Sketcher Basics
advertisement

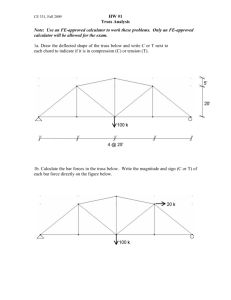
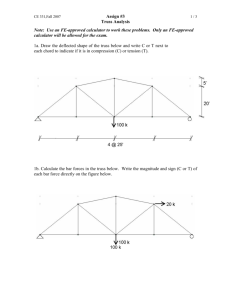
ME 201 Engineering Mechanics: Statics Chapter 6 – Part A 6.1 Simple Trusses 6.2 Method of Joints 6.3 Zero Force Members Simple Truss A structure composed of slender members joined together at their end points “Planar Truss” Simple Truss To Design members and connections of a truss, necessary to determine forces developed in each member Assumptions: All loadings are applied at the joints Members are joined together by smooth pins Assumptions satisfactory for bolted or welded joints Simple Truss Each truss member acts as a 2-force member Force directed along axis of member Tension – pull, elongation Compression – push, shorten Several analytical approaches to solving Method of Joints If truss is in equilibrium, each joint must also be in equilibrium Approach: Sketch Free Body Diagram of Entire Truss Solve for Reactions Sketch Free Body Diagrams of Each Joint 2 unknown limit per FBD ∑ Fx =0 ∑ Fy =0 ∑ Mo =0 Example Problem B F 2m Given: F = 500 N θ = 45º Find: Force in each member θ A 2m C Example Problem Solution B 2 m 45º A Ax F F 2m 2m Ay 0 Ax 500 0 Ax 500 or 500 N 2m θ Cy x M 0 C y 2 500 2 0 C y 500 N F 500 N A 0 Ay 500 0 Ay 500 or 500 N y B 2m Given: F = 500 N θ = 45º Find: Force in each member Solution: 1-FBD 2-Support Reactions B 500 N 2 m 45º A C 500 N 500 N 500 N C Example Problem Solution B Joint A 500 N 2m Given: F = 500 N θ = 45º Find: Force in each member Solution: 1-FBD 2-Support Reactions 3-Joint FBDs 2 m 45º A C 500 N 500 N 500 N Joint B Joint C AB 500 N AC 500 N 500 N 45º 45º AB BC BC AC 500 N Example Problem Solution Given: F = 500 N θ = 45º Find: Force in each member Solution: 1-FBD 2-Support Reactions 3-Joint FBDs Joint B Joint A AB 500 N 45º AC 500 N AB 500 N 500 N F 0 AC 500 0 AC 500 N T x F 0 AB 500 0 AB 500 N T y BC F 0 500 BC sin 45 0 BC 707 N C x B 500 T Results shown in a force diagram A 500 T C Zero Force Members Zero Force Members support NO loading Used for: Stability Changing Applied Loads Zero Force Members If only 2 members form a truss joint AND no external load or support reaction is applied to the joint, then the members must be Zero Force Members X X X X Zero Force Members If 3 members form a truss joint for which 2 members are collinear, the 3rd member is a Zero Force Member, provided no external force or support reaction is applied to the joint. X X