Insulin Basics." American Diabetes Association. American Diabetes Association, 7 June 2013. 13 Mar. 2015. Web. immune- "Diabetes Mellitus - Insulin Treatment in Dogs." VCA Animal Hospitals. N.p., n.d. Web. 25 Mar. 2015. <http://www.vcahospitals.com/main/pet-health-information/article/animalhealth/diabetesmellitus-insulin-treatment-in-dogs/746>. Zimmermann, By Kim Ann. "Endocrine System: Facts, Functions and Diseases." LiveScience. TechMedia Network, 20 Nov. 2014. Web. 17 Mar. 2015. "Human Regulation." Human Regulation. N.p., n.d. Web. 25 Mar. 2015.