Document
advertisement

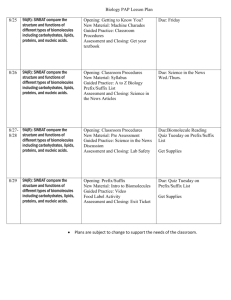
Carbohydrates Proteins Lipids Nucleic Acids Eagle Zone • You will have 3 minutes at the sound of the bell to get out the following items: – Lab book (notes section) – Crossword – Biochemistry vocabulary review sheet – Food label sheet • Failure to have these items out on your desk when the 3 minutes is over will result in a 0 daily grade today. Learning Objectives • • • • • • • • Bio.9A Compare the structures and functions of different types of biomolecules, including carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids; Bio.9C Identify and investigate the role of enzymes ; and • Understand the structure/function and how it affects the reaction rate • Discuss how enzyme activity is influenced by temperature, pH, concentration and inhibitors Bio.9D Analyze and evaluate the evidence regarding formation of simple organic molecules and their organization into long complex molecules having information such as the DNA molecule for self-replicating life. • Discuss how the monomers make-up polymers Engage • Make a list of all the things you like to eat at the State Fair. Explore 1 • Food Label Investigation– Students will look at food labels to determine what types of biomolecules might be found in their foods Molecular Organization (explain) Cell: Collection of compounds, smallest unit of living organism Compound: Combination of 2 or more elements Molecule: Bonding of 1 or more elements Element: made of one type of atom Atom: smallest unit CO2 NaCl C6H12O6 OR H Li 6 Essential Elements He Be B C N O F Ne Na Mg Al Si P S Cl K Ca Sc Rb Sr Y Ti V Cr Mn Fe Co Ni Cu Zn Ga Ge As Se Br Kr Zr Nb Mo Tc Ru Rh Pd Ag Cd In Sn Sb Te Cs Ba La Hf Ta W Re Os Ir Fr Pt Au Hg Ti Pb Bi I H N O P These six elements make up all living organisms. Xe Po At Rn Ra Ac Rf Ha Ha C Ar S Carbon is an element. H Li He Be B C N O F Ne Na Mg Al C Si P S Cl K Ca Sc Rb Sr Y Ti V Cr Mn Fe Co Ni Cu Zn Ga Ge As Se Br Kr Zr Nb Mo Tc Ru Rh Pd Ag Cd In Sn Sb Te Cs Ba La Hf Ta W Re Os Ir Fr Ar Pt Au Hg Ti Ra Ac Rf Ha Ha • Let’s talk about carbon. Pb Bi I Xe Po At Rn Carbon is an element. 6 + + + + + + S C carbon 12.11 6 atomic number How many protons? = 6 atomic mass How many neutrons? How many energy levels? 2 How many electrons? 6 Chemical Bonding • What is a bond? – Attraction that holds atoms together, resulting in different forms of matter. • Ex: NaCl-a.k.a Table Salt – Sodium (Na) is a metal that explodes in water. – Chlorine (Cl) is a poisonous gas. – When bonded together, they become the compound salt. Types of Bonds • Covalent Bonds – sharing of electrons • Ionic Bonds – gaining or losing electrons • Hydrogen Bonds – how polar molecules “stick” together. (not a chemical bond) Organic vs. Inorganic • Organic Compounds contain a carbonhydrogen bond (C6H12O6, CH4) C6H12O6 • Inorganic Compounds do not contain a carbon-hydrogen bond (CO2, H2O) Water-Organic or Inorganic? • Polarity – Cohesive • Adhesion • High Heat Capacity • Universal Solvent • Surface Tension • Forms Hydrogen Bonds Carbon • Remember the element carbon? • Carbon is the basis of all organic compounds Carbon can make 4 bonds Hydrocarbon • Backbone of all organic compounds • Composed of carbon chains surrounded by hydrogens H H H H H H H C C C C C C H H H H H H H Remember that carbon can make 4 bonds Functional Groups • Functional groups bond to the carbon in place of an H to give the compound unique chemical and physical properties. 1. H H H C C H H C O OH Found in Proteins and Lipids (fatty acids) Carboxyl Group Functional Groups 2. H H C H H Hydroxyl Group C OH H Found in Carbohydrates and Lipids (glycerol) 3. H H C H H C H O O P O O _ Found in Nucleic Acids _ Phosphate Group Functional Groups 4. H H H C C H H H N H Amine Group Found in Proteins 5. H H H C C C O H H H Found in Carbohydrates Carbonyl Group Building Organic Compounds • Monomers • Polymer How are monomers similar to links in a chain? Eagle Zone-12 minutes 1)How do you find the number of protons in an atom? 2)How do you calculate the number of neutrons in an atom? 3)What is the difference between organic and inorganic? 