Cardiovascular Test
advertisement

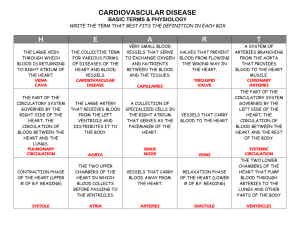
Cardiovascular Test ID # Directions: Read each section carefully. Read each question/problem carefully. When forming your answer, first refer to your notes and the book, then the Internet. Referring back to previous chapters and their notes may be beneficial as well. Please answer with COMPLETE sentences and correct spelling (if a word has the red marks from spellchecker, then double check to make sure you spelled it correctly)! Again, do not copy answers from another student, and please cite sources for your responses. 1. When functioning properly, the human heart is the most efficient compared to other nonmammals as it maximizes the amount of oxygenated blood that is sent out to tissues of the body. The oxygen is used in cellular respiration to create energy for the cells, and the deoxygenated blood is sent back to the heart. a. What are the four chambers of the heart, and what is the main function of each? b. What are the four valves of the heart, and where are they located? c. What are the three layers of the heart’s wall? d. Why is the endothelium of the epicardium important for cardiac function? e. What are the two circulation systems, and what purpose does each serve? 2. The blood vessels make up the vascular system that transports blood and its materials throughout the body. Depending on the direction of the blood, and if the oxygen is being deposited in an area, the structure of the vessels will vary. a. What are the two main vessels that take blood away and back to the heart, and which does what? b. Draw a picture representing the order of the vessels (include all five types) that the blood flows through from and back to the heart. c. What are two main structural differences between arteries and veins? d. What is the main cause of the structural differences between arteries and veins? e. Describe the function of the arterial expansion and recoiling. 3. As blood is initially pumped out of the heart in the arteries of the systemic circulation, a force is exerted onto the arterial wall. This blood pressure is helpful in pushing the blood out to the extremities of the body. However, when blood pressure is out of a healthy range then negative effects will occur with or without being observable. a. Describe the two measurements that are taken when doing a person’s blood pressure. b. Where is the greatest amount of pressure experienced? c. Why is the brachial artery used for measuring blood pressure? d. Why is the aorta such an important and protected artery? e. What can blood pressure tell us about a person’s health? 4. The heart is an important and unique organ that includes its own conduction system to stimulate muscle contractions. The contractions must be timed specifically to ensure a smooth flow of blood through the vascular system. a. What are the names for the heart’s conduction system? b. Why is the sinoatrial node called the pacemaker? c. What is the path of a signal from the SA node through the heart to trigger contractions (include the nodes, bundles, fibers)? d. What would happen if the atrioventricular node did not work? e. Describe the three main steps of the cardiac cycle. 5. Considering how intricately designed the heart is, yet sturdy enough to last a lifetime, there are a number of homeostatic imbalances that may occur with the heart. Fortunately, many heart conditions can be detected. Unfortunately, the results of a condition can range in seriousness and usually require attention. a. Atherosclerosis is a major contributor to heart attacks. What is atherosclerosis? b. What are three ways to prevent atherosclerosis? c. Hardened arteries can occur from age or a lifelong diet lacking in vitamin C. What kind of effect would hardened arteries have on a person’s health? d. Mitral valve prolapse is a congenital heart defect affecting roughly 1 out of 10 people. What is mitral valve prolapsed and what effect does it have on the heart? e. What would happen if the interventricular septum had a hole between the right and left sides? 6. The development of the fetal heart is specific and timed to coincide with the needs of the developing baby. By the end of the ninth week of pregnancy, the heart is fully formed and functioning. a. How does the timelines of pregnancy and conception differ? b. What is a heart tube and how does its form resemble/mold into an adult heart? c. How does the heart tube resemble the fetal heart of other non-mammal animals? d. What is the importance of the foramen ovale? e. What causes blue baby syndrome?