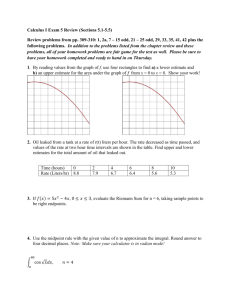
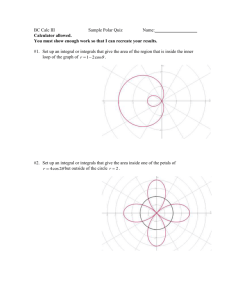
Sec 11.3
advertisement

Sec 11.3: THE INTEGRAL TEST AND ESTIMATES OF SUMS THEOREM: (Integral Test) f (x ) a continuous, positive, decreasing function on [1, inf) an Convergent n 1 an Divergent n 1 1 1 f (n) an f ( x)dx Convergent f ( x)dx Dinvergent Example: Example: Test the series for convergence or divergence. Test the series for convergence or divergence. 1 2 n 1 n 1 ln n n 1 n Sec 11.3: THE INTEGRAL TEST AND ESTIMATES OF SUMS THEOREM: (Integral Test) f (x ) a continuous, positive, decreasing function on [1, inf) an Convergent n 1 an Divergent n 1 1 1 f ( x)dx Convergent f ( x)dx Dinvergent REMARK: When we use the Integral Test, it is not necessary to start the series or the integral at n = 1 . For instance, in testing the series 1 2 n 4 ( n 3) 4 f (n) an dx (x 3) 2 Sec 11.3: THE INTEGRAL TEST AND ESTIMATES OF SUMS THEOREM: (Integral Test) f (x ) a continuous, positive, decreasing function on [1, inf) an Convergent n 1 an Divergent n 1 1 REMARK: f ( x)dx Convergent f ( x)dx Dinvergent REMARK: When we use the Integral Test, it is not necessary to start the series or the integral at n = 1 . For instance, in testing the series 1 2 n 4 ( n 3) 1 f (n) an 4 dx (x 3) 2 Also, it is not necessary that f(x) be always decreasing. What is important is that f(x) be ultimately decreasing, that is, decreasing for larger than some number N. Sec 11.3: THE INTEGRAL TEST AND ESTIMATES OF SUMS THEOREM: (Integral Test) f (x ) a continuous, positive, decreasing function on [1, inf) an Convergent n 1 an Divergent n 1 1 1 f (n) an f ( x)dx Convergent f ( x)dx Dinvergent Special Series: Example: For what values of p is the series convergent? 1 p n 1 n ar 1) Geometric Series n 1 n 1 2) Harmonic Series n 1 3) Telescoping Series 4) p-series 1 p n 1 n 1 n (b b n 1 n n 1 ) Sec 11.3: THE INTEGRAL TEST AND ESTIMATES OF SUMS THEOREM: (Integral Test) f (x ) a continuous, positive, decreasing function on [1, inf) an Convergent n 1 an Divergent n 1 Example: 1 1 f (n) an f ( x)dx Convergent f ( x)dx Dinvergent P Series: For what values of p is the series convergent? 1 p n 1 n convg 1 p n 1 n divg p 1 p 1 Sec 11.3: THE INTEGRAL TEST AND ESTIMATES OF SUMS Example: P Series: For what values of p is the series convergent? 1 p n n 1 Example: convg 1 p n 1 n divg p 1 p 1 Example: Test the series for convergence or divergence. 1 3 n 1 n Test the series for convergence or divergence. 1 1/ 3 n 1 n Sec 11.3: THE INTEGRAL TEST AND ESTIMATES OF SUMS FINAL-081 Sec 11.3: THE INTEGRAL TEST AND ESTIMATES OF SUMS THEOREM: (Integral Test) f (x ) a continuous, positive, decreasing function on [1, inf) an Convergent n 1 an Divergent n 1 Integral Test just test if convergent or divergent. But if it is convergent what is the sum?? 1 REMARK: 1 f (n) an f ( x)dx Convergent f ( x)dx Dinvergent REMARK: We should not infer from the Integral Test that the sum of the series is equal to the value of the integral. In fact, 1 2 2 6 n 1 n 1 1 dx 1 2 x Sec 11.3: THE INTEGRAL TEST AND ESTIMATES OF SUMS REMARK: We should not infer from the Integral Test that the sum of the series is equal to the value of the integral. In fact, 1 2 2 6 n 1 n 1 1 dx 1 2 x ESTIMATING THE SUM OF A SERIES a n 1 n n th partial sum a n 1 a1 a2 an an 1 an 2 n a1 a2 an sn n th partial sum Example: Estimate the sum 1 3 n 1 n How accurate is this estimation? Sec 11.3: THE INTEGRAL TEST AND ESTIMATES OF SUMS REMARK: We should not infer from the Integral Test that the sum of the series is equal to the value of the integral. In fact, 1 2 2 6 n 1 n 1 1 dx 1 2 x ESTIMATING THE SUM OF A SERIES a n 1 n Rn a1 a2 an an 1 an 2 n th partial sum a i n 1 i Rn s sn reminder Rn an 1 an 2 reminder Rn Sec 11.3: THE INTEGRAL TEST AND ESTIMATES OF SUMS ESTIMATING THE SUM OF A SERIES Rn a i i n 1 Rn s sn an 1 an 2 reminder Rn REMAINDER ESTIMATE FOR THE INTEGRAL TEST n 1 f ( x)dx Rn f ( x)dx n Sec 11.3: THE INTEGRAL TEST AND ESTIMATES OF SUMS REMAINDER ESTIMATE FOR THE INTEGRAL TEST n 1 f ( x)dx Rn f ( x)dx n Rn s sn sn n 1 f ( x)dx s sn f ( x)dx n Sec 11.3: THE INTEGRAL TEST AND ESTIMATES OF SUMS Sec 11.3: THE INTEGRAL TEST AND ESTIMATES OF SUMS TERM-102