Grade 11 Worksheet (Forces)
advertisement

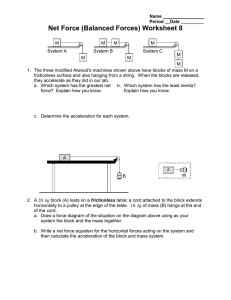
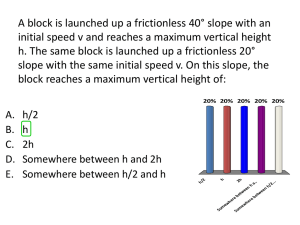
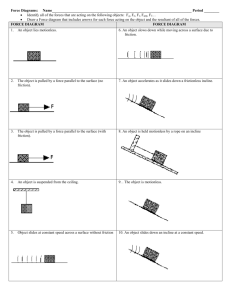
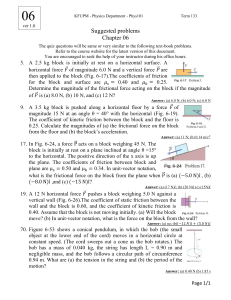
QUESTION 1 An 8 kg block is attached to a 2 kg block by a light rope as shown below. The 8kg block accelerates down the rough inclined plane. QUESTION 2 A 23.4 kg object sits on a frictionless inclined plane with an angle of 30.0° from the horizontal. Draw the diagram, show and label the forces. What is the value of (a) weight (b) normal force, and (c) parallel force. QUESTION 3 1.1 Draw a free-body diagram to show ALL the forces acting on the 2 kg and 8 kg mass respectively. 1.2 Calculate the weight acting on the 2 kg block. 1.3 Calculate the magnitude of the force which causes the 8 kg block to slide down the slope. 1.4 If the co-efficient of kinetic friction for the surface is 0.16, calculate the frictional force acting on the 8 kg block. Ball X of mass 3 kg is attached to trolley Y of mass 4 kg by a light string which passes over a frictionless pulley as shown in the diagram. Initially the trolley is at rest on a slope AB, which makes an angle of 30o with the horizontal. When the ball is released it falls to the ground and the trolley moves up the slope. The coefficient of kinetic friction along slope AB is µk = 0,2. QUESTION 4 A block of mass 2 kg is at rest on a rough horizontal surface. The block is connected with a light inextensible string, that is hanging over a frictionless pulley, to another block of mass 1,5 kg. A force of 20 N to the right is applied on the 2 kg block while the block is experiencing a constant frictional force of 3,1 N. 3.1 Draw a labelled free body diagram to show ALL the forces acting on the T trolley as it moves up the slope. 3.2 Show that a friction force of 6,79 N acts on the trolley as it moves up the slope. 3.3 If the tension (T) in the string is 30 N, calculate the net force acting on the 4 kg trolley. 4.1 Draw a labelled free body diagram to show ALL the forces acting on the 2 kg block. 4.2 Calculate the net force acting on the 2 kg block if the tension (T) is 17 N. QUESTION 5 A 5 kg block, resting on a rough horizontal table, is connected by a light inextensible string passing over a light frictionless pulley to another block of mass 2 kg. The 2 kg block hangs vertically as shown in the diagram below. A force of 60 N is applied to the 5 kg block at an angle of 10o to the horizontal, causing the block to accelerate to the left. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the 5 kg block and the surface of the table is 0,5. Ignore the effects of air friction. 5.1 Draw a labelled free-body diagram showing ALL the forces acting on the 5 kg block. 5.2 Calculate the magnitude of the: 5.2.1 Vertical component of the 60 N force 5.2.2 Horizontal component of the 60 N force 5.3 Calculate the magnitude of the Normal force acting on the 5 kg block. QUESTION 6 A block of mass 20 kg is pulled at constant velocity to the right on a rough horizontal surface by a force, F, of magnitude 29 N. F acts at an angle of 36o to the horizontal as shown in the diagram below: 6.1 Draw a labelled free body diagram to show all the forces that act on the block as it moves to the right. 6.2 Calculate the magnitude of the frictional force that acts on the block as it moves to the Right.