4)What are the names of the 4 biomolecules? Mini Quiz #1 • 1. Give the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons in the following elements: – Carbon (atomic # 6, atomic mass=12g) – Sulfur (atomic #=16, atomic mass = 32) – Oxygen (atomic #=8, atomic mass=16) • 2. Is the compound C6H12O6 organic or inorganic? Why or why not? • 3. Is water an organic compound? Why or why not? • 4. How are monomers similar to links in a chain? • 5. Provide the name and the elements present for the following functional groups: – Carbohydrates --Lipids Explore 2- Building Polymers • Students will explore how monomers are linked, chain-like, into polymers with a building blocks activity Eagle Zone • If you did not finish your conclusion questions for the enzyme lab, do so at this time. It will be due TODAY, no exceptions, by the end of Eagle Zone time • You have 12 minutes to complete today’s assignment • If you are done with the questions, answer this: – Name the 4 biomolecules and give an example of each Eagle Zone • Name the four carbon compounds (biomolecules) • What element are all biomolecules made of? • Provide the name of the bond that is the weakest and that can be found in water molecules. Eagle zone- Write the questions and answer them. 16 minutes 1) 2) 3) 4) Provide the name of the 4 organic compounds. Provide a simple definition for “functional group.” What element are all biomolecules made of? A monosaccharide is a type of-a) Carbohydrate b) Lipid c) Nucleic acid d) Protein 5) The structure of a lipid contains one ___________ and three __________ _____________ tails. 6)What were the 2 tests we did for carbohydrates? 7) What was the test we did for lipids? Eagle Zone-write the questions and answer them • 1) Which of the following correctly describes the parts of a nucleotide? (use the book for this one) A) deoxyribose sugar, phosphate, nitrogen base B) ribose sugar, protein, lipid, nitrogen base C) Nitrogen base, phosphate, ribose sugar • 2) Saliva breaks down food that you have eaten and changes it into simple carbohydrates. If a potato was chewed for two minutes and then spit into a test tube, the organic substance that would give a positive test would be a A)Lipid B)sugar C)starch • 3)Which substance would store the most energy? A) one gram of fat B) one gram of carbohydrate C) one gram of protein 4) Copy the class calendar into your agenda for the days you are in this class. Homework is in red. Study for quiz on Friday over biomolecules. Quiz next week on enzymes Carbohydrates 1. Elements: C, H, O 2. Monomers: Monosaccharide H 3. Structure: Glucose (C6H12O6) H H C HO C OH C O H OH H C C H OH H C OH Carbohydrates Carbohydrates have 3 monomers: -Glucose -Fructose -Galactose “ose” indicates sugar What would this tell you about the taste of monosaccharides? Building Carbohydrates • Many monosaccharides bonded together form polysaccharides. C6H12O6 C6H12O6 C6H12O6 C6H12O6 C6H12O6 Polysaccharide • How many water molecules would be removed by making the polysaccharide? • Polysaccharides are known as starches. • Will the taste of starches be the same as sugars? Functions of Carbohydrates • To provide a quick source of energy (by breaking the C-H bonds) C6H12O6 C6H12O6 C6H12O6 Functions of Carbohydrates • To provide a quick source of energy (by breaking the C-H bonds) C6H12O6 C6H12O6 C6H12O6 • Animals store excess sugars as a starch known as glycogen. • Plants store excess sugars as a starch known as cellulose. Lipids 1. Elements: C, H, O 2. Monomer: Technically, none 3. Structure: Glycerol H H H H C C C H OH OH OH HO HO HO Fatty Acid Tails O H H H C C C C O H H H H H H C C C C O H H H H H H C C C C H H H H H H Lipids • The different types of lipids are determined by the number of C-H bonds in the fatty acid chain. HO O H H H C C C C H H H H Saturated Fatty Acid: maximum number of C-H bonds. Unsaturated Fatty Acid: contains HO one double C-C bond. HO O H C C C C H H H H H C C H O H H H C C C C H H Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid: many double C-C bonds. Functions of Lipids • Lipids store energy, due to their numerous C-H bonds. •Because they are insoluble in water (polar), lipids are found in animal cell membranes. •Fats, oils, waxes and many hormones (steroids) are lipids Proteins 1. Elements: C, H, O, N, S 2. Monomer: Amino Acids (20) 3. Structure: H H N H C R O C OH “R” is the functional group that varies Functions of Proteins • Proteins are a major structural component for living organisms (ex. muscle) • Proteins function as enzymes to carry out chemical reactions in the body. Functions of Proteins • Some hormones are protein (peptide hormones). • Proteins also function to transport or carry substances in and out of cells. Cell membrane channel protein Nucleic Acids 1. Elements: C, H, O, N, P 2. Monomer: nucleotide 3. Structure: O O P O 1. 2. O C H2 C H3 C O CH 3. HC C H CH HO H O O C CH N N C O Adenine H Nucleic Acids Nucleotide 1. 1. Phosphate Group 2. 2. 5-Carbon Sugar (Dexoyribose or Ribose) 3. Nitrogen Base O O P O 3. 3. 1. 2. O C H2 C H3 C O CH HC C H CH HO H O O C CH N N C O H Function of Nucleic Acids • Store genetic code (ATCG) - DNA Remember, all living organisms share a universal genetic code! • Help make proteins (RNA) Overview Now you should fill in the notes page that I have provided to you (the 2 front/back pages) • The 4 biomolecules: – – – – Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic acids • Other terms for biomolecules: – – – – Carbon compounds Organic compounds Organic molecules macromolecules Carbohydrates Elements Present Used by organisms for ... Building Block Related Terms & Info dissaccharide = 2 connected carbon hydrogen oxygen C:H:O = 1: 2 : 1 always Monosaccharides energy structure (simple sugars) ex: glucose C6H12O6 monosaccarides (ex: maltose) polysaccharide 3 or more connected monosaccarides (ex: starch, glycogen, chitin, cellulose) Proteins Elements Present Used by organisms for ... Related Terms & Info carbon hydrogen oxygen NITROGEN structure & movement (muscles) peptide bond = the bond that holds amino acids together in protein molecules (always those 4) antibodies phosphorus sulfur (possibly) hormones enzymes pigments amino acids Building Block of Proteins: dipeptide = two connected amino acids polypeptide = 3 or more connected amino acids Lipids Elements Present Carbon Hydrogen Oxygen ONLY ! There is no specific H:O ratio. Used by Organisms for ... Stored Energy Structure (important part of cell membranes) fatty acid : Building Blocks of Lipids glycerol : Related Terms & Info saturated fat = C-C bonds are all single bonds unsaturated fat = contain at least one double or triple C-C bond Nucleic Acids DNA RNA FULL NAME Deoxyribonucleic acid Ribonucleic acid BASIC STRUCTURE 2 long twisting strands of nucleotides in the form of a "double helix" 1 single strand of nucleotides NUCLEOTIDE SUGAR Deoxyribose Ribose NITROGENOUS BASES guanine (G) cytosine (C) adenine (A) thymine (T) guanine (G) cytosine (C) adenine (A) uracil (U) LOCATION IN A CELL Nucleus (the chromosomes) Nucleus, in the cytoplasm, & at the ribosomes FUNCTION the hereditary material of a cell, directs & controls cell activities involved in protein synthesis Explore Lab • Students will test the presence or absence of the groups of biomolecules through a series of activities using compound indicators Elaborate • Indicators: – Determine what class of organic compound foods belong to when testing them using indicators (McMush Lab) Evaluate • The student will construct a flip chart that organizes the biomolecules, their building blocks, polymer, characteristics, and examples • The student will keep a Nutrition Log for one week to organize the foods they ate and classify those foods into the biomolecule groups Mini Quiz #2 1) Fructose is a compound found in many fruits which give them their sweet taste. The suffix “ose” lets us know that fructose can be classified as aa) Carbon b) starch c)sugar d)protein 2) Starch and sugar are two types of _________. 3) The biomolecule which has functional groups that contain elements carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen is________. Mini Quiz #3 1) Proteins are made up of molecules called _______ ________. 2) Lipids contain the following structures 1) Carbon chain and an “r” group 2) A glycerol and 3 fatty acids 3) A glycerol and an amine group Evaluate I CANNOT HELP YOU 1. Create a data table in your journal similar to the one below Sample # Color change biomolecule 2. Obtain 3 test tubes and label them a, b,c 3. Choose a sample and record the sample number in your data table. Add 3 mL of the sample substance to each test tube 4. Add 8 drops of iodine to test tube “a” 5. Add 10 drops of benedict’s to test tube “b” 6. Add 1 mL of biuret’s to test tube “c” 7. Record the color change and tell which type of biomolecule is present based on the color 8. Clean out your test tubes and repeat steps 3-7 using a different sample #. Clean out test tubes when you are done